The ins and outs of type I iNKT cell development
- PMID: 30502719
- PMCID: PMC6331266
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molimm.2018.09.023
The ins and outs of type I iNKT cell development
Abstract
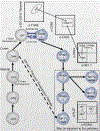
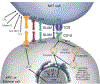
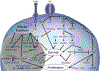
Natural killer T (NKT) cells are innate-like lymphocytes that bridge the gap between the innate and adaptive immune responses. Like innate immune cells, they have a mature, effector phenotype that allows them to rapidly respond to threats, compared to adaptive cells. NKT cells express T cell receptors (TCRs) like conventional T cells, but instead of responding to peptide antigen presented by MHC class I or II, NKT cell TCRs recognize glycolipid antigen in the context of CD1d. NKT cells are subdivided into classes based on their TCR and antigen reactivity. This review will focus on type I iNKT cells that express a semi invariant Vα14Jα18 TCR and respond to the canonical glycolipid antigen, α-galactosylceramide. The innate-like effector functions of these cells combined with their T cell identity make their developmental path quite unique. In addition to the extrinsic factors that affect iNKT cell development such as lipid:CD1d complexes, co-stimulation, and cytokines, this review will provide a comprehensive delineation of the cell intrinsic factors that impact iNKT cell development, differentiation, and effector functions - including TCR rearrangement, survival and metabolism signaling, transcription factor expression, and gene regulation.
Keywords: CD1d; Innate lymphocytes; NKT cells; Natural killer T; T cell development; iNKT.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Becker AM, Blevins JS, omson FL, Eitson JL, Medeiros JJ, Yarovinsky F, Norgard MV, van Oers NSC, 2010. Invariant NKT cell development requires a full complement of functional D3 ζ immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motifs. J. Immunol. (Baltimore, Md 1950) 184, 6822–6832. 10.4049/jimmunol.0902058 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bedel R, Berry R, Mallevaey T, Matsuda JL, Zhang J, Godfrey DI, Rossjohn J, Kappler JW, Marrack P, Gapin L, 2014. Effective functional maturation of invariant natural killer T cells is constrained by negative selection and T-cell antigen receptor affinity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 111, E119–28. 10.1073/pnas.1320777110 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

