Anti-NKG2A mAb Is a Checkpoint Inhibitor that Promotes Anti-tumor Immunity by Unleashing Both T and NK Cells
- PMID: 30503213
- PMCID: PMC6292840
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.10.014
Anti-NKG2A mAb Is a Checkpoint Inhibitor that Promotes Anti-tumor Immunity by Unleashing Both T and NK Cells
Abstract
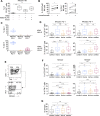
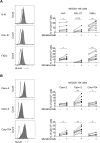
Checkpoint inhibitors have revolutionized cancer treatment. However, only a minority of patients respond to these immunotherapies. Here, we report that blocking the inhibitory NKG2A receptor enhances tumor immunity by promoting both natural killer (NK) and CD8+ T cell effector functions in mice and humans. Monalizumab, a humanized anti-NKG2A antibody, enhanced NK cell activity against various tumor cells and rescued CD8+ T cell function in combination with PD-x axis blockade. Monalizumab also stimulated NK cell activity against antibody-coated target cells. Interim results of a phase II trial of monalizumab plus cetuximab in previously treated squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck showed a 31% objective response rate. Most common adverse events were fatigue (17%), pyrexia (13%), and headache (10%). NKG2A targeting with monalizumab is thus a novel checkpoint inhibitory mechanism promoting anti-tumor immunity by enhancing the activity of both T and NK cells, which may complement first-generation immunotherapies against cancer.
Keywords: CD8(+) T cells; cancer immunotherapy; immunce checkpoint inhibitor; inhibitory receptors; lymphocytes; natural killer cells; therapeutic monoclonal antibodies.
Copyright © 2018 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures





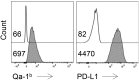

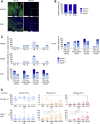
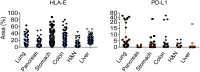
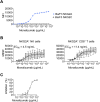

Comment in
-
Checkpoint ahead - be prepared to stop!Nat Rev Cancer. 2019 Feb;19(2):61. doi: 10.1038/s41568-018-0096-2. Nat Rev Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30542080 No abstract available.
-
NKG2A, a New Kid on the Immune Checkpoint Block.Cell. 2018 Dec 13;175(7):1720-1722. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.11.048. Cell. 2018. PMID: 30550781
-
Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: Anti-NKG2A Antibodies on Board.Trends Immunol. 2019 Feb;40(2):83-85. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2018.12.009. Epub 2019 Jan 1. Trends Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30609967
References
-
- André P., Brunet C., Guia S., Gallais H., Sampol J., Vivier E., Dignat-George F. Differential regulation of killer cell Ig-like receptors and CD94 lectin-like dimers on NK and T lymphocytes from HIV-1-infected individuals. Eur. J. Immunol. 1999;29:1076–1085. - PubMed
-
- Baumeister S.H., Freeman G.J., Dranoff G., Sharpe A.H. Coinhibitory pathways in immunotherapy for cancer. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2016;34:539–573. - PubMed
-
- Bertone S., Schiavetti F., Bellomo R., Vitale C., Ponte M., Moretta L., Mingari M.C. Transforming growth factor-beta-induced expression of CD94/NKG2A inhibitory receptors in human T lymphocytes. Eur. J. Immunol. 1999;29:23–29. - PubMed
-
- Brady J., Hayakawa Y., Smyth M.J., Nutt S.L. IL-21 induces the functional maturation of murine NK cells. J. Immunol. 2004;172:2048–2058. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

