Recent developments in topoisomerase-targeted cancer chemotherapy
- PMID: 30505655
- PMCID: PMC6251812
- DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2018.07.008
Recent developments in topoisomerase-targeted cancer chemotherapy
Abstract
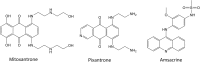
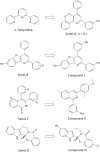
The DNA topoisomerase enzymes are essential to cell function and are found ubiquitously in all domains of life. The various topoisomerase enzymes perform a wide range of functions related to the maintenance of DNA topology during DNA replication, and transcription are the targets of a wide range of antimicrobial and cancer chemotherapeutic agents. Natural product-derived agents, such as the camptothecin, anthracycline, and podophyllotoxin drugs, have seen broad use in the treatment of many types of cancer. Selective targeting of the topoisomerase enzymes for cancer treatment continues to be a highly active area of basic and clinical research. The focus of this review will be to summarize the current state of the art with respect to clinically used topoisomerase inhibitors for targeted cancer treatment and to discuss the pharmacology and chemistry of promising new topoisomerase inhibitors in clinical and pre-clinical development.
Keywords: ADP, adenosine diphosphate; AQD, anti-cancer quinolone derivative; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; Cancer; Clinical; DNA, deoxyribonucleic acid; Inhibition; MTD, maximum tolerated dose; NCI, National Cancer Institute; NCT, national clinical trial; Oncology; PD, pharmacodynamics; PFS, progression free survival; Pre-clinical; Topoisomerase.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Topoisomerase II inhibitors design: Early studies and new perspectives.Bioorg Chem. 2023 Jul;136:106548. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2023.106548. Epub 2023 Apr 20. Bioorg Chem. 2023. PMID: 37094479 Review.
-
Topoisomerase inhibitors. A review of their therapeutic potential in cancer.Drugs. 1995 Jan;49(1):11-9. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199549010-00002. Drugs. 1995. PMID: 7705211 Review.
-
Recent advancements in the medicinal chemistry of bacterial type II topoisomerase inhibitors.Bioorg Chem. 2020 Nov;104:104266. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2020.104266. Epub 2020 Sep 3. Bioorg Chem. 2020. PMID: 33142421 Review.
-
Voreloxin is an anticancer quinolone derivative that intercalates DNA and poisons topoisomerase II.PLoS One. 2010 Apr 15;5(4):e10186. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010186. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20419121 Free PMC article.
-
DNA topoisomerase II enzymes as molecular targets for cancer chemotherapy.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2010 Nov;10(7):758-71. doi: 10.2174/156800910793605785. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2010. PMID: 20578986 Review.
Cited by
-
Dianhydrogalactitol synergizes with topoisomerase poisons to overcome DNA repair activity in tumor cells.Cell Death Dis. 2020 Jul 24;11(7):577. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-02780-8. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 32709853 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Promising Drug Candidates against Prostate Cancer through Computationally-Driven Drug Repurposing.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 5;24(4):3135. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043135. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36834548 Free PMC article.
-
Drug Repositioning Based on the Reversal of Gene Expression Signatures Identifies TOP2A as a Therapeutic Target for Rectal Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Oct 31;13(21):5492. doi: 10.3390/cancers13215492. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34771654 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of New Schiff Bases Tethered Pyrazole Moiety: Design, Synthesis, Biological Evaluation, and Molecular Docking Study as Dual Targeting DHFR/DNA Gyrase Inhibitors with Immunomodulatory Activity.Molecules. 2020 Jun 2;25(11):2593. doi: 10.3390/molecules25112593. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32498469 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the Molecular Complexity of Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma (ACC): A Comprehensive Exploration of Hub Genes, Protein-Protein Interaction (PPI) Networks, microRNA (miRNA) Involvement, and Drug-Gene Interactions (DGIs).Cureus. 2024 Feb 22;16(2):e54730. doi: 10.7759/cureus.54730. eCollection 2024 Feb. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38524085 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Champoux J.J. DNA topoisomerases: structure, function, and mechanism. Annu Rev Biochem. 2001;70:369–413. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

