Mesalazine-related lung disease in a patient with ulcerative colitis: A case report
- PMID: 30508908
- PMCID: PMC6283093
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000013242
Mesalazine-related lung disease in a patient with ulcerative colitis: A case report
Abstract
Rationale: Mesalazine is widely used to treat inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). However, discriminating between pulmonary manifestations of IBD and drug-related lung disease remains a challenge. There were few case reports of mesalazine-related organizing pneumonia so far.
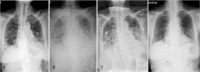
Patient concerns: A 75-year-old female was diagnosed with ulcerative colitis and took mesalazine over a period of 2 years and 8 months. She presented with progressive shortness of breath for 3 days and visited our emergency department. Chest radiography showed increased bilateral infiltrates. During hospitalization her clinical condition deteriorated, and she was transferred to our intensive care unit under noninvasive ventilator support.
Diagnosis: Computed tomography (CT) scan showed diffuse peribronchial and subpleural consolidations in bilateral lungs. Possible etiologies of interstitial lung disease were surveyed, including various infectious diseases and connective tissue diseases. Transbronchial lung biopsy showed characteristic features of organizing pneumonia.
Interventions: Under the consideration of mesalazine-related lung disease, mesalazine was discontinued early in disease course and steroid therapy was given.
Outcomes: The patient was discharged from hospital with improved clinical symptoms and radiographic images.
Lessons: Although this patient suffered a life-threatening adverse event, prompt diagnosis with proper management can result in a favorable outcome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


References
-
- Kuo C-J, Yu K-H, See L-C, et al. The trend of inflammatory bowel diseases in Taiwan: a population-based study. Dig Dis Sci 2015;60:2454–62. - PubMed
-
- Tanigawa K, Sugiyama K, Matsuyama H, et al. Mesalazine-induced eosinophilic pneumonia. Respiration 1999;66:69–72. - PubMed
-
- Kevans D, Greene J, Galvin L, et al. Mesalazine-induced bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia (BOOP) in a patient with ulcerative colitis and primary sclerosing cholangitis. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2011;17:E137–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

