Substance use and universal access to HIV testing and treatment in sub-Saharan Africa: implications and research priorities
- PMID: 30515311
- PMCID: PMC6248849
- DOI: 10.1016/S2055-6640(20)30342-3
Substance use and universal access to HIV testing and treatment in sub-Saharan Africa: implications and research priorities
Abstract
As universal testing and treatment for HIV, or 'treat all', expands across sub-Saharan Africa (SSA), substance use will likely have a negative impact on the success of scale-up efforts for antiretroviral treatment (ART). Overwhelming evidence highlights the negative impact of substance use on HIV care and treatment outcomes. Yet, as many countries in SSA expand ART, evidence of the extent of substance use, and its impact in the region, is more limited. Stigma, and the psychoactive effects of substance use, are barriers to seeking HIV treatment and adhering to ART regimens for persons with heavy alcohol use or substance use. As a result, we identified several implementation and operations research priorities and metrics for monitoring the impact of substance use and Treat All. Identifying barriers and facilitators to the integration of the prevention and treatment of substance use with HIV care, and assessing effects on HIV outcomes, through longitudinal studies are priorities that will determine the impacts of substance use on 'treat all' in SSA. Future research must use existing infrastructure, including large networks of HIV clinics, to enhance our understanding of the implementation and service delivery of substance use screening, referral and treatment. These networks will also inform robust and standardised substance use estimates and interventions within the 'treat all' era in SSA.
Keywords: injection drug use, non-injection drug use, alcohol, antiretroviral treatment, Africa.
Figures
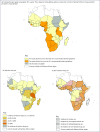
References
-
- Kasirye R. Diffusion of evidence-based interventions in HIV and substance user programs: flaws and lessons from the sub-Saharan African region. Subst Use Misuse 2015; 50: 1110– 1116. - PubMed
-
- Mathers BM, Degenhardt L, Phillips B et al. . Global epidemiology of injecting drug use and HIV among people who inject drugs: a systematic review. Lancet 2008; 372: 1733– 1745. - PubMed
-
- Raguin G, Lepretre A, Ba I et al. . Drug use and HIV in West Africa: a neglected epidemic. Trop Med Int Health 2011; 16: 1131– 1133. - PubMed
-
- * United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime World Drug Report 2016. (United Nations publication, Sales No. E.16.XI.7); Available at: www.unodc.org/wdr2016 ( accessed September 2018).
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
