The modified transforaminal endoscopic technique in treating intracanalicular combining foraminal and/or extraforaminal lumbar disc herniations
- PMID: 30505722
- PMCID: PMC6218206
- DOI: 10.21037/qims.2018.10.02
The modified transforaminal endoscopic technique in treating intracanalicular combining foraminal and/or extraforaminal lumbar disc herniations
Abstract
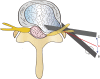
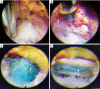
Background: To develop a modified transforaminal endoscopic spine system (TESSYS®) technique for treating intracanalicular combining foraminal and/or extraforaminal lumbar disc herniation (ICFE-LDH), and evaluate the technical efficacy and safety.
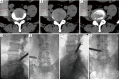
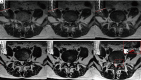
Methods: Twenty-three patients with ICFE-LDH underwent the modified TESSYS technique were enrolled. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) was used to verify the reduction of herniated disc. Pre- and post-operative neurological functions were compared by visual analogue scale (VAS) score, Oswestry disability index (ODI) and the modified MacNab criteria. The technical safety was evaluated by surgical complications.
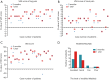
Results: MRI demonstrated reductions of disc herniations in 22 patients (95.7%) after surgeries. The VAS scores were significantly improved at 1 year follow-up (low back: P=0.001, lower limbs: P<0.001), as well as ODI scores (P<0.001). 22 patients had achieved excellent and good recovery postoperatively according to the modified MacNab criteria. One patient (4.3%) underwent a reoperation due to postoperative recurrence of disc herniation. Another patient complained postoperative causalgia in 8 weeks, the symptom alleviated after conservative treatment at 1 year follow-up (VAS: back, 3, lower limbs, 0; ODI: 20%). The incidence rate of surgical complication was 8.7%.
Conclusions: The modified TESSYS technique is a minimally-invasive, effective and safe surgery for treating ICFE-LDHs in selected patients.
Keywords: Modified transforaminal endoscopic spine system (modified TESSYS); efficacy; lumbar disc herniation; safety.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transforaminal Percutaneous Endoscopic Discectomy for L3/4 and L4/5 Foraminal and Extraforaminal Lumbar Disc Herniation: Clinical Outcomes and Technical Note.Asian J Neurosurg. 2025 Mar 10;20(2):337-343. doi: 10.1055/s-0045-1805018. eCollection 2025 Jun. Asian J Neurosurg. 2025. PMID: 40485789 Free PMC article.
-
Radiographic and clinical outcomes of huge lumbar disc herniations treated by transforaminal endoscopic discectomy.Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2019 Oct;185:105485. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2019.105485. Epub 2019 Aug 9. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2019. PMID: 31421587
-
Combining YESS and TESSYS techniques during percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy for multilevel lumbar disc herniation.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Jul;97(28):e11240. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000011240. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 29995758 Free PMC article.
-
Percutaneous Endoscopic Transforaminal Outside-In Outside Technique for Foraminal and Extraforaminal Lumbar Disc Herniations-Operative Technique.World Neurosurg. 2019 Oct;130:244-253. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2019.07.005. Epub 2019 Jul 9. World Neurosurg. 2019. PMID: 31299304
-
Application of a targeted and quantificational foraminoplasty device in percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy for L5-S1 disc herniation: preliminary clinical outcomes.J Orthop Surg Res. 2021 Jun 22;16(1):398. doi: 10.1186/s13018-021-02533-z. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021. PMID: 34158087 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Comparable effectiveness of transforaminal endoscopic spine system technique combined with selective nerve root block between far lateral lumbar disc herniation and central or paracentral herniation.Jt Dis Relat Surg. 2022;33(3):513-520. doi: 10.52312/jdrs.2022.761. Epub 2022 Oct 21. Jt Dis Relat Surg. 2022. PMID: 36345178 Free PMC article.
-
Percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy for different types of lumbar disc herniation: A retrospective study.J Int Med Res. 2021 Oct;49(10):3000605211055045. doi: 10.1177/03000605211055045. J Int Med Res. 2021. PMID: 34706589 Free PMC article.
-
A Retrospective Comparative Study of Modified Percutaneous Endoscopic Transforaminal Discectomy and Open Lumbar Discectomy for Gluteal Pain Caused by Lumbar Disc Herniation.Front Surg. 2022 Jun 22;9:930036. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.930036. eCollection 2022. Front Surg. 2022. PMID: 35813040 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the application value of two commonly used minimally invasive spinal surgery in the treatment of lumbar disc herniation.Exp Ther Med. 2021 Apr;21(4):299. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.9730. Epub 2021 Jan 28. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 33717242 Free PMC article.
-
Full-endoscopic lumbar discectomy via lateral superior articular process approach for treating far lateral lumbar disc herniation: a retrospective study and technical note.Int Orthop. 2023 Nov;47(11):2843-2850. doi: 10.1007/s00264-023-05937-0. Epub 2023 Aug 26. Int Orthop. 2023. PMID: 37632529
References
-
- Joswig H, Richter H, Haile SR, Hildebrandt G, Fournier JY. Introducing interlaminar full-endoscopic lumbar diskectomy: a critical analysis of complications, recurrence rates, and outcome in view of two spinal surgeons' learning curves. J Neurol Surg A Cent Eur Neurosurg 2016;77:406-15. 10.1055/s-0035-1570343 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Genevay S, Courvoisier DS, Konstantinou K, Kovacs FM, Marty M, Rainville J, Norberg M, Kaux JF, Cha TD, Katz JN, Atlas SJ. Clinical classification criteria for radicular pain caused by lumbar disc herniation: the radicular pain caused by disc herniation (RAPIDH) criteria. Spine J 2017;17:1464-71. 10.1016/j.spinee.2017.05.005 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
