Effect of computer navigation-assisted minimally invasive direct lateral interbody fusion in the treatment of patients with lumbar tuberculosis: A retrospective study
- PMID: 30508977
- PMCID: PMC6283231
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000013484
Effect of computer navigation-assisted minimally invasive direct lateral interbody fusion in the treatment of patients with lumbar tuberculosis: A retrospective study
Abstract
The benefits of navigation-assisted technologies are not entirely understood. Therefore, this study aimed to examine the outcomes of patients with lumbar tuberculosis who received computer navigation-assisted minimally invasive direct lateral interbody fusion (DLIF).This was a retrospective study of 33 patients with lumbar tuberculosis who underwent minimally invasive DLIF at the Department of Spine and Orthopedics of Guigang People's Hospital (Guangxi, China) between January 2015 and December 2016. The patients were pathologically diagnosed as lumbar tuberculosis and grouped into the navigation-assisted fluoroscopy (NAV; n = 18) and non-navigation-assisted fluoroscopy (non-NAV; n = 15) groups. X-ray exposure and operation times were assessed in all patients.All surgical procedures were successfully completed. No case was converted into open surgery. The NAV group had longer surgical preparation time but shorter operation time compared with the non-NAV group (both P <.01). Total operation time showed no significant difference between the 2 groups (P = .1). The time of radiation exposure in the non-NAV group was longer compared with that of the NAV group (53.2 ± 9.9 vs 13.5 ± 2.6 s; P <.01). There were no significant differences regarding intraoperative blood loss, postoperative drainage volume, length of hospital stay, bone fusion and complications between the 2 groups (all P >.05).Computer navigation-assisted minimally invasive DLIF could significantly reduce intraoperative radiation exposure, with no increase in total operation time.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
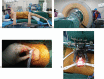


References
-
- World Health, Oragnization Global tuberculosis report 2015. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2015.
-
- Results of directly observed short-course chemotherapy in 112,842 Chinese patients with smear-positive tuberculosis. China Tuberculosis Control Collaboration. Lancet 1996;347:358–62. - PubMed
-
- Wang L, Zhang H, Ruan Y, et al. Tuberculosis prevalence in China, 1990-2010; a longitudinal analysis of national survey data. Lancet 2014;383:2057–64. - PubMed
-
- Dye C, Maher D, Weil D, et al. Targets for global tuberculosis control. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 2006;10:460–2. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

