Discovery of common and rare genetic risk variants for colorectal cancer
- PMID: 30510241
- PMCID: PMC6358437
- DOI: 10.1038/s41588-018-0286-6
Discovery of common and rare genetic risk variants for colorectal cancer
Abstract
To further dissect the genetic architecture of colorectal cancer (CRC), we performed whole-genome sequencing of 1,439 cases and 720 controls, imputed discovered sequence variants and Haplotype Reference Consortium panel variants into genome-wide association study data, and tested for association in 34,869 cases and 29,051 controls. Findings were followed up in an additional 23,262 cases and 38,296 controls. We discovered a strongly protective 0.3% frequency variant signal at CHD1. In a combined meta-analysis of 125,478 individuals, we identified 40 new independent signals at P < 5 × 10-8, bringing the number of known independent signals for CRC to ~100. New signals implicate lower-frequency variants, Krüppel-like factors, Hedgehog signaling, Hippo-YAP signaling, long noncoding RNAs and somatic drivers, and support a role for immune function. Heritability analyses suggest that CRC risk is highly polygenic, and larger, more comprehensive studies enabling rare variant analysis will improve understanding of biology underlying this risk and influence personalized screening strategies and drug development.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests Statement
Goncalo R Abecasis has received compensation from 23andMe and Helix. He is currently an employee of Regeneron Pharmaceuticals. Heather Hampel performs collaborative research with Ambry Genetics, InVitae Genetics, and Myriad Genetic Laboratories, Inc., is on the scientific advisory board for InVitae Genetics and Genome Medical, and has stock in Genome Medical. Rachel Pearlman has participated in collaborative funded research with Myriad Genetics Laboratories and Invitae Genetics but has no financial competitive interest.
Figures
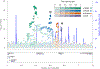

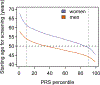
References
-
- Ferlay J et al. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer 136, E359–86 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Lichtenstein P et al. Environmental and heritable factors in the causation of cancer--analyses of cohorts of twins from Sweden, Denmark, and Finland. N Engl J Med 343, 78–85 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Czene K, Lichtenstein P & Hemminki K Environmental and heritable causes of cancer among 9.6 million individuals in the Swedish Family-Cancer Database. Int J Cancer 99, 260–266 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Sud A, Kinnersley B & Houlston RS Genome-wide association studies of cancer: current insights and future perspectives. Nat Rev Cancer 17, 692–704 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Tomlinson I et al. A genome-wide association scan of tag SNPs identifies a susceptibility variant for colorectal cancer at 8q24.21. Nat Genet 39, 984–988 (2007). - PubMed
METHODS-ONLY REFERENCES
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30 CA015704/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DK110267/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK058404/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA164930/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA074794/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA207371/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016058/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 10589/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- R01 CA059045/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA197350/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 CA197735/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES010126/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA204279/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA037429/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA182883/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA160356/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189974/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA189184/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA137088/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K23 DK103119/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA074794/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 CA191312/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA206110/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 19167/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- U01 CA167551/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA185094/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA014089/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA081488/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA143237/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA201407/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K05 CA152715/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 10822/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- S10 OD020069/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- 10119/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 25004/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- P01 CA196569/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 CA182883/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201200008I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA152756/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 001/WHO_/World Health Organization/International
- R01 CA193677/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- MR/L01629X/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 10124/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 16561/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- U19 CA148107/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

