Deletion of high-molecular-weight glutenin subunits in wheat significantly reduced dough strength and bread-baking quality
- PMID: 30509162
- PMCID: PMC6276161
- DOI: 10.1186/s12870-018-1530-z
Deletion of high-molecular-weight glutenin subunits in wheat significantly reduced dough strength and bread-baking quality
Abstract
Background: High-molecular-weight glutenin subunits (HMW-GS) play important roles in the elasticity of dough made from wheat. The HMW-GS null line is useful for studying the contribution of HMW-GS to the end-use quality of wheat.
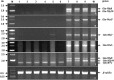
Methods: In a previous work, we cloned the Glu-1Ebx gene from Thinopyrum bessarabicum and introduced it into the wheat cultivar, Bobwhite. In addition to lines expressing the Glu-1Ebx gene, we also obtained a transgenic line (LH-11) with all the HMW-GS genes silenced. The HMW-GS deletion was stably inherited as a dominant and conformed to Mendel's laws. Expression levels of HMW-GS were determined by RT-PCR and epigenetic changes in methylation patterns and small RNAs were analyzed. Glutenins and gliadins were separated and quantitated by reversed-phase ultra-performance liquid chromatography. Measurement of glutenin macropolymer, and analysis of agronomic traits and end-use quality were also performed.
Results: DNA methylation and the presence of small double-stranded RNA may be the causes of post-transcriptional gene silencing in LH-11. The accumulation rate and final content of glutenin macropolymer (GMP) in LH-11 were significantly lower than in wild-type (WT) Bobwhite. The total protein content was not significantly affected as the total gliadin content increased in LH-11 compared to WT. Deletion of HMW-GS also changed the content of different gliadin fractions. The ratio of ω-gliadin increased, whereas α/β- and γ-gliadins declined in LH-11. The wet gluten content, sedimentation value, development time and stability time of LH-11 were remarkably lower than that of Bobwhite. Bread cannot be made using the flour of LH-11.
Conclusions: Post-transcriptional gene silencing through epigenetic changes and RNA inhibition appear to be the causes for the gene expression deficiency in the transgenic line LH-11. The silencing of HMW-GW in LH-11 significantly reduced the dough properties, GMP content, wet gluten content, sedimentation value, development time and stability time of flour made from this wheat cultivar. The HMW-GS null line may provide a potential material for biscuit-making because of its low dough strength.
Keywords: Common wheat; Dough quality; Gliadin content; Glutenin macropolymer; High-molecular-weight glutenin subunits; Post-transcriptional gene silencing.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Effect of high molecular weight glutenin subunit composition in common wheat on dough properties and steamed bread quality.J Sci Food Agric. 2014 Oct;94(13):2801-6. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.6635. Epub 2014 Mar 31. J Sci Food Agric. 2014. PMID: 24591045
-
Influences of high-molecular-weight glutenin subunits and rye translocations on dough-mixing properties and sugar-snap cookie-baking quality of soft winter wheat.J Sci Food Agric. 2020 Aug;100(10):3850-3856. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.10423. Epub 2020 May 23. J Sci Food Agric. 2020. PMID: 32297322
-
Effect of high-molecular-weight glutenin subunits silencing on dough aggregation characteristics.Food Chem. 2024 May 30;441:138371. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2024.138371. Epub 2024 Jan 8. Food Chem. 2024. PMID: 38218148
-
Wheat gluten: high molecular weight glutenin subunits--structure, genetics, and relation to dough elasticity.J Food Sci. 2007 Apr;72(3):R56-63. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3841.2007.00292.x. J Food Sci. 2007. PMID: 17995810 Review.
-
High-Molecular-Weight Glutenin Subunits: Genetics, Structures, and Relation to End Use Qualities.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 26;22(1):184. doi: 10.3390/ijms22010184. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33375389 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Disruption of Xylanase inhibitor protein (XIP) Gene Improved the Dough Quality of Common Wheat.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Apr 5;13:811668. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.811668. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35449885 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid and Easy High-Molecular-Weight Glutenin Subunit Identification System by Lab-on-a-Chip in Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.).Plants (Basel). 2020 Nov 9;9(11):1517. doi: 10.3390/plants9111517. Plants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33182289 Free PMC article.
-
Diversity in Grain, Flour, Amino Acid Composition, Protein Profiling, and Proportion of Total Flour Proteins of Different Wheat Cultivars of North India.Front Nutr. 2020 Sep 8;7:141. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2020.00141. eCollection 2020. Front Nutr. 2020. PMID: 33015119 Free PMC article.
-
Variability in grain, flour, functional properties and protein profiling in newly developed wheat genotypes grown in temperate climate of Western Himalayas.Front Nutr. 2025 Jul 15;12:1604775. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1604775. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40735232 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome and Proteome Analysis Revealed the Influence of High-Molecular-Weight Glutenin Subunits (HMW-GSs) Deficiency on Expression of Storage Substances and the Potential Regulatory Mechanism of HMW-GSs.Foods. 2023 Jan 12;12(2):361. doi: 10.3390/foods12020361. Foods. 2023. PMID: 36673453 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shewry P, Halford N, Tatham A. High molecular weight subunits of wheat glutenin. J Cereal Sci. 1992;15(2):105–120. doi: 10.1016/S0733-5210(09)80062-3. - DOI
-
- Lindsay MP, Skerritt JH. Immunocytochemical localization of gluten proteins uncovers structural organization of glutenin macropolymer. Cereal Chem. 2000;77(3):360–369. doi: 10.1094/CCHEM.2000.77.3.360. - DOI
-
- Gianibelli MC, Gupta RB, Lafiandra D, Margiotta B, MacRitchie F. Polymorphism of high Mr glutenin subunits in Triticum tauschii: characterisation by chromatography and electrophoretic methods. J Cereal Sci. 2001;33(1):39–52. doi: 10.1006/jcrs.2000.0328. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HBCT2018010201/Modern Agricultural Industry Technology System - Hebei Province Wheat Innovation Team Construction
- 2017YF00100603/Cultivation of New Wheat Varieties with High Yield, High Quality and Water-Saving in North of Yellow and Huai Winter wheat Region
- 494-0402-YBN-RDC4/Modern Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Project of Hebei Province
- 494-0402-JBN-C7GQ/Modern Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Project of Hebei Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

