The effects of switching EGFR-TKI treatments for non-small cell lung cancer because of adverse events
- PMID: 30506897
- PMCID: PMC7379949
- DOI: 10.1111/ajco.13103
The effects of switching EGFR-TKI treatments for non-small cell lung cancer because of adverse events
Abstract
Background: Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR-TKIs) are used to treat patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and EGFR driver mutations. Although some patients discontinued these treatments because of adverse events, it is unclear whether switching EGFR-TKI because of adverse events provides a benefit.
Methods: This retrospective study evaluated data from 22 patients with EGFR mutation-positive NSCLC who received at least two EGFR-TKIs that were switched because of adverse events (March 2011 to September 2017). Progression-free survival 2 (PFS2) was defined as the time from starting of the first EGFR-TKI treatment to disease progression during the second EGFR-TKI treatment.
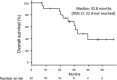
Results: Seventeen patients received gefitinib as the first EGFR-TKI treatment, while four patients received afatinib and one patient received erlotinib. The median time to failure of the first EGFR-TKI treatment was 1.6 months. The EGFR-TKIs were switched because of hepatotoxicity (n = 16), interstitial lung disease (n = 3), and other reasons (n = 3). The median washout period was 1.1 months. Seventeen patients received erlotinib as the second EGFR-TKI treatment, while three patients received gefitinib and two patients received afatinib. The median PFS for the second EGFR-TKI treatment was 15.2 months. The median PFS2 was 17.7 months and the median overall survival was 32.8 months.
Conclusions: Switching EGFR-TKIs because of adverse events provided a clinical benefit for patients with EGFR mutation-positive NSCLC. Appropriate judgment regarding switching from one EGFR-TKI to another may improve the performance status and prognosis of patients with EGFR mutation-positive NSCLC.
Keywords: epidermal growth factor receptor; non-small cell lung cancer; tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
© 2018 The Authors. Asia-Pacific Journal of Clinical Oncology Published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Hanna N, Johnson D, Temin S, Jr , et al. Systemic therapy for stage IV Non–Small‐Cell lung cancer: American society of clinical oncology clinical practice guideline update. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35:3484–3515. - PubMed
-
- Novello S, Barlesi F, Califano R, et al. Metastatic non‐small‐cell lung cancer: eSMO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow‐up. Ann Oncol. 2016;27(Suppl 5):v1–v27. - PubMed
-
- Maemondo M, Inoue A, Kobayashi K, et al. Gefitinib or chemotherapy for non‐small‐cell lung cancer with mutated EGFR. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:2380–2388. - PubMed
-
- Rosell R, Carcereny E, Gervais R, et al. Erlotinib versus standard chemotherapy as first‐line treatment for European patients with advanced EGFR mutation‐positive non‐small‐cell lung cancer (EURTAC): a multicentre, open‐label, randomized phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012;13:239–246. - PubMed
-
- Sequist LV, Yang JC, Yamamoto N, et al. Phase III study of afatinib or cisplatin plus pemetrexed in patients with metastatic lung adenocarcinoma with EGFR mutations. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:3327–3334. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

