Polyomic tools for an emerging livestock parasite, the rumen fluke Calicophoron daubneyi; identifying shifts in rumen functionality
- PMID: 30509301
- PMCID: PMC6278170
- DOI: 10.1186/s13071-018-3225-6
Polyomic tools for an emerging livestock parasite, the rumen fluke Calicophoron daubneyi; identifying shifts in rumen functionality
Abstract
Background: Diseases caused by parasitic flatworms of rumen tissues (paramphistomosis) are a significant threat to global food security as a cause of morbidity and mortality in ruminant livestock in subtropical and tropical climates. Calicophoron daubneyi is currently the only paramphistome species commonly infecting ruminant livestock in temperate European climates. However, recorded incidences of C. daubneyi infection in European livestock have been increasing over the last decade. Whilst clinical paramphistomosis caused by adult worms has not been confirmed in Europe, fatalities have been attributed to severe haemorrhagic enteritis of the small intestine resulting from the migration of immature paramphistomes. Large numbers of mature adults can reside in the rumen, yet to date, the impact on rumen fermentation, and consequently on productivity and economic management of infected livestock, have not been resolved. Limited publicly available nucleotide and protein sequences for C. daubneyi underpin this lack of biological and economic understanding. Here we present for the first time a de novo assembled transcriptome, with functional annotations, for adult C. daubneyi, which provides a reference database for protein and nucleotide sequence identification to facilitate fundamental biology, anthelmintic, vaccine and diagnostics discoveries.
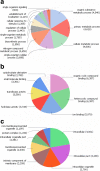
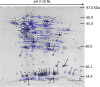
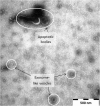
Results: This dataset identifies a number of genes potentially unique to C. daubneyi and, by comparison to an existing transcriptome for the related Paramphistomum cervi, identifies novel genes which may be unique to the paramphistome group of platyhelminthes. Additionally, we present the first coverage of the excretory/secretory and soluble somatic proteome profiles for adult C. daubneyi and identify the release of extracellular vesicles from adult C. daubneyi parasites during in vitro, ex-host culture. Finally, we have performed the first analysis of rumen fluke impacting upon rumen fermentation parameters using an in vitro gas production study resulting in a significant increase in propionate production.
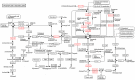
Conclusions: The resulting data provide a discovery platform (transcriptome, proteomes, EV isolation pipeline and in vitro fermentation system) to further study C. daubneyi-host interaction. In addition, the acetate: propionate ratio has been demonstrated to decrease with rumen fluke infection suggesting that acidotic conditions in the rumen may occur.
Keywords: Calicophoron daubneyi; In vitro; Paramphistome; Proteomics; Rumen fermentation; Transcriptome.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Transcriptome and Secretome Analysis of Intra-Mammalian Life-Stages of Calicophoron daubneyi Reveals Adaptation to a Unique Host Environment.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2021;20:100055. doi: 10.1074/mcp.RA120.002175. Epub 2021 Feb 11. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2021. PMID: 33581320 Free PMC article.
-
Rumen fluke in Irish sheep: prevalence, risk factors and molecular identification of two paramphistome species.BMC Vet Res. 2016 Jul 18;12(1):143. doi: 10.1186/s12917-016-0770-0. BMC Vet Res. 2016. PMID: 27430977 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of the rumen fluke, Calicophoron daubneyi, in GB livestock: possible implications for liver fluke diagnosis.Vet Parasitol. 2013 Jul 1;195(1-2):65-71. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2013.01.014. Epub 2013 Jan 24. Vet Parasitol. 2013. PMID: 23411375
-
Paramphistomosis of Ruminants: An Emerging Parasitic Disease in Europe.Trends Parasitol. 2017 Nov;33(11):836-844. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2017.07.002. Epub 2017 Jul 25. Trends Parasitol. 2017. PMID: 28754416 Review.
-
[Paramphistomidosis - an overview on epidemiology and clinical signs].Tierarztl Prax Ausg G Grosstiere Nutztiere. 2019 Jun;47(3):184-191. doi: 10.1055/a-0880-6381. Epub 2019 Jun 18. Tierarztl Prax Ausg G Grosstiere Nutztiere. 2019. PMID: 31212344 Review. German.
Cited by
-
The Calicophoron daubneyi genome provides new insight into mechanisms of feeding, eggshell synthesis and parasite-microbe interactions.BMC Biol. 2025 Jan 13;23(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s12915-025-02114-0. BMC Biol. 2025. PMID: 39800692 Free PMC article.
-
Post-Translational Protein Deimination Signatures in Serum and Serum-Extracellular Vesicles of Bos taurus Reveal Immune, Anti-Pathogenic, Anti-Viral, Metabolic and Cancer-Related Pathways for Deimination.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Apr 19;21(8):2861. doi: 10.3390/ijms21082861. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32325910 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of Rumen Microbes Through Extracellular Vesicle Released by the Rumen Fluke Calicophoron daubneyi.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Apr 20;11:661830. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.661830. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33959516 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence of Immune Modulators in the Secretome of the Equine Tapeworm Anoplocephala perfoliata.Pathogens. 2021 Jul 20;10(7):912. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10070912. Pathogens. 2021. PMID: 34358062 Free PMC article.
-
Detoxome Capacity of the Adult Rumen Fluke Calicophoron daubneyi Extends into Its Secreted Extracellular Vesicles.J Proteome Res. 2025 Feb 7;24(2):624-638. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.4c00615. Epub 2025 Jan 19. J Proteome Res. 2025. PMID: 39829022 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sanabria REF, Romero JR. Review and update of paramphistomosis. Helminthologia. 2008;45:64–68. doi: 10.2478/s11687-008-0012-5. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

