Swept-source optical coherence tomography and optical coherence tomography angiography in acquired toxoplasmic chorioretinitis: a case report
- PMID: 30509327
- PMCID: PMC6278094
- DOI: 10.1186/s13256-018-1902-x
Swept-source optical coherence tomography and optical coherence tomography angiography in acquired toxoplasmic chorioretinitis: a case report
Abstract
Purpose: To describe swept-source optical coherence tomography and optical coherence tomography angiography retinal changes in a case of acute toxoplasmic chorioretinitis both at the time of diagnosis and after healing.
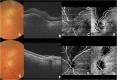
Case presentation: A 57-year-old white woman suffering from acquired toxoplasmic chorioretinitis underwent swept-source optical coherence tomography and optical coherence tomography angiography both at the time of diagnosis and after healing. In the acute phase of the disease, swept-source optical coherence tomography clearly showed retinal and choroidal involvement in the superficial retina and in the choroidal swelling. Optical coherence tomography angiography showed a complete loss of deep and superficial capillary networks and of choroidal vessels in the area of the inflammation. After healing, swept-source optical coherence tomography showed a retinal thinning of the area involved, with a subversion of retinal layers and no visible change at the choroid level. On the other hand, optical coherence tomography angiography showed the persistence of a vascular occlusion at the retina and choroid level.
Conclusion: This is the first case in the optical coherence tomography angiography literature that shows the imaging of toxoplasmic chorioretinal lesions. This case confirms the involvement of the retina and choroid in toxoplasmic uveitis and the disruptive potential of such inflammation. The optical coherence tomography angiography performed after healing showed a persistent ablation of the retina, choriocapillaris, and choroidal vessels. The non-invasive optical coherence tomography angiography imaging technique may have diagnostic and prognostic value in regard to toxoplasmic uveitis.
Keywords: Angio-OCT; Swept-source OCT; Toxoplasmic uveitis.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this case report and any accompanying images. A copy of the written consent is available for review by the Editor-in-Chief of this journal. The local ethics committee ruled that no formal ethics approval was required in this particular case.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this case report and any accompanying images. A copy of the written consent is available for review by the Editor-in-Chief of this journal. The patient consented to the submission of the case report to the journal.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SINGLE ACQUISITION OF THE VITREOUS, RETINA AND CHOROID WITH SWEPT-SOURCE OPTICAL COHERENCE TOMOGRAPHY IN ACUTE TOXOPLASMOSIS.Retin Cases Brief Rep. 2016 Summer;10(3):217-20. doi: 10.1097/ICB.0000000000000230. Retin Cases Brief Rep. 2016. PMID: 26510002
-
Morphological characteristics of ocular toxoplasmosis and its regression pattern on swept-source optical coherence tomography angiography: a case report.BMC Ophthalmol. 2019 Sep 5;19(1):199. doi: 10.1186/s12886-019-1209-8. BMC Ophthalmol. 2019. PMID: 31488090 Free PMC article.
-
Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography of Retinal-Choroidal Anastomosis in Toxoplasmosis Chorioretinitis.JAMA Ophthalmol. 2019 Mar 1;137(3):e184091. doi: 10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2018.4091. Epub 2019 Mar 14. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2019. PMID: 30869760 No abstract available.
-
Retinal applications of swept source optical coherence tomography (OCT) and optical coherence tomography angiography (OCTA).Prog Retin Eye Res. 2021 Sep;84:100951. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2021.100951. Epub 2021 Jan 28. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2021. PMID: 33516833 Review.
-
Multimodal Imaging in Ocular Toxoplasmosis.Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2020 Nov 16;28(8):1196-1204. doi: 10.1080/09273948.2020.1737142. Epub 2020 Mar 11. Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2020. PMID: 32160073 Review.
Cited by
-
Choroidal thickness in patients with thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy, as determined by swept-source optical coherence tomography.Br J Ophthalmol. 2024 Jul 23;108(8):1081-1087. doi: 10.1136/bjo-2023-323694. Br J Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 37857455 Free PMC article.
-
Measurement of the active toxoplasma retinochoroiditis lesion size during the disease course with swept-source optical coherence tomography angiography: A retrospective image analysis.Int Ophthalmol. 2021 Dec;41(12):4127-4135. doi: 10.1007/s10792-021-01985-w. Epub 2021 Jul 23. Int Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 34297304
-
Neuroretinitis and Juxtapapillary Retinochoroiditis as Atypical Presentations of Ocular Toxoplasmosis.Int Med Case Rep J. 2021 Sep 22;14:657-661. doi: 10.2147/IMCRJ.S332147. eCollection 2021. Int Med Case Rep J. 2021. PMID: 34588823 Free PMC article.
-
New findings useful for clinical practice using swept-source optical coherence tomography angiography in the follow-up of active ocular toxoplasmosis.Int J Retina Vitreous. 2020 Jul 8;6:30. doi: 10.1186/s40942-020-00231-2. eCollection 2020. Int J Retina Vitreous. 2020. PMID: 32670613 Free PMC article.
-
Ocular Toxoplasmosis: Advances in Toxoplasma gondii Biology, Clinical Manifestations, Diagnostics, and Therapy.Pathogens. 2024 Oct 14;13(10):898. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13100898. Pathogens. 2024. PMID: 39452769 Free PMC article. Review.

