Deletion of high-molecular-weight glutenin subunits in wheat significantly reduced dough strength and bread-baking quality
- PMID: 30509162
- PMCID: PMC6276161
- DOI: 10.1186/s12870-018-1530-z
Deletion of high-molecular-weight glutenin subunits in wheat significantly reduced dough strength and bread-baking quality
Abstract
Background: High-molecular-weight glutenin subunits (HMW-GS) play important roles in the elasticity of dough made from wheat. The HMW-GS null line is useful for studying the contribution of HMW-GS to the end-use quality of wheat.
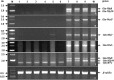
Methods: In a previous work, we cloned the Glu-1Ebx gene from Thinopyrum bessarabicum and introduced it into the wheat cultivar, Bobwhite. In addition to lines expressing the Glu-1Ebx gene, we also obtained a transgenic line (LH-11) with all the HMW-GS genes silenced. The HMW-GS deletion was stably inherited as a dominant and conformed to Mendel's laws. Expression levels of HMW-GS were determined by RT-PCR and epigenetic changes in methylation patterns and small RNAs were analyzed. Glutenins and gliadins were separated and quantitated by reversed-phase ultra-performance liquid chromatography. Measurement of glutenin macropolymer, and analysis of agronomic traits and end-use quality were also performed.
Results: DNA methylation and the presence of small double-stranded RNA may be the causes of post-transcriptional gene silencing in LH-11. The accumulation rate and final content of glutenin macropolymer (GMP) in LH-11 were significantly lower than in wild-type (WT) Bobwhite. The total protein content was not significantly affected as the total gliadin content increased in LH-11 compared to WT. Deletion of HMW-GS also changed the content of different gliadin fractions. The ratio of ω-gliadin increased, whereas α/β- and γ-gliadins declined in LH-11. The wet gluten content, sedimentation value, development time and stability time of LH-11 were remarkably lower than that of Bobwhite. Bread cannot be made using the flour of LH-11.
Conclusions: Post-transcriptional gene silencing through epigenetic changes and RNA inhibition appear to be the causes for the gene expression deficiency in the transgenic line LH-11. The silencing of HMW-GW in LH-11 significantly reduced the dough properties, GMP content, wet gluten content, sedimentation value, development time and stability time of flour made from this wheat cultivar. The HMW-GS null line may provide a potential material for biscuit-making because of its low dough strength.
Keywords: Common wheat; Dough quality; Gliadin content; Glutenin macropolymer; High-molecular-weight glutenin subunits; Post-transcriptional gene silencing.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures




References
-
- Shewry P, Halford N, Tatham A. High molecular weight subunits of wheat glutenin. J Cereal Sci. 1992;15(2):105–120. doi: 10.1016/S0733-5210(09)80062-3. - DOI
-
- Lindsay MP, Skerritt JH. Immunocytochemical localization of gluten proteins uncovers structural organization of glutenin macropolymer. Cereal Chem. 2000;77(3):360–369. doi: 10.1094/CCHEM.2000.77.3.360. - DOI
-
- Gianibelli MC, Gupta RB, Lafiandra D, Margiotta B, MacRitchie F. Polymorphism of high Mr glutenin subunits in Triticum tauschii: characterisation by chromatography and electrophoretic methods. J Cereal Sci. 2001;33(1):39–52. doi: 10.1006/jcrs.2000.0328. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HBCT2018010201/Modern Agricultural Industry Technology System - Hebei Province Wheat Innovation Team Construction
- 2017YF00100603/Cultivation of New Wheat Varieties with High Yield, High Quality and Water-Saving in North of Yellow and Huai Winter wheat Region
- 494-0402-YBN-RDC4/Modern Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Project of Hebei Province
- 494-0402-JBN-C7GQ/Modern Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Project of Hebei Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

