Anti-ophidian activity of Bredemeyera floribunda Willd. (Polygalaceae) root extract on the local effects induced by Bothrops jararacussu venom
- PMID: 30517287
- PMCID: PMC6293447
- DOI: 10.1590/1414-431X20187581
Anti-ophidian activity of Bredemeyera floribunda Willd. (Polygalaceae) root extract on the local effects induced by Bothrops jararacussu venom
Abstract
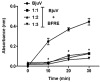
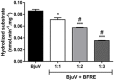
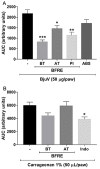
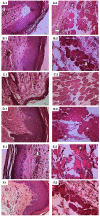
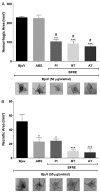
Bredemeyera floribunda roots are popularly used to treat snakebites in the semiarid region of Northeast Brazil, and previous studies indicate the anti-ophidian actions of triterpenoid saponins found in its roots. To assess B. floribunda root extract (BFRE) activity against the effects of Bothrops jararacussu venom (BjuV), antiphospholipasic, antiproteolytic, antihemorrhagic, antinecrotic, and anti-edematogenic activities were investigated in mice. Phytochemical analysis revealed the presence of saponins, flavonoids, and sugars, with rutin and saccharose being the major constituents of BFRE. Acute toxicity was determined and BFRE was nontoxic to mice. Phospholipase A2 and proteolytic activities induced by BjuV were inhibited in vitro by BFRE at all concentrations tested herein. BFRE (150 mg/kg) inhibited paw edema induced by BjuV (50 µg/animal), reducing total edema calculated by area under the curve, but carrageenan-induced paw edema was unchanged. Hemorrhagic and necrotizing actions of BjuV (50 µg/animal) were considerably decreased by BFRE treatment. Thus, BFRE blocked the toxic actions of B. jararacussu venom despite having no anti-inflammatory activity, which points to a direct inhibition of venom's toxins, as demonstrated in the in vitro assays. The larger amounts of rutin found in BFRE may play a role in this inhibition, since 3',4'-OH flavonoids are known inhibitors of phospholipases A2.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Counteraction of Bothrops snake venoms by Combretum leprosum root extract and arjunolic acid.J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 Aug 8;155(1):552-62. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.05.056. Epub 2014 Jun 18. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24952279
-
Antiophidic activity of the extract of the Amazon plant Humirianthera ampla and constituents.J Ethnopharmacol. 2013 Jan 9;145(1):50-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2012.10.033. Epub 2012 Nov 1. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23123799
-
A comparison of the ability of Bellucia dichotoma Cogn. (Melastomataceae) extract to inhibit the local effects of Bothrops atrox venom when pre-incubated and when used according to traditional methods.Toxicon. 2014 Jul;85:59-68. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2014.04.009. Epub 2014 May 9. Toxicon. 2014. PMID: 24814014
-
Plant-derived secondary metabolites against Bothrops envenomation: A review.Toxicon. 2025 Apr;258:108340. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2025.108340. Epub 2025 Apr 2. Toxicon. 2025. PMID: 40185249 Review.
-
Bredemeyera Willd.: an integrative review of its therapeutic potential and chemical aspects.Nat Prod Res. 2025 May 21:1-10. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2025.2506782. Online ahead of print. Nat Prod Res. 2025. PMID: 40395119 Review.
Cited by
-
Enhanced production of prodigiosin by Serratia marcescens UCP 1549 using agrosubstrates in solid-state fermentation.Arch Microbiol. 2021 Sep;203(7):4091-4100. doi: 10.1007/s00203-021-02399-z. Epub 2021 May 30. Arch Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34052891
-
Acute Toxicity of Aqueous Extract from Bredemeyera floribunda Root Bark in an Animal Model.ScientificWorldJournal. 2024 Jun 24;2024:8991384. doi: 10.1155/2024/8991384. eCollection 2024. ScientificWorldJournal. 2024. PMID: 38957454 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive review of biosurfactant production and its uses in the pharmaceutical industry.Arch Microbiol. 2024 Jan 10;206(2):60. doi: 10.1007/s00203-023-03786-4. Arch Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38197951 Review.
-
Targets Involved in the Pharmacology of Bothrops Snakebite: Statu Quo and Future Perspectives.Curr Drug Targets. 2025;26(7):454-469. doi: 10.2174/0113894501352925250225045555. Curr Drug Targets. 2025. PMID: 40017248 Review.
-
Cordia salicifolia and Lafoensia pacari plant extracts against the local effects of Bothrops jararacussu and Philodryas olfersii snake venoms.J Venom Res. 2020 Jul 20;10:32-37. eCollection 2020. J Venom Res. 2020. PMID: 33024546 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

