Salinization effects on coastal ecosystems: a terrestrial model ecosystem approach
- PMID: 30509924
- PMCID: PMC6283962
- DOI: 10.1098/rstb.2018.0251
Salinization effects on coastal ecosystems: a terrestrial model ecosystem approach
Abstract
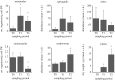
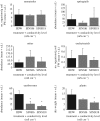
In coastal areas, intrusion/irrigation with seawater can threaten biodiversity along with crop yields, and the leaching of salts from areas affected by these processes can increase the salinity of water bodies nearby. The aims of this study were to evaluate the effects of salinization on coastal soil ecosystems due to saline intrusion/irrigation. Terrestrial model ecosystems were used to simulate two soil salinization scenarios: (i) seawater intrusion and irrigation with distilled water and (ii) seawater intrusion and irrigation with saline water. Three sampling periods were established: T0-after acclimation period; T1-salinization effects; and T2-populations' recovery. In each sampling period, the abundance of nematodes, enchytraeids, springtails, mites and earthworms, and plant biomass were measured. Immediate negative effects on enchytraeid abundance were detected, especially at the higher level of saltwater via intrusion+irrigation. Eight weeks after the cessation of saline irrigation, the abundance of enchytraeids fully recovered, and some delayed effects were observed in earthworm abundance and plant biomass, especially at the higher soil conductivity level. The observed low capacity of soil to retain salts suggests that, particularly at high soil conductivities, nearby freshwater bodies can also be endangered. Under saline conditions similar to the ones assayed, survival of some soil communities can be threatened, leading to the loss of biodiversity.This article is part of the theme issue 'Salt in freshwaters: causes, ecological consequences and future prospects'.
Keywords: climate change; intrusion; irrigation; sea-level rise; soil invertebrates.
© 2018 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
We declare we have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Seawater intrusion: an appraisal of taxa at most risk and safe salinity levels.Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2022 Feb;97(1):361-382. doi: 10.1111/brv.12803. Epub 2021 Oct 9. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2022. PMID: 34626061 Review.
-
Salt in freshwaters: causes, effects and prospects - introduction to the theme issue.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2018 Dec 3;374(1764):20180002. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2018.0002. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30509904 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of NaCl and seawater induced salinity on survival and reproduction of three soil invertebrate species.Chemosphere. 2015 Sep;135:116-22. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.03.094. Epub 2015 Apr 27. Chemosphere. 2015. PMID: 25930052
-
Sensitivity of freshwater species under single and multigenerational exposure to seawater intrusion.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2018 Dec 3;374(1764):20180252. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2018.0252. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30509925 Free PMC article.
-
Salinity impacts on river ecosystem processes: a critical mini-review.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2018 Dec 3;374(1764):20180010. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2018.0010. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30509912 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Geographical origin determines responses to salinity of Mediterranean caddisflies.PLoS One. 2020 Jan 13;15(1):e0220275. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0220275. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 31929552 Free PMC article.
-
Microbial diversity and functions in saline soils: A review from a biogeochemical perspective.J Adv Res. 2024 May;59:129-140. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2023.06.015. Epub 2023 Jun 29. J Adv Res. 2024. PMID: 37392974 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biodiversity and distribution of zoobenthos in the ecological water replenishment area of the Yellow River estuary coastal wetland revealed by eDNA metabarcoding.PLoS One. 2024 Dec 18;19(12):e0315346. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0315346. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39693381 Free PMC article.
-
Ontogenetic variation in salinity tolerance and ecophysiology of coastal dune plants.Ann Bot. 2020 Feb 3;125(2):301-314. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcz097. Ann Bot. 2020. PMID: 31162531 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Nutrient Uptake by Saltmarsh Plants Is Modified by Increasing Salinity.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Jul 29;12:709453. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.709453. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 34394167 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Church JA, et al. 2013. Sea level change. In Climate change 2013: the physical science basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (eds Stocker TF, et al.), p. 1137 Cambridge, UK, New York, NY: Cambridge University Press.
-
- Werner AD, Bakker M, Post VEA, Vandenbohede A, Lu C, Ataie-Ashtiani B, Simmons CT, Barry DA. 2013. Seawater intrusion processes, investigation and management: Recent advances and future challenges. Adv. Water Resour. 51, 3–26. (10.1016/j.advwatres.2012.03.004) - DOI
-
- Tsanis IK, Daliakopoulos IN, Koutroulis AG, Karatzas GP, Varouchakis E, Kourgialas N.2016. Soil salinization. In Soil threats in Europe: status, methods, drivers and effects on ecosystem services. Review report, RECARE project, European Union (eds J Stolte, M Tesfai, L Oygarden, S Kvaerno, J Keizer, F Verheijen, P Panagos, C Ballabio, R Hessel), pp.104–117. Luxembourg; European Union. (doi:10.2788/828742) - PubMed
-
- Van Weert F, Van der Gun J, Reckman J.. 2009. Global overview of saline groundwater occurrence and genesis. Report no. GP 2009-1. Delft, The Netherlands: International Groundwater Resources Assessment Centre. See https://www.un-igrac.org/sites/default/files/resources/files/Global%20Ov....
-
- Bablani SA, Soomro SA. 2006. Evaluation of seawater intrusions in left bank sediments of coastal district Thatta, Sindh, Pakistan In Proc. 1st SWIM-SWICA Joint Saltwater Intrusion Conf., Cagliari-Chia Laguna, Italy, 24–29 September 2006, pp. 205–212. See http://www.swim-site.nl/pdf/swim19/pages_205_212.pdf.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

