Spinal direct current stimulation (tsDCS) in hereditary spastic paraplegias (HSP): A sham-controlled crossover study
- PMID: 30508408
- PMCID: PMC7919872
- DOI: 10.1080/10790268.2018.1543926
Spinal direct current stimulation (tsDCS) in hereditary spastic paraplegias (HSP): A sham-controlled crossover study
Abstract
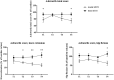
Objective: Hereditary spastic paraplegia (HSP) represents a heterogeneous group of neurodegenerative diseases characterized by progressive spasticity and lower limb weakness. We assessed the effects of transcutaneous spinal direct current stimulation (tsDCS) in HSP.Design: A double-blind, randomized, crossover and sham-controlled study.Setting: Fondazione IRCCS Cà Granda, Ospedale Maggiore Policlinico, Milan.Participants: eleven patients with HSP (six men, mean age ± SD: 37.3 ± 8.1 years), eight affected by spastin/SPG4,1 by atlastin1/SPG3a, 1 by paraplegin/SPG7 and 1 by ZFYVE26/SPG15.Interventions: tsDCS (anodal or sham, 2.0 mA, 20', five days) delivered over the thoracic spinal cord (T10-T12).Outcome measures: Motor-evoked potentials (MEPs), the H-reflex (Hr), F-waves, the Ashworth scale for clinical spasticity, the Five Minutes Walking test and the Spastic Paraplegia Rating Scale (SPRS) were assessed. Patients were evaluated before tsDCS (T0), at the end of the stimulation (T1), after one week (T2), one month (T3) and two months (T4).Results: The score of the Ashworth scale improved in the anodal compared with sham group, up to two months following the end of stimulation (T1, P = .0137; T4, P = .0244), whereas the Five Minutes Walking test and SPRS did not differ between the two groups. Among neurophysiological measures, both anodal and sham tsDCS left Hr, F-waves and MEPs unchanged over time.Conclusions: Anodal tsDCS significantly decreases spasticity and might be a complementary strategy for the treatment of spasticity in HSP.
Keywords: Hereditary spastic paraplegias; Movement disorders; Non-invasive spinal stimulation; Spasticity treatment; Transcutaneous spinal direct current stimulation.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
