Latent viruses can cause disease by disrupting the competition for the limiting factor p300/CBP
- PMID: 30505323
- PMCID: PMC6260892
- DOI: 10.1186/s11658-018-0121-1
Latent viruses can cause disease by disrupting the competition for the limiting factor p300/CBP
Abstract
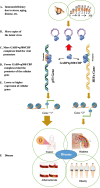
CBP and p300 are histone acetyltransferase coactivators that control the transcription of numerous genes in humans, viruses, and other organisms. Although two separate genes encode CBP and p300, they share a 61% sequence identity, and they are often mentioned together as p300/CBP. Zhou et al. showed that under hypoxic conditions, HIF1α and the tumor suppressor p53 compete for binding to the limiting p300/CBP coactivator. Jethanandani & Kramer showed that δEF1 and MYOD genes compete for the limited amount of p300/CBP in the cell. Bhattacharyya et al. showed that the limiting availability of p300/CBP in the cell serves as a checkpoint for HIF1α activity. Here, we use the microcompetition model to explain how latent viruses with a specific viral cis-regulatory element in their promoter/enhancer can disrupt this competition, causing diseases such as cancer, diabetes, atherosclerosis, and obesity.
Keywords: HIF1α, p53, CBP; Limiting; MYOD; Microcompetition; Transcription factor; p300; δEF1.
Conflict of interest statement
Not applicableBoth authors consent to the publication of the article.The authors declare that they have no competing interests.Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dynamics of sequestering the limiting p300/CBP, viral cis-regulatory elements, and disease.J Biosci. 2020;45:79. J Biosci. 2020. PMID: 32515361 Review.
-
Alpha7 integrin expression is negatively regulated by deltaEF1 during skeletal myogenesis.J Biol Chem. 2005 Oct 28;280(43):36037-46. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M508698200. Epub 2005 Aug 28. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 16129691
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitors synergize p300 autoacetylation that regulates its transactivation activity and complex formation.Cancer Res. 2007 Mar 1;67(5):2256-2264. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-3985. Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17332356 Free PMC article.
-
Binding and modulation of p53 by p300/CBP coactivators.Nature. 1997 Jun 19;387(6635):823-7. doi: 10.1038/42981. Nature. 1997. PMID: 9194565
-
p300/CBP as a Key Nutritional Sensor for Hepatic Energy Homeostasis and Liver Fibrosis.Biomed Res Int. 2018 May 15;2018:8168791. doi: 10.1155/2018/8168791. eCollection 2018. Biomed Res Int. 2018. PMID: 29862292 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Active chromatin marks drive spatial sequestration of heterochromatin in C. elegans nuclei.Nature. 2019 May;569(7758):734-739. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1243-y. Epub 2019 May 22. Nature. 2019. PMID: 31118512
-
CPI-637 as a Potential Bifunctional Latency-Reversing Agent That Targets Both the BRD4 and TIP60 Proteins.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Jul 19;11:686035. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.686035. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34350133 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in Cancer RNAi Therapies.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Oct 25;12(11):3119. doi: 10.3390/cancers12113119. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33113880 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptional co-activators: emerging roles in signaling pathways and potential therapeutic targets for diseases.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023 Nov 13;8(1):427. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01651-w. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023. PMID: 37953273 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Inflammation in Diabetic Retinopathy.Front Immunol. 2020 Nov 6;11:583687. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.583687. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33240272 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

