Impact of adherence to long-term oxygen therapy on patients with COPD and exertional hypoxemia followed for one year
- PMID: 30517340
- PMCID: PMC6467586
- DOI: 10.1590/S1806-37562017000000019
Impact of adherence to long-term oxygen therapy on patients with COPD and exertional hypoxemia followed for one year
Abstract
Objective: To determine the impact of adherence to long-term oxygen therapy (LTOT) on quality of life, dyspnea, and exercise capacity in patients with COPD and exertional hypoxemia followed for one year.
Methods: Patients experiencing severe hypoxemia during a six-minute walk test (6MWT) performed while breathing room air but not at rest were included in the study. At baseline and after one year of follow-up, all patients were assessed for comorbidities, body composition, SpO2, and dyspnea, as well as for anxiety and depression, having also undergone spirometry, arterial blood gas analysis, and the 6MWT with supplemental oxygen. The Saint George's Respiratory Questionnaire (SGRQ) was used in order to assess quality of life, and the Body mass index, airflow Obstruction, Dyspnea, and Exercise capacity (BODE) index was calculated. The frequency of exacerbations and the mortality rate were noted. Treatment nonadherence was defined as LTOT use for < 12 h per day or no LTOT use during exercise.
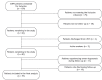
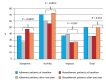
Results: A total of 60 patients with COPD and exertional hypoxemia were included in the study. Of those, 10 died and 11 experienced severe hypoxemia during follow-up, 39 patients therefore being included in the final analysis. Of those, only 18 (46.1%) were adherent to LTOT, showing better SGRQ scores, higher SpO2 values, and lower PaCO2 values than did nonadherent patients. In all patients, SaO2, the six-minute walk distance, and the BODE index worsened after one year. There were no differences between the proportions of adherence to LTOT at 3 and 12 months of follow-up.
Conclusions: Quality of life appears to be lower in patients with COPD and exertional hypoxemia who do not adhere to LTOT than in those who do. In addition, LTOT appears to have a beneficial effect on COPD symptoms (as assessed by SGRQ scores). (Brazilian Registry of Clinical Trials - ReBEC; identification number RBR-9b4v63 [http://www.ensaiosclinicos.gov.br]).
Objetivo:: Determinar o impacto da adesão à oxigenoterapia de longa duração (OLD) na qualidade de vida, dispneia e capacidade de exercício em pacientes com DPOC e hipoxemia decorrente do esforço acompanhados durante um ano.
Métodos:: Foram incluídos no estudo pacientes que apresentaram hipoxemia grave durante um teste de caminhada de seis minutos (TC6) realizado enquanto respiravam ar ambiente, mas não em repouso. No início e após um ano de acompanhamento, todos os pacientes foram avaliados quanto a comorbidades, composição corporal, SpO2 e dispneia, bem como quanto a ansiedade e depressão, além de terem sido submetidos a espirometria, gasometria arterial e TC6 com oxigênio suplementar. O Saint George’s Respiratory Questionnaire (SGRQ) foi usado para avaliar a qualidade de vida, e o índice Body mass index, airflow Obstruction, Dyspnea, and Exercise capacity (BODE; índice de massa corporal, obstrução do fluxo aéreo, dispneia e capacidade de exercício) foi calculado. A frequência de exacerbações e a taxa de mortalidade foram registradas. Usar OLD durante < 12 h por dia ou não usar OLD durante o exercício caracterizaram não adesão ao tratamento.
Resultados:: Foram incluídos no estudo 60 pacientes com DPOC e hipoxemia decorrente do esforço. Destes, 10 morreram e 11 apresentaram hipoxemia grave durante o acompanhamento; portanto, foram incluídos na análise final 39 pacientes. Destes, apenas 18 (46,1%) aderiram à OLD, apresentando melhor pontuação no SGRQ, maior SpO2 e menor PaCO2 do que os pacientes que não aderiram à OLD. Em todos os pacientes, a SaO2, a distância percorrida no TC6 e o índice BODE pioraram após um ano. Não houve diferenças entre as proporções de adesão à OLD aos 3 e 12 meses de acompanhamento.
Conclusões::
A qualidade de vida parece ser menor em pacientes com DPOC e hipoxemia decorrente do esforço que não aderem à OLD do que naqueles que o fazem. Além disso, a OLD parece ter efeito benéfico nos sintomas da DPOC (avaliados pela pontuação obtida no SGRQ). (Registro Brasileiro de Ensaios Clínicos - ReBEC; número de identificação
Figures
Similar articles
-
Myocardial performance index correlates with the BODE index and affects quality of life in COPD patients.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2016 Sep 16;11:2261-2268. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S110779. eCollection 2016. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2016. PMID: 27695314 Free PMC article.
-
The cross-sectional and longitudinal association of the BODE index with quality of life in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Chin Med J (Engl). 2009 Dec 20;122(24):2939-44. Chin Med J (Engl). 2009. PMID: 20137478
-
Long-Term Oxygen Therapy in COPD Patients Who Do Not Meet the Actual Recommendations.COPD. 2017 Jun;14(3):351-366. doi: 10.1080/15412555.2017.1319918. Epub 2017 May 16. COPD. 2017. PMID: 28506089 Review.
-
Effectiveness of pulmonary rehabilitation in COPD patients receiving long-term oxygen therapy.Clin Respir J. 2018 Apr;12(4):1439-1446. doi: 10.1111/crj.12680. Epub 2017 Aug 13. Clin Respir J. 2018. PMID: 28776954
-
Exertional desaturation in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.COPD. 2009 Dec;6(6):478-87. doi: 10.3109/15412550903341497. COPD. 2009. PMID: 19938972 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of Exertional Hypoxia and Its Implications in SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2020 Oct;103(4):1742-1743. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.20-1012. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2020. PMID: 32851969 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Clinical and Cost-Effectiveness of Telehealth-Supported Home Oxygen Therapy on Adherence, Hospital Readmission, and Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients With Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.J Med Internet Res. 2025 Jul 8;27:e73010. doi: 10.2196/73010. J Med Internet Res. 2025. PMID: 40631803 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mobile application for monitoring patients under home oxygen therapy: a protocol for a randomized controlled trial.BMC Fam Pract. 2021 May 26;22(1):104. doi: 10.1186/s12875-021-01450-8. BMC Fam Pract. 2021. PMID: 34039277 Free PMC article.
-
Adherence to long-term home oxygen therapy in patients with chronic respiratory disease in two cities in the state of Minas Gerais, Brazil.J Bras Pneumol. 2021 Jun 23;47(3):e20210055. doi: 10.36416/1806-3756/e20210055. J Bras Pneumol. 2021. PMID: 34190863 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
November 18: World COPD Day 2020. Is it a date to celebrate?J Bras Pneumol. 2021 Jan 8;46(6):e20200575. doi: 10.36416/1806-3756/e20200575. J Bras Pneumol. 2021. PMID: 33439927 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease . Global Strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: GOLD Executive Summary, updated 2015. Bethesda: GOLD; 2015.
-
- Medical Research Council Working Party Long term domiciliary oxygen therapy in chronic hypoxic cor pulmonale complicating chronic bronchitis and emphysema Report of the Medical Research Council Working Party. Lancet. 1981;1(8222):681–686. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical