Long-term follow-up of the DeKAF cross-sectional cohort study
- PMID: 30506642
- PMCID: PMC7653899
- DOI: 10.1111/ajt.15204
Long-term follow-up of the DeKAF cross-sectional cohort study
Abstract
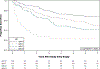
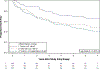
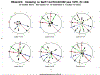
The DeKAF study was developed to better understand the causes of late allograft loss. Preliminary findings from the DeKAF cross-sectional cohort (with follow-up < 20 months) have been published. Herein, we present long-term outcomes in those recipients (mean follow-up ± SD, 6.6 ± 0.7 years). Eligibility included being transplanted prior to October 1, 2005; serum creatinine ≤ 2.0 mg/dL on January 1, 2006; and subsequently developing new-onset graft dysfunction leading to a biopsy. Mean time from transplant to biopsy was 7.5 ± 6.1 years. Histologic findings and DSA were studied in relation to postbiopsy outcomes. Long-term follow-up confirms and expands the preliminary results of each of 3 studies: (1) increasing inflammation in area of atrophy (irrespective of inflammation in nonscarred areas [Banff i]) was associated with increasingly worse postbiopsy death-censored graft survival; (2) hierarchical analysis based on Banff scores defined clusters (entities) that differed in long-term death-censored graft survival; and (3) C4d-/DSA- recipients had significantly better (and C4d+/DSA+ worse) death-censored graft survival than other groups. C4d+/DSA- and C4d-/DSA+ had similar intermediate death-censored graft survival. Clinical and histologic findings at the time of new-onset graft dysfunction define high- vs low-risk groups for long-term death-censored graft survival, even years posttransplant. These findings can help differentiate groups for potential intervention studies.
Keywords: antibody biology; chronic allograft nephropathy; classification systems: Banff classification; clinical research/practice; clinical trial; graft survival; kidney transplantation/nephrology.
© 2018 The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons.
Figures


References
-
- Meier-Kriesche HU, Schold JD, Srinivas TR, Kaplan B. Lack of improvement in renal allograft survival despite a marked decrease in acute rejection rates over the most recent era. Am J Transplant. 2004;4(3):378–383. - PubMed
-
- Matas AJ, Smith JM, Skeans MA, et al. OPTN/SRTR 2013 annual data report: kidney. Am J Transplant. 2015;15(suppl 2):1–34. - PubMed
-
- Almond PS, Matas A, Gillingham K, et al. Risk factors for chronic rejection in renal allograft recipients. Transplantation. 1993;55(4):752–756; discussion 756-757. - PubMed
-
- Cosio FG, Pelletier RP, Falkenhain ME, et al. Impact of acute rejection and early allograft function on renal allograft survival. Transplantation. 1997;63(11):1611–1615. - PubMed
-
- Monaco AP, Burke JF Jr, Ferguson RM, et al. Current thinking on chronic renal allograft rejection: issues, concerns, and recommendations from a 1997 roundtable discussion. Am J Kidney Dis. 1999;33(1):150–160. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

