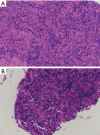
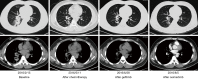
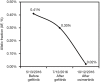
A combined subtype of small cell lung cancer and adenocarcinoma with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation responds to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors
- PMID: 30505514
- PMCID: PMC6236185
- DOI: 10.21037/jtd.2018.09.101
A combined subtype of small cell lung cancer and adenocarcinoma with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation responds to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors for epidermal growth factor receptor gene mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancers: an update for recent advances in therapeutics.J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2016 Jun;22(3):461-76. doi: 10.1177/1078155215577810. Epub 2015 Apr 8. J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2016. PMID: 25855240 Review.
-
Impact of epidermal growth factor receptor gene expression level on clinical outcomes in epidermal growth factor receptor mutant lung adenocarcinoma patients taking first-line epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors.Tumour Biol. 2017 Mar;39(3):1010428317695939. doi: 10.1177/1010428317695939. Tumour Biol. 2017. PMID: 28351317
-
Clinical impact of switching to a second EGFR-TKI after a severe AE related to a first EGFR-TKI in EGFR-mutated NSCLC.Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2012 Jun;42(6):528-33. doi: 10.1093/jjco/hys042. Epub 2012 Mar 28. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22457323
-
[Plasma relative abundance of epidermal growth factor receptor mutations predicts clinical response to epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors in patients with advanced lung adenocarcinoma].Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 2019 Jan 1;58(1):49-55. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0578-1426.2019.01.009. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 30605951 Chinese.
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors as initial therapy for non-small cell lung cancer: focus on epidermal growth factor receptor mutation testing and mutation-positive patients.Cancer Treat Rev. 2013 Dec;39(8):839-50. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2013.05.001. Epub 2013 Jun 12. Cancer Treat Rev. 2013. PMID: 23768755 Review.
Cited by
-
Osimertinib is associated with improved outcomes in pre-treated non-small cell lung cancer leptomeningeal metastases: A systematic review and meta-analysiss.Heliyon. 2024 Apr 17;10(9):e29668. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e29668. eCollection 2024 May 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38698967 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
