Exocyst dynamics during vesicle tethering and fusion
- PMID: 30510181
- PMCID: PMC6277416
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-07467-5
Exocyst dynamics during vesicle tethering and fusion
Erratum in
-
Publisher Correction: Exocyst dynamics during vesicle tethering and fusion.Nat Commun. 2019 Jan 15;10(1):326. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-08322-x. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 30644403 Free PMC article.
Abstract
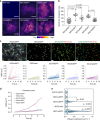
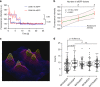
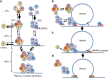
The exocyst is a conserved octameric complex that tethers exocytic vesicles to the plasma membrane prior to fusion. Exocyst assembly and delivery mechanisms remain unclear, especially in mammalian cells. Here we tagged multiple endogenous exocyst subunits with sfGFP or Halo using Cas9 gene-editing, to create single and double knock-in lines of mammary epithelial cells, and interrogated exocyst dynamics by high-speed imaging and correlation spectroscopy. We discovered that mammalian exocyst is comprised of tetrameric subcomplexes that can associate independently with vesicles and plasma membrane and are in dynamic equilibrium with octamer and monomers. Membrane arrival times are similar for subunits and vesicles, but with a small delay (~80msec) between subcomplexes. Departure of SEC3 occurs prior to fusion, whereas other subunits depart just after fusion. About 9 exocyst complexes are associated per vesicle. These data reveal the mammalian exocyst as a remarkably dynamic two-part complex and provide important insights into assembly/disassembly mechanisms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
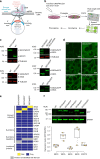
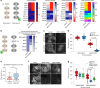


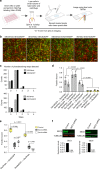
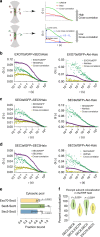
Comment in
-
Exocytosis: A New Exocyst Movie.Curr Biol. 2019 Jan 7;29(1):R30-R32. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2018.11.022. Curr Biol. 2019. PMID: 30620914
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

