Preharvest application of ethephon and postharvest UV-B radiation improve quality traits of beetroot (Beta vulgaris L. ssp. vulgaris) as source of colourant
- PMID: 30509181
- PMCID: PMC6276243
- DOI: 10.1186/s12870-018-1556-2
Preharvest application of ethephon and postharvest UV-B radiation improve quality traits of beetroot (Beta vulgaris L. ssp. vulgaris) as source of colourant
Abstract
Background: Betanins have become excellent replacers for artificial red-purple food colourants. Red beet (Beta vulgaris L. spp. vulgaris) known as beetroot, is a rich source of betalains, which major forms are betanin (red to purple) and vulgaxanthin (yellow). Betalains and phenolic compounds are secondary metabolites, accumulation of which is often triggered by elicitors during plant stress responses. In the present study, pre-harvest applications of ethephon (an ethylene-releasing compound) and postharvest UV-B radiation were tested as elicitors of betalains and phenolic compounds in two beetroot cultivars. Their effects on quality parameters were investigated, and the expression of biosynthetic betalain genes in response to ethephon was determined.
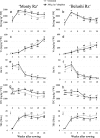
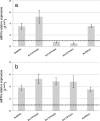
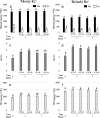
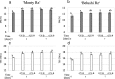
Results: Ethephon was applied as foliar spray during the growth of beetroot, resulting in increased betanin (22.5%) and decreased soluble solids contents (9.4%), without detrimental effects on beetroot yield. The most rapid accumulation rate for betanin and soluble solids was observed between 3 and 6 weeks after sowing in both untreated and ethephon-treated beetroots. Overall, the expression of the betalain biosynthetic genes (CYP76AD1, CYP76AD5, CYP76AD6 and DODA1), determining the formation of both betanin and vulgaxanthin, increased in response to ethephon treatment, as did the expression of the betalain pathway activator BvMYB1. In the postharvest environment, the use of short-term UV-B radiation (1.23 kJ m- 2) followed by storages for 3 and 7 days at 15 °C resulted in increased betanin to vulgaxanthin ratio (51%) and phenolic content (15%).
Conclusions: The results of this study provide novel strategies to improve key profitability traits in betalain production. High betanin concentration and high betanin to vulgaxanthin ratio increase the commercial value of the colourant product. In addition, lowering soluble solids levels facilitates higher concentration of beetroot colour during processing. Moreover, we show that enhanced betanin content in ethephon-treated beetroots is linked to increased expression of betalain biosynthetic genes.
Keywords: Beetroot; Betalain biosynthetic pathway; Betanin; Ethephon; UV-B radiation; Vulgaxanthin.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors are listed as inventors on a submitted European patent application related to the ethephon use described in this paper.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Betalain and betaine composition of greenhouse- or field-produced beetroot ( Beta vulgaris L.) and inhibition of HepG2 cell proliferation.J Agric Food Chem. 2014 Feb 12;62(6):1324-31. doi: 10.1021/jf404648u. Epub 2014 Feb 3. J Agric Food Chem. 2014. PMID: 24467616
-
Foliar-applied ethephon enhances the content of anthocyanin of black carrot roots (Daucus carota ssp. sativus var. atrorubens Alef.).BMC Plant Biol. 2017 Apr 4;17(1):70. doi: 10.1186/s12870-017-1021-7. BMC Plant Biol. 2017. PMID: 28376712 Free PMC article.
-
pH-dependent stability of major betalains in the encapsulated beetroot extracts (Beta vulgaris L.).J Food Sci. 2024 May;89(5):2761-2773. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.17046. Epub 2024 Mar 29. J Food Sci. 2024. PMID: 38551035
-
Biological effects of red beetroot and betalains: A review.Phytother Res. 2020 Aug;34(8):1847-1867. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6653. Epub 2020 Mar 14. Phytother Res. 2020. PMID: 32171042 Review.
-
Red Beetroot Betalains: Perspectives on Extraction, Processing, and Potential Health Benefits.J Agric Food Chem. 2020 Oct 21;68(42):11595-11611. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.0c04241. Epub 2020 Oct 11. J Agric Food Chem. 2020. PMID: 33040529 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of WRKY gene family members in amaranth based on a transcriptome database and functional analysis of AtrWRKY42-2 in betalain metabolism.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Dec 5;14:1300522. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1300522. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 38130485 Free PMC article.
-
Reactive oxygen species derived from NADPH oxidase as signaling molecules regulate fatty acids and astaxanthin accumulation in Chromochloris zofingiensis.Front Microbiol. 2024 Apr 29;15:1387222. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1387222. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38741732 Free PMC article.
-
Betalains and their applications in food: The current state of processing, stability and future opportunities in the industry.Food Chem (Oxf). 2022 Feb 21;4:100089. doi: 10.1016/j.fochms.2022.100089. eCollection 2022 Jul 30. Food Chem (Oxf). 2022. PMID: 35415668 Free PMC article.
-
Gene Regulatory Network Guided Investigations and Engineering of Storage Root Development in Root Crops.Front Plant Sci. 2020 Jun 17;11:762. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.00762. eCollection 2020. Front Plant Sci. 2020. PMID: 32625220 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nutritional and Physiological Effects of Postharvest UV Radiation on Vegetables: A Review.J Agric Food Chem. 2023 Jul 5;71(26):9951-9972. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.3c00481. Epub 2023 Jun 21. J Agric Food Chem. 2023. PMID: 37344965 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- McCann D, Barrett A, Cooper A, Crumpler D, Dalen L, Grimshaw K, Kitchin E, Lok K, Porteous L, Prince E, Sonuga-Barke E, Warner JO, Stevenson J. Food additives and hyperactive behaviour in 3-year-old and 8/9-year-old children in the community: a randomised, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2007;370:1560–1567. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61306-3. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Clement JS, Mabry TJ. Pigment evolution in the caryophyllales: a systematic overview. Bot Acta. 1996;109:360–367. doi: 10.1111/j.1438-8677.1996.tb00584.x. - DOI
-
- Stintzing FC, Herbach KM, Mosshammer MR, Kugler F, Betalain Pigments CR, Quality C. In: Colour quality of fresh and processed foods. Culver CA, Wrolstad RE, editors. Washington: American Chemical Society; 2008. pp. 82–101.
-
- Goldman IL, Eagen KA, Breitbach DN, Gabelman WH. Simultaneous selection is effective in increasing Betalain pigment concentration but not Total dissolved solids in red beet. J Am Soc Hortic Sci. 1996;121(1):23–26.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

