Radiation-induced gray matter atrophy in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma after intensity modulated radiotherapy: a MRI magnetic resonance imaging voxel-based morphometry study
- PMID: 30505719
- PMCID: PMC6218213
- DOI: 10.21037/qims.2018.10.09
Radiation-induced gray matter atrophy in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma after intensity modulated radiotherapy: a MRI magnetic resonance imaging voxel-based morphometry study
Abstract
Background: Gray matter (GM) damage after radiotherapy (RT) in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) patients can result in cognitive impairment, while there may be no visible brain tissue change according to the conventional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). This study investigated radiation-induced GM volume differences between NPC patients who received RT and those who did not.
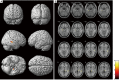
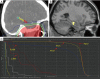
Methods: High-resolution brain structural MRI data from two groups of patients were acquired. The pre-RT group was composed of 56 newly diagnosed but not yet medically treated NPC patients, while the after-RT group consisted of 40 NPC patients who had completed RT more than 1 year ago. Voxel-based morphometry (VBM) was applied to assess GM volumes. Two sample t-test was used to analyze GM volumes voxel-by-voxel using the VBM8 toolbox built in the SPM software. Radiation-induced cortical volume alteration in all NPC patients after RT and dosimetry of 36 patients were analyzed.
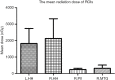
Results: Compared to pre-treatment group, cortical volumes of GM were significantly smaller in the left hippocampus, the right pulvinar and the right middle temporal gyrus (MTG, P<0.001, AlphaSim correction, cluster size ≥157). The mean dose (Dmean) for bilateral hippocampal heads were significantly higher than other different parts of the brain (P<0.001). No significant correlations between the GM volume in any brain regions and the mean dose of corresponding position of these brain regions were observed (P>0.05).
Conclusions: Radiation to the NPC patients can not only induce damage of the hippocampus, but also other secondary damages of GM.
Keywords: Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC); gray matter volume; magnetic resonance imaging (MRI); radiotherapy (RT).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Mao YP, Zhou GQ, Liu LZ, Guo R, Sun Y, Li L, Lin AH, Zeng MS, Kang TB, Jia WH, Shao JY, Mai HQ, Ma J.Comparison of radiological and clinical features of temporal lobe necrosis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients treated with 2D radiotherapy or intensity-modulated radiotherapy. Br J Cancer 2014;110:2633-9. 10.1038/bjc.2014.243 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
