An ATF6-tPA pathway in hepatocytes contributes to systemic fibrinolysis and is repressed by DACH1
- PMID: 30504459
- PMCID: PMC6376283
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2018-07-864843
An ATF6-tPA pathway in hepatocytes contributes to systemic fibrinolysis and is repressed by DACH1
Abstract
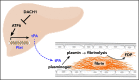
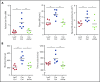
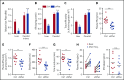
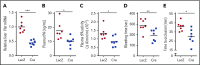
Tissue-type plasminogen activator (tPA) is a major mediator of fibrinolysis and, thereby, prevents excessive coagulation without compromising hemostasis. Studies on tPA regulation have focused on its acute local release by vascular cells in response to injury or other stimuli. However, very little is known about sources, regulation, and fibrinolytic function of noninjury-induced systemic plasma tPA. We explore the role and regulation of hepatocyte-derived tPA as a source of basal plasma tPA activity and as a contributor to fibrinolysis after vascular injury. We show that hepatocyte tPA is downregulated by a pathway in which the corepressor DACH1 represses ATF6, which is an inducer of the tPA gene Plat Hepatocyte-DACH1-knockout mice show increases in liver Plat, circulating tPA, fibrinolytic activity, bleeding time, and time to thrombosis, which are reversed by silencing hepatocyte Plat Conversely, hepatocyte-ATF6-knockout mice show decreases in these parameters. The inverse correlation between DACH1 and ATF6/PLAT is conserved in human liver. These findings reveal a regulated pathway in hepatocytes that contributes to basal circulating levels of tPA and to fibrinolysis after vascular injury.
© 2019 by The American Society of Hematology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures




Comment in
-
Hepatocyte tPA: where have you been hiding?Blood. 2019 Feb 14;133(7):631-632. doi: 10.1182/blood-2018-12-891515. Blood. 2019. PMID: 30765497 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cesarman-Maus G, Hajjar KA. Molecular mechanisms of fibrinolysis. Br J Haematol. 2005;129(3):307-321. - PubMed
-
- Wiman B, Collen D. Molecular mechanism of physiological fibrinolysis. Nature. 1978;272(5653):549-550. - PubMed
-
- Medved L, Nieuwenhuizen W. Molecular mechanisms of initiation of fibrinolysis by fibrin. Thromb Haemost. 2003;89(3):409-419. - PubMed
-
- Wun TC, Capuano A. Initiation and regulation of fibrinolysis in human plasma at the plasminogen activator level. Blood. 1987;69(5):1354-1362. - PubMed
-
- Kooistra T, Schrauwen Y, Arts J, Emeis JJ. Regulation of endothelial cell t-PA synthesis and release. Int J Hematol. 1994;59(4):233-255. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL123098/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 HL135789/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK064819/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007343/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K99 DK115778/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL087123/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK063608/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA132115/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK106045/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K08 HL121131/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR027050/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN276201200017C/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA013696/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

