Long-term Follow-up on NRG Oncology RTOG 0915 (NCCTG N0927): A Randomized Phase 2 Study Comparing 2 Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy Schedules for Medically Inoperable Patients With Stage I Peripheral Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- PMID: 30513377
- PMCID: PMC6454873
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2018.11.051
Long-term Follow-up on NRG Oncology RTOG 0915 (NCCTG N0927): A Randomized Phase 2 Study Comparing 2 Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy Schedules for Medically Inoperable Patients With Stage I Peripheral Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Abstract
Purpose: To present long-term results of RTOG 0915/NCCTG N0927, a randomized lung stereotactic body radiation therapy trial of 34 Gy in 1 fraction versus 48 Gy in 4 fractions.
Methods and materials: This was a phase 2 multicenter study of patients with medically inoperable non-small cell lung cancer with biopsy-proven peripheral T1 or T2 N0M0 tumors, with 1-year toxicity rates as the primary endpoint and selected failure and survival outcomes as secondary endpoints. The study opened in September 2009 and closed in March 2011. Final data were analyzed through May 17, 2018.
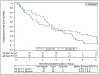
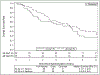
Results: Eighty-four of 94 patients accrued were eligible for analysis: 39 in arm 1 and 45 in arm 2. Median follow-up time was 4.0 years for all patients and 6.0 years for those alive at analysis. Rates of grade 3 and higher toxicity were 2.6% in arm 1 and 11.1% in arm 2. Median survival times (in years) for 34 Gy and 48 Gy were 4.1 versus 4.6, respectively. Five-year outcomes (95% confidence interval) for 34 Gy and 48 Gy were a primary tumor failure rate of 10.6% (3.3%-23.1%) versus 6.8% (1.7%-16.9%); overall survival of 29.6% (16.2%-44.4%) versus 41.1% (26.6%-55.1%); and progression-free survival of 19.1% (8.5%-33.0%) versus 33.3% (20.2%-47.0%). Distant failure as the sole failure or a component of first failure occurred in 6 patients (37.5%) in the 34 Gy arm and in 7 (41.2%) in the 48 Gy arm.
Conclusions: No excess in late-appearing toxicity was seen in either arm. Primary tumor control rates at 5 years were similar by arm. A median survival time of 4 years for each arm suggests similar efficacy, pending any larger studies appropriately powered to detect survival differences.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: Nothing to disclose Ajlouni, Belani, Choy, Gomez-Suescun, Iyengar, Komaki, McGarry, Olivier, Parker, Singh, Stephans, Urbanic, Videtic and Yom. Dr. Bradley reports grants and personal fees from Mevion Medical Systems, Inc., personal fees and other from Varian Medical Systems. Dr. Chang reports other from Global Oncology One, grants from BMS. Dr. Gopaul reports personal fees from Bayer, personal fees from Jansen. Ms. Paulus reports a grant from National Cancer Institute during the conduct of the study. Dr. Robinson reports grants, personal fees and non-financial support from Varian, personal fees and non-financial support from ViewRay, grants from Elekta, other from Radialogica; has a patent ECGI and SBRT for cardiac arrhythmia pending. Dr. Timmerman reports grants from Varian Medical Systems, grants from Elekta Oncology, grants from Accuray, Inc.
Figures
Comment in
-
Single Fraction SBRT for Early Stage Lung Cancer-Less is More?Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2019 Apr 1;103(5):1085-1087. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2018.12.041. Epub 2019 Mar 13. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2019. PMID: 30900559 No abstract available.
-
In Regard to Videtic et al.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2019 Jun 1;104(2):466-467. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2019.02.012. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2019. PMID: 31047631 No abstract available.
-
In Reply to Yilmaz et al.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2019 Jun 1;104(2):467. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2019.02.013. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2019. PMID: 31047633 No abstract available.
-
Single-fraction SBRT for Early Stage NSCLC-A Viable Option in "These Uncertain Times"?Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2021 Jan 1;109(1):1-4. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2020.08.031. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2021. PMID: 33308692 No abstract available.
References
-
- Videtic GM, Stephans KL. The role of stereotactic body radiotherapy in the management of non-small cell lung cancer: An emerging standard for the medically inoperable patient? Curr Oncol Rep 2010; 12:235–241. - PubMed
-
- Videtic GM, Hu C, Singh AK, et al. A randomized phase 2 study comparing 2 stereotactic body radiation therapy schedules for medically inoperable patients with stage I peripheral non-small cell lung cancer: NRG oncology RTOG 0915 (NCCTG N0927). Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2015;93:757–764. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Thorax. Greene, editor. AJCC Cancer Staging Handbook. 6th ed. New York, NY: Springer; 2002.
-
- Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J, et al. New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: Revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer 2009;45:228–247. - PubMed