Evaluation of a temperature-restricted, mucosal tuberculosis vaccine in guinea pigs
- PMID: 30514501
- PMCID: PMC6296365
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tube.2018.10.006
Evaluation of a temperature-restricted, mucosal tuberculosis vaccine in guinea pigs
Abstract
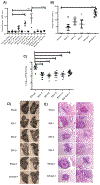
Tuberculosis (TB) is currently the leading cause of death in humans by a single infectious agent, Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) vaccine prevents pulmonary TB with variable efficacy, but can cause life-threatening systemic infection in HIV-infected infants. In this study, TBvac85, a derivative of Mycobacterium shottsii expressing M. tuberculosis Antigen 85B, was examined as a safer alternative to BCG. Intranasal vaccination of guinea pigs with TBvac85, a naturally temperature-restricted species, resulted in serum Ag85B-specific IgG antibodies. Delivery of the vaccine by this route also induced protection equivalent to intradermal BCG based on organ bacterial burdens and lung pathology six weeks after aerosol challenge with M. tuberculosis strain Erdman. These results support the potential of TBvac85 as the basis of an effective TB vaccine. Next-generation derivatives expressing multiple M. tuberculosis immunogens are in development.
Keywords: Intranasal; Mycobacterium; TBvac85; Tuberculosis; Vaccine.
Copyright © 2018. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest
FDQ, CM, and RKK patented the described vaccine platform through the University of Georgia Foundation and formed for-profit biotechnology company Pathens Incorporated to develop and advance vaccines based on this technology. KTS serves as the CEO of this company. MP invented the AeroVaxTM device used in the study and CDC patented the device. The technology was licensed to AerovectRx, Inc., but the company is no longer operating and the device is not a commercial product. MP had no financial interest in AeroVectRx, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization. Genevaeditor. report Global tuberculosis report. 2017.
-
- Talbot EA, Perkins MD, Silva SF, Frothingham R. Disseminated bacille Calmette-Guerin disease after vaccination: case report and review. Clin Infect Dis 1997;24(6):1139–46. - PubMed
-
- Besnard M, Sauvion S, Offredo C, Gaudelus J, Gaillard JL, Veber F, Blanche S. Bacillus Calmette-Guerin infection after vaccination of human immunodeficiency virus-infected children. Pediatr Infect Dis J 1993;12(12):993–7. - PubMed
-
- Revised BCG vaccination guidelines for infants at risk for HIV infection. Wkly Epidemiol Rec 2007;82(21):193–6. - PubMed
-
- McShane H, Pathan AA, Sander CR, Goonetilleke NP, Fletcher HA, Hill AV. Boosting BCG with MVA85A: the first candidate subunit vaccine for tuberculosis in clinical trials. Tuberculosis (Edinb) 2005;85(1-2):47–52. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

