Ultrasound-responsive droplets for therapy: A review
- PMID: 30503398
- PMCID: PMC6459400
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2018.11.028
Ultrasound-responsive droplets for therapy: A review
Abstract
The last two decades have seen the development of acoustically activated droplets, also known as phase-change emulsions, from a diagnostic tool to a therapeutic agent. Through bubble effects and triggered drug release, these superheated agents have found potential applications from oncology to neuromodulation. The aim of this review is to summarise the key developments in therapeutic droplet design and use, to discuss the current challenges slowing clinical translation, and to highlight the new frontiers progressing towards clinical implementation. The literature is summarised by addressing the droplet design criteria and by carrying out a multiparametric study of a range of droplet formulations and their associated vaporisation thresholds.
Keywords: Cavitation; Focused ultrasound; Phase-change emulsions.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


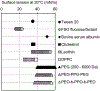
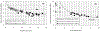

References
-
- Stride EP and Coussios CC, Cavitation and contrast: the use of bubbles in ultrasound imaging and therapy. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part H: Journal of Engineering in Medicine. 2010; 224(2): 171–191. - PubMed
-
- Ilyichev VI, Koretz VL and Melnikov NP, Spectral characteristics of acoustic cavitation Ultrasonics. 1989; 27(6): 357–361. - PubMed
-
- Dayton P, Klibanov A, Brandenburger G and Ferrara K, Acoustic radiation force in vivo: a mechanism to assist targeting of microbubbles, Ultrasound in Medicine and Biology. 1999; 25(8): 1195–1201. - PubMed
-
- Arvanitis CD, Bazan-Peregrino M, Rifai B, Seymour LW and Coussios CC, Cavitation-enhanced extravasation for drug delivery. Ultrasound in Medicine and Biology. 2011; 37(11): 1838–1852. - PubMed
-
- Mulvana H, Browning RJ, Luan Y, de Jong N, Tang MX, Eckersley RJ and Stride E, Characterization of contrast agent microbubbles for ultrasound imaging and therapy research, IEEE transactions on ultrasonics, ferroelectrics, and frequency control. 2017; 64(1): 232–251. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

