The establishment of resident memory B cells in the lung requires local antigen encounter
- PMID: 30510223
- PMCID: PMC6392030
- DOI: 10.1038/s41590-018-0260-6
The establishment of resident memory B cells in the lung requires local antigen encounter
Abstract
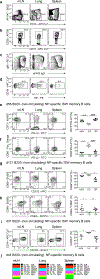
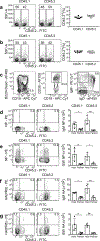
Memory B cells are found in lymphoid and non-lymphoid tissues, suggesting that some may be tissue-resident cells. Here we show that pulmonary influenza infection elicited lung-resident memory B cells (BRM cells) that were phenotypically and functionally distinct from their systemic counterparts. BRM cells were established in the lung early after infection, in part because their placement required local antigen encounter. Lung BRM cells, but not systemic memory B cells, contributed to early plasmablast responses following challenge infection. Following secondary infection, antigen-specific BRM cells differentiated in situ, whereas antigen-non-specific BRM cells were maintained as memory cells. These data demonstrate that BRM cells are an important component of immunity to respiratory viruses such as influenza virus and suggest that vaccines designed to elicit BRM cells must deliver antigen to the lungs.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement.
The authors do not have any competing financial or non-financial interests as defined by Nature Research.
Figures






Comment in
-
Recent Advances in Lung Immunobiology.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2019 Dec;61(6):786-788. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2019-0183RO. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 31291124 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Dorner T & Radbruch A Antibodies and B cell memory in viral immunity. Immunity 27, 384–392 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Phan TG & Tangye SG Memory B cells: total recall. Curr. Opin. Immunol 45, 132–140 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Bannard O & Cyster JG Germinal centers: programmed for affinity maturation and antibody diversification. Curr. Opin. Immunol 45, 21–30 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Shlomchik MJ & Weisel F Germinal center selection and the development of memory B and plasma cells. Immunol. Rev 247, 52–63 (2012). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

