Regulations are needed to protect freshwater ecosystems from salinization
- PMID: 30509918
- PMCID: PMC6283961
- DOI: 10.1098/rstb.2018.0019
Regulations are needed to protect freshwater ecosystems from salinization
Abstract
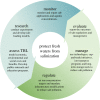
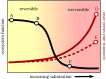
Anthropogenic activities such as mining, agriculture and industrial wastes have increased the rate of salinization of freshwater ecosystems around the world. Despite the known and probable consequences of freshwater salinization, few consequential regulatory standards and management procedures exist. Current regulations are generally inadequate because they are regionally inconsistent, lack legal consequences and have few ion-specific standards. The lack of ion-specific standards is problematic, because each anthropogenic source of freshwater salinization is associated with a distinct set of ions that can present unique social and economic costs. Additionally, the environmental and toxicological consequences of freshwater salinization are often dependent on the occurrence, concentration and ratios of specific ions. Therefore, to protect fresh waters from continued salinization, discrete, ion-specific management and regulatory strategies should be considered for each source of freshwater salinization, using data from standardized, ion-specific monitoring practices. To develop comprehensive monitoring, regulatory, and management guidelines, we recommend the use of co-adaptive, multi-stakeholder approaches that balance environmental, social, and economic costs and benefits associated with freshwater salinization.This article is part of the theme issue 'Salt in freshwaters: causes, ecological consequences and future prospects'.
Keywords: ecosystem functions; ecosystem services; freshwater degradation; global change; human health.
© 2018 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
We declare we have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lost in translation: the German literature on freshwater salinization.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2018 Dec 3;374(1764):20180007. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2018.0007. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30509909 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Salt in freshwaters: causes, effects and prospects - introduction to the theme issue.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2018 Dec 3;374(1764):20180002. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2018.0002. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30509904 Free PMC article.
-
Naturalizing pollution: a critical social science view on the link between potash mining and salinization in the Llobregat river basin, northeast Spain.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2018 Dec 3;374(1764):20180006. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2018.0006. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30509908 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel 'chemical cocktails' in inland waters are a consequence of the freshwater salinization syndrome.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2018 Dec 3;374(1764):20180017. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2018.0017. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30509916 Free PMC article.
-
Salinity impacts on river ecosystem processes: a critical mini-review.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2018 Dec 3;374(1764):20180010. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2018.0010. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30509912 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Distribution of Denitrification among Haloarchaea: A Comprehensive Study.Microorganisms. 2021 Aug 4;9(8):1669. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9081669. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 34442748 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Approach to Developing Thresholds for Total Dissolved Solids Using Standardized and Experimental Toxicity Test Methods.Environ Toxicol Chem. 2022 Nov;41(11):2782-2796. doi: 10.1002/etc.5466. Epub 2022 Oct 4. Environ Toxicol Chem. 2022. PMID: 35975448 Free PMC article.
-
Impacts of water hardness and road deicing salt on zooplankton survival and reproduction.Sci Rep. 2023 Feb 20;13(1):2975. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-30116-x. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36806739 Free PMC article.
-
Ion Clusters Reveal the Sources, Impacts, and Drivers of Freshwater Salinization.Environ Sci Technol. 2025 Jul 15;59(27):14053-14062. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.5c04512. Epub 2025 Jun 16. Environ Sci Technol. 2025. PMID: 40521754 Free PMC article.
-
Acute Toxicity of Major Geochemical Ions to Fathead Minnows (Pimephales Promelas): Part A-Observed Relationships for Individual Salts and Salt Mixtures.Environ Toxicol Chem. 2022 Sep;41(9):2078-2094. doi: 10.1002/etc.5390. Epub 2022 Aug 3. Environ Toxicol Chem. 2022. PMID: 35622012 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mester T, Szabó G, Bessenyei É, Karancsi G, Barkóczi N, Balla D. 2017. The effects of uninsulated sewage tanks on groundwater. A case study in an eastern Hungarian settlement. J. Water Land Dev. 33, 123–129. (10.1515/jwld-2017-0027) - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

