Trends and emerging directions in HIV risk and prevention research in the Philippines: A systematic review of the literature
- PMID: 30517178
- PMCID: PMC6281194
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0207663
Trends and emerging directions in HIV risk and prevention research in the Philippines: A systematic review of the literature
Abstract
Background: The Philippines is experiencing one of the fastest growing epidemics globally. Evidence-based public health policies are needed. To describe the public health literature on HIV risk groups and prevention approaches in the Philippines, we reviewed published empirical studies with HIV-related outcomes.
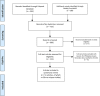
Methods: Based on an a priori systematic review protocol, we searched PubMed, PsycINFO and CINAHL databases for quantitative studies conducted in the Philippines that reported on HIV risk groups factors and interventions to prevent HIV. The search included studies published as of April 2018.
Results: We identified 755 records, screened 699 unique titles and abstracts, and conducted full text review of 122 full reports of which 51 articles met inclusion criteria. The majority were cross-sectional studies describing HIV and STI prevalence and risk factors in samples recruited from the Philippines. Four HIV prevention programs conducted in the Philippines were identified, all of which reported improvements on HIV knowledge, attitudes, and behaviors. Overall, female sex workers (FSWs) constituted the primary study population, and few studies reported data from men who have sex with men (MSM), people who inject drugs (PWIDs), and youth. No studies reported on transgender populations. Most studies were focused on examining condom use-related outcomes and STI history, few had biomarkers for HIV, and none addressed biomedical HIV prevention strategies.
Conclusion: This review identifies an agenda for future HIV research that is needed to address the growing and shifting nature of the HIV epidemic in the Philippines.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
HIV, Sexually Transmitted Infection, and Substance Use Continuum of Care Interventions Among Criminal Justice-Involved Black Men Who Have Sex With Men: A Systematic Review.Am J Public Health. 2018 Nov;108(S4):e1-e9. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.2018.304698. Am J Public Health. 2018. PMID: 30383433 Free PMC article.
-
Estimating prevalence and modelling correlates of HIV test positivity among female sex workers, men who have sex with men, people who inject drugs, transgender people and prison inmates in Sierra Leone, 2021.AIDS Res Ther. 2023 Sep 27;20(1):70. doi: 10.1186/s12981-023-00566-4. AIDS Res Ther. 2023. PMID: 37759241 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Physical Violence on Sexually Transmitted Infections and Treatment Seeking Behaviour among Female Sex Workers in Thane District, Maharashtra, India.PLoS One. 2016 Mar 2;11(3):e0150347. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0150347. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26933884 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of interventions for changing HIV related risk behaviours among key populations in low-income setting: A Meta-Analysis, 2001-2016.Sci Rep. 2020 Feb 10;10(1):2197. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-58767-0. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32041979 Free PMC article.
-
A Systematic Review of Gender-Based Violence Prevention and Response Interventions for HIV Key Populations: Female Sex Workers, Men Who Have Sex With Men, and People Who Inject Drugs.Trauma Violence Abuse. 2022 Apr;23(2):676-694. doi: 10.1177/15248380211029405. Epub 2022 Feb 11. Trauma Violence Abuse. 2022. PMID: 35144502
Cited by
-
Evaluating Translation of HIV-Related Legal Protections Into Practice: A Qualitative Assessment Among HIV-Positive Gay, Bisexual, and Other Men Who Have Sex With Men in Manila, Philippines.Crit Public Health. 2021;31(5):573-583. doi: 10.1080/09581596.2020.1739226. Epub 2020 Mar 25. Crit Public Health. 2021. PMID: 35210713 Free PMC article.
-
Interactive Mobile Phone HIV Adherence Support for Men Who Have Sex With Men in the Philippines Connect for Life Study: Mixed Methods Approach to Intervention Development and Pilot Testing.JMIR Form Res. 2022 Feb 3;6(2):e30811. doi: 10.2196/30811. JMIR Form Res. 2022. PMID: 35113030 Free PMC article.
-
Using structural equation modelling to characterise multilevel socioecological predictors and mediators of condom use among transgender women and cisgender men who have sex with men in the Philippines.BMJ Glob Health. 2020 Jul;5(7):e002463. doi: 10.1136/bmjgh-2020-002463. BMJ Glob Health. 2020. PMID: 32699154 Free PMC article.
-
Characterizing Problematic Drug Use Among Transgender Women and Cisgender Men During the Emerging HIV Crisis in the Philippines: Implications for Policy Research.AIDS Educ Prev. 2022 Apr;34(2):116-130. doi: 10.1521/aeap.2022.34.2.116. AIDS Educ Prev. 2022. PMID: 35438540 Free PMC article.
-
Prioritizing HIV Services for Transgender Women and Men Who Have Sex With Men in Manila, Philippines: An Opportunity for HIV Provider Interventions.J Assoc Nurses AIDS Care. 2020 Jul-Aug;31(4):405-416. doi: 10.1097/JNC.0000000000000131. J Assoc Nurses AIDS Care. 2020. PMID: 31592803 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS). (2017). UNAIDS Data 2017. Available at: http://www.unaids.org/sites/default/files/media_asset/20170720_Data_book... - PubMed
-
- Philippines Department of Health. HIV/AIDS and ART Registry of the Philippines: Newly Diagnosed HIV cases in the Philippines Philippines Department of Health Bureau of Epidemiology; 2017.
-
- Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS [UNAIDS]. Global AIDS Response Progress Reporting: Country Progress Report Philippines. UNAIDS; 2014.
-
- Ross AG, Ditangco RA, Belimac JG, Olveda RM, Mercado ES, Chau TN, et al. The dire sexual health crisis among MSM in the Philippines: an exploding HIV epidemic in the absence of essential health services. International Journal of Infectious Diseases. 2015;37:6–8. 10.1016/j.ijid.2015.06.001 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous