A comparison of adductor canal block and femoral nerve block after total-knee arthroplasty regarding analgesic effect, effectiveness of early rehabilitation, and lateral knee pain relief in the early stage
- PMID: 30508936
- PMCID: PMC6283224
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000013391
A comparison of adductor canal block and femoral nerve block after total-knee arthroplasty regarding analgesic effect, effectiveness of early rehabilitation, and lateral knee pain relief in the early stage
Abstract
Background: The aim of this study was to compare the analgesic effect on the lateral and overall knee and early rehabilitation between adductor canal block (ACB) and femoral nerve block (FNB) after total-knee arthroplasty.
Method: Two hundred patients randomly participated in the study and were divided into the ACB group and FNB group in a randomized manner. All patients received standardized anesthesia and analgesia upon hospitalization. Outcome evaluations included visual analog scale (VAS) scores at rest and during activity, quadriceps strength, range of motion (ROM), total opioid consumption and complication occurrence, sleep interruptions caused by pain, postoperative nausea and vomiting (PONV), and postoperative length of stay (PLOS) before discharge in all groups. In the 90-day postoperative follow-up, we also observed the acute deep periprosthetic joint infection, wound breakdown, readmission, reoperations, inpatient falls, ROM, and patient satisfaction score.
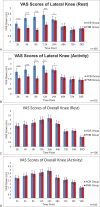
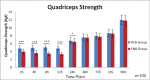
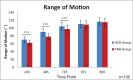
Results: The lateral knee VAS scores are lower in the FNB group at rest and during activity (2-24 hours postoperatively) compared with those in the ACB group. However, the overall knee VAS score, total opioid consumption and complication occurrence, sleep interruptions caused by pain, and PONV are similar between the FNB and ACB groups. When evaluating early rehabilitation, the quadriceps strength in the ACB group is superior to that in the FNB group 24 hours postoperatively. At 24, 48, and 72 hours postoperatively, ROM in the ACB group is significantly better than that in the FNB group. Furthermore, the ACB group has a shorter PLOS (4.5 ± 0.60 days) than the FNB group (5.3 ± 0.7 days). However, patient satisfaction score, readmission rate, inpatient falls, acute deep periprosthetic joint infection, and wound breakdown are not statistically significantly different between the 2 groups.
Conclusion: The ACB does not relieve lateral knee pain in the early stage but provides similar analgesic effect and better effectiveness of early rehabilitation compared with FNB in patients undergoing TKA.
Figures
References
-
- Parvizi J, Miller AG, Gandhi K. Multimodal pain management after total joint arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2011;93A:1075–84. - PubMed
-
- Vendittoli PA, Makinen P, Drolet P, et al. A multimodal analgesia protocol for total knee arthroplasty - a randomized, controlled study. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2006;88A:282–9. - PubMed
-
- Abdul-Hadi O, Parvizi J, Austin MS, et al. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in orthopaedics. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2009;91A:2020–7. - PubMed
-
- Barrington MJ, Olive D, Low K, et al. Continuous femoral nerve blockade or epidural analgesia after total knee replacement: a prospective randomized controlled trial. Anesth Analg 2005;101:1824–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

