Cu-Catalyzed Decarboxylative Borylation
- PMID: 30505624
- PMCID: PMC6257631
- DOI: 10.1021/acscatal.8b02928
Cu-Catalyzed Decarboxylative Borylation
Abstract
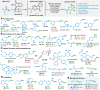
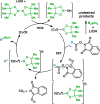
A simple method for the conversion of carboxylic acids to boronic esters via redox-active esters (RAEs) is reported using copper catalysis. The scope of this transformation is broad, and compared with the known protocols available, it represents the most inexpensive, rapid, and operationally simple option. In addition to a full exploration of the scope, a kinetic study was performed to elucidate substrate and reagent concentration dependences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



References
-
- Trippier P. C.; McGuigan C. Boronic Acids in Medicinal Chemistry: Anticancer, Antibacterial and Antiviral Applications. MedChemComm 2010, 1, 183–198. 10.1039/c0md00119h. - DOI
- Draganov A.; Wang D.; Wang B.. The Future of Boron in Medicinal Chemistry: Therapeutic and Diagnostic Applications. In Atypical Elements in Drug Design, Schwarz J., Ed.; Springer, 2014; pp 1–27.
- Ballatore C.; Huryn D. M.; Smith A. B. 3rd Carboxylic Acid (Bio)Isosteres in Drug Design. ChemMedChem 2013, 8, 385–395. 10.1002/cmdc.201200585. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
-
Redox-active esters were also employed in sp2-boronic ester formation, see:
- Candish L.; Teders M.; Glorius F. Transition-Metal-Free, Visible-Light-Enabled Decarboxylative Borylation of Aryl N-Hydroxyphthalimide Esters. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 7440–7443. 10.1021/jacs.7b03127. - DOI - PubMed
- Cheng W.-M.; Shang R.; Zhao B.; Xing W.-L.; Fu Y. Isonicotinate Ester Catalyzed Decarboxylative Borylation of (Hetero)Aryl and Alkenyl Carboxylic Acids through N-Hydroxyphthalimide Esters. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 4291–4294. 10.1021/acs.orglett.7b01950. - DOI - PubMed
-
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
