Fiber-associated spirochetes are major agents of hemicellulose degradation in the hindgut of wood-feeding higher termites
- PMID: 30504145
- PMCID: PMC6304966
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1810550115
Fiber-associated spirochetes are major agents of hemicellulose degradation in the hindgut of wood-feeding higher termites
Abstract
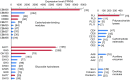
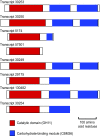
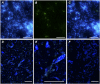
Symbiotic digestion of lignocellulose in wood-feeding higher termites (family Termitidae) is a two-step process that involves endogenous host cellulases secreted in the midgut and a dense bacterial community in the hindgut compartment. The genomes of the bacterial gut microbiota encode diverse cellulolytic and hemicellulolytic enzymes, but the contributions of host and bacterial symbionts to lignocellulose degradation remain ambiguous. Our previous studies of Nasutitermes spp. documented that the wood fibers in the hindgut paunch are consistently colonized not only by uncultured members of Fibrobacteres, which have been implicated in cellulose degradation, but also by unique lineages of Spirochaetes. Here, we demonstrate that the degradation of xylan, the major component of hemicellulose, is restricted to the hindgut compartment, where it is preferentially hydrolyzed over cellulose. Metatranscriptomic analysis documented that the majority of glycoside hydrolase (GH) transcripts expressed by the fiber-associated bacterial community belong to family GH11, which consists exclusively of xylanases. The substrate specificity was further confirmed by heterologous expression of the gene encoding the predominant homolog. Although the most abundant transcripts of GH11 in Nasutitermes takasagoensis were phylogenetically placed among their homologs of Firmicutes, immunofluorescence microscopy, compositional binning of metagenomics contigs, and the genomic context of the homologs indicated that they are encoded by Spirochaetes and were most likely obtained by horizontal gene transfer among the intestinal microbiota. The major role of spirochetes in xylan degradation is unprecedented and assigns the fiber-associated Treponema clades in the hindgut of wood-feeding higher termites a prominent part in the breakdown of hemicelluloses.
Keywords: fiber-associated community; metatranscriptome; spirochetes; termite hindgut; xylanase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Comparative metagenomic and metatranscriptomic analysis of hindgut paunch microbiota in wood- and dung-feeding higher termites.PLoS One. 2013 Apr 12;8(4):e61126. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061126. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23593407 Free PMC article.
-
Metagenomic and functional analysis of hindgut microbiota of a wood-feeding higher termite.Nature. 2007 Nov 22;450(7169):560-5. doi: 10.1038/nature06269. Nature. 2007. PMID: 18033299
-
Comparison of microbial diversity and carbohydrate-active enzymes in the hindgut of two wood-feeding termites, Globitermes sulphureus (Blattaria: Termitidae) and Coptotermes formosanus (Blattaria: Rhinotermitidae).BMC Microbiol. 2024 Nov 12;24(1):470. doi: 10.1186/s12866-024-03623-8. BMC Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39533168 Free PMC article.
-
Lignocellulose-degrading enzymes from termites and their symbiotic microbiota.Biotechnol Adv. 2013 Nov;31(6):838-50. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2013.04.005. Epub 2013 Apr 23. Biotechnol Adv. 2013. PMID: 23623853 Review.
-
Functional symbiosis and communication in microbial ecosystems. The case of wood-eating termites and cockroaches.Int Microbiol. 2015 Sep;18(3):159-69. doi: 10.2436/20.1501.01.246.. Int Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 27036743 Review.
Cited by
-
Bacterial diversity in the clarki ecotype of the photosynthetic sacoglossan, Elysia crispata.Microbiologyopen. 2020 Sep;9(9):e1098. doi: 10.1002/mbo3.1098. Epub 2020 Jun 30. Microbiologyopen. 2020. PMID: 32602643 Free PMC article.
-
Unique pool of carbohydrate-degrading enzymes in novel bacteria assembled from cow and buffalo rumen metagenomes.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022 Jun;106(12):4643-4654. doi: 10.1007/s00253-022-12020-y. Epub 2022 Jun 14. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35699736
-
Genetic innovations in animal-microbe symbioses.Nat Rev Genet. 2022 Jan;23(1):23-39. doi: 10.1038/s41576-021-00395-z. Epub 2021 Aug 13. Nat Rev Genet. 2022. PMID: 34389828 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Termites and subsocial roaches inherited many bacterial-borne carbohydrate-active enzymes (CAZymes) from their common ancestor.Commun Biol. 2024 Nov 6;7(1):1449. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-07146-w. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 39506101 Free PMC article.
-
Lethal disruption of the bacterial gut community in Eastern subterranean termite caused by boric acid.J Econ Entomol. 2024 Dec 28;117(6):2599-2607. doi: 10.1093/jee/toae221. J Econ Entomol. 2024. PMID: 39401329 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cornwell WK, et al. Plant traits and wood fates across the globe: Rotted, burned, or consumed? Glob Change Biol. 2009;15:2431–2449.
-
- Ni J, Tokuda G. Lignocellulose-degrading enzymes from termites and their symbiotic microbiota. Biotechnol Adv. 2013;31:838–850. - PubMed
-
- Lo N, Eggleton P. Termite phylogenetics and co-cladogenesis with symbionts. In: Bignell DE, Roisin Y, Lo N, editors. Biology of Termites: A Modern Synthesis. Springer; Dordrecht, The Netherlands: 2011. pp. 27–50.
-
- Brune A. Symbiotic digestion of lignocellulose in termite guts. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2014;12:168–180. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

