Drebrin-like (Dbnl) Controls Neuronal Migration via Regulating N-Cadherin Expression in the Developing Cerebral Cortex
- PMID: 30504273
- PMCID: PMC6343645
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1634-18.2018
Drebrin-like (Dbnl) Controls Neuronal Migration via Regulating N-Cadherin Expression in the Developing Cerebral Cortex
Abstract
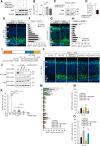
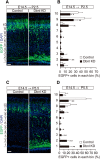
The actin cytoskeleton is crucial for neuronal migration in the mammalian developing cerebral cortex. The adaptor protein Drebrin-like (Dbnl) plays important roles in reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton, dendrite formation, and endocytosis by interacting with F-actin, cobl, and dynamin. Although Dbnl is known to be expressed in the brain, the functions of this molecule during brain development are largely unknown. In this study, to examine the roles of Dbnl in the developing cerebral cortex, we conducted experiments using mice of both sexes with knockdown of Dbnl, effected by in utero electroporation, in the migrating neurons of the embryonic cortex. Time-lapse imaging of the Dbnl-knockdown neurons revealed that the presence of Dbnl is a prerequisite for appropriate formation of processes in the multipolar neurons in the multipolar cell accumulation zone or the deep part of the subventricular zone, and for neuronal polarization and entry into the cortical plate. We found that Dbnl knockdown decreased the amount of N-cadherin protein expressed on the plasma membrane of the cortical neurons. The defect in neuronal migration caused by Dbnl knockdown was rescued by moderate overexpression of N-cadherin and αN-catenin or by transfection of the phospho-mimic form (Y337E, Y347E), but not the phospho-resistant form (Y337F, Y347F), of Dbnl. These results suggest that Dbnl controls neuronal migration, neuronal multipolar morphology, and cell polarity in the developing cerebral cortex via regulating N-cadherin expression.SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT Disruption of neuronal migration can cause neuronal disorders, such as lissencephaly and subcortical band heterotopia. During cerebral cortical development, the actin cytoskeleton plays a key role in neuronal migration; however, the mechanisms of regulation of neuronal migration by the actin cytoskeleton still remain unclear. Herein, we report that the novel protein Dbnl, an actin-binding protein, controls multiple events during neuronal migration in the developing mouse cerebral cortex. We also showed that this regulation is mediated by phosphorylation of Dbnl at tyrosine residues 337 and 347 and αN-catenin/N-cadherin, suggesting that the Dbnl-αN-catenin/N-cadherin pathway is important for neuronal migration in the developing cortex.
Keywords: cerebral cortex; development; neuronal migration; phosphorylation.
Copyright © 2019 the authors 0270-6474/19/390678-14$15.00/0.
Figures




Similar articles
-
A phosphatidylinositol lipids system, lamellipodin, and Ena/VASP regulate dynamic morphology of multipolar migrating cells in the developing cerebral cortex.J Neurosci. 2012 Aug 22;32(34):11643-56. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0738-12.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22915108 Free PMC article.
-
Coronin 2B Regulates Neuronal Migration via Rac1-Dependent Multipolar-Bipolar Transition.J Neurosci. 2023 Jan 11;43(2):211-220. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1087-22.2022. Epub 2022 Dec 5. J Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36639906 Free PMC article.
-
Ablation of the 14-3-3gamma Protein Results in Neuronal Migration Delay and Morphological Defects in the Developing Cerebral Cortex.Dev Neurobiol. 2016 Jun;76(6):600-14. doi: 10.1002/dneu.22335. Epub 2015 Aug 28. Dev Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 26297819
-
The multipolar stage and disruptions in neuronal migration.Trends Neurosci. 2006 Jul;29(7):407-413. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2006.05.006. Epub 2006 May 19. Trends Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16713637 Review.
-
Control of Neuronal Migration and Aggregation by Reelin Signaling in the Developing Cerebral Cortex.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2017 Apr 26;5:40. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2017.00040. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2017. PMID: 28507985 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Is Associated With Upregulation of Cofilin-1 in the Motor Cortex.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Mar 11;9:634347. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.634347. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33777942 Free PMC article.
-
Fbxo45 Binds SPRY Motifs in the Extracellular Domain of N-Cadherin and Regulates Neuron Migration during Brain Development.Mol Cell Biol. 2020 Jun 29;40(14):e00539-19. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00539-19. Print 2020 Jun 29. Mol Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 32341084 Free PMC article.
-
A Unique "Reversed" Migration of Neurons in the Developing Claustrum.J Neurosci. 2023 Feb 1;43(5):693-708. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0704-22.2022. Epub 2023 Jan 11. J Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36631266 Free PMC article.
-
Translational and Posttranslational Dynamics in a Model Peptidergic System.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2023 May;22(5):100544. doi: 10.1016/j.mcpro.2023.100544. Epub 2023 Apr 6. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2023. PMID: 37030596 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mechanisms of Cadherin Function During Cortical Migration.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Sep 15;8:588152. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.588152. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 33043020 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cooke MP, Perlmutter RM (1989) Expression of a novel form of the fyn proto-oncogene in hematopoietic cells. New Biol 1:66–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
