Single-Cell Sequencing of iPSC-Dopamine Neurons Reconstructs Disease Progression and Identifies HDAC4 as a Regulator of Parkinson Cell Phenotypes
- PMID: 30503143
- PMCID: PMC6327112
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2018.10.023
Single-Cell Sequencing of iPSC-Dopamine Neurons Reconstructs Disease Progression and Identifies HDAC4 as a Regulator of Parkinson Cell Phenotypes
Abstract
Induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived dopamine neurons provide an opportunity to model Parkinson's disease (PD), but neuronal cultures are confounded by asynchronous and heterogeneous appearance of disease phenotypes in vitro. Using high-resolution, single-cell transcriptomic analyses of iPSC-derived dopamine neurons carrying the GBA-N370S PD risk variant, we identified a progressive axis of gene expression variation leading to endoplasmic reticulum stress. Pseudotime analysis of genes differentially expressed (DE) along this axis identified the transcriptional repressor histone deacetylase 4 (HDAC4) as an upstream regulator of disease progression. HDAC4 was mislocalized to the nucleus in PD iPSC-derived dopamine neurons and repressed genes early in the disease axis, leading to late deficits in protein homeostasis. Treatment of iPSC-derived dopamine neurons with HDAC4-modulating compounds upregulated genes early in the DE axis and corrected PD-related cellular phenotypes. Our study demonstrates how single-cell transcriptomics can exploit cellular heterogeneity to reveal disease mechanisms and identify therapeutic targets.
Keywords: Parkinson’s disease; histone deacetylase 4; induced pluripotent stem cells; single-cell RNA sequencing.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

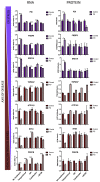
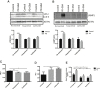
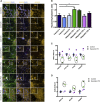
References
-
- Armstrong A.J., Häggman M., Stadler W.M., Gingrich J.R., Assikis V., Polikoff J., Damber J.E., Belkoff L., Nordle Ö., Forsberg G. Long-term survival and biomarker correlates of tasquinimod efficacy in a multicenter randomized study of men with minimally symptomatic metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013;19:6891–6901. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beavan M.S., Schapira A.H. Glucocerebrosidase mutations and the pathogenesis of Parkinson disease. Ann. Med. 2013;45:511–521. - PubMed
-
- Beevers J.E., Lai M.C., Collins E., Booth H.D.E., Zambon F., Parkkinen L., Vowles J., Cowley S.A., Wade-Martins R., Caffrey T.M. MAPT genetic variation and neuronal maturity alter isoform expression affecting axonal transport in iPSC-derived dopamine neurons. Stem Cell Reports. 2017;9:587–599. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Blanco-Arias P., Einholm A.P., Mamsa H., Concheiro C., Gutiérrez-de-Terán H., Romero J., Toustrup-Jensen M.S., Carracedo A., Jen J.C., Vilsen B., Sobrido M.J. A C-terminal mutation of ATP1A3 underscores the crucial role of sodium affinity in the pathophysiology of rapid-onset dystonia-parkinsonism. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2009;18:2370–2377. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- MR/M00919X/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G84/6443/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 26988/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- MC_UP_A320_1004/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_00016/15/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12009/16/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 27723/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_16034/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 090532/Z/09/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MC_EX_MR/N50192X/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/L023784/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/L006340/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- WTISSF121302/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- J-0901/PUK_/Parkinson's UK/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12021/4/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/L023784/2/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 27125/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- MR/M024962/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

