Immune cells and CNS physiology: Microglia and beyond
- PMID: 30504438
- PMCID: PMC6314530
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20180199
Immune cells and CNS physiology: Microglia and beyond
Abstract
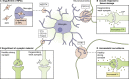
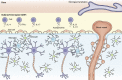
Recent advances have directed our knowledge of the immune system from a narrative of "self" versus "nonself" to one in which immune function is critical for homeostasis of organs throughout the body. This is also the case with respect to the central nervous system (CNS). CNS immunity exists in a segregated state, with a marked partition occurring between the brain parenchyma and meningeal spaces. While the brain parenchyma is patrolled by perivascular macrophages and microglia, the meningeal spaces are supplied with a diverse immune repertoire. In this review, we posit that such partition allows for neuro-immune crosstalk to be properly tuned. Convention may imply that meningeal immunity is an ominous threat to brain function; however, recent studies have shown that its presence may instead be a steady hand directing the CNS to optimal performance.
© 2018 Norris and Kipnis.
Figures
References
-
- A-Gonzalez N., Quintana J.A., García-Silva S., Mazariegos M., González de la Aleja A., Nicolás-Ávila J.A., Walter W., Adrover J.M., Crainiciuc G., Kuchroo V.K., et al. . 2017. Phagocytosis imprints heterogeneity in tissue-resident macrophages. J. Exp. Med. 214:1281–1296. 10.1084/jem.20161375 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ajami B., Samusik N., Wieghofer P., Ho P.P., Crotti A., Bjornson Z., Prinz M., Fantl W.J., Nolan G.P., and Steinman L.. 2018. Single-cell mass cytometry reveals distinct populations of brain myeloid cells in mouse neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration models. Nat. Neurosci. 21:541–551. 10.1038/s41593-018-0100-x - DOI - PMC - PubMed

