ISRE-Reporter Mouse Reveals High Basal and Induced Type I IFN Responses in Inflammatory Monocytes
- PMID: 30517866
- PMCID: PMC6317368
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.11.030
ISRE-Reporter Mouse Reveals High Basal and Induced Type I IFN Responses in Inflammatory Monocytes
Abstract
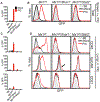
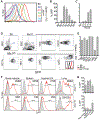
Type I and type III interferons (IFNs) are critical for controlling viral infections. However, the precise dynamics of the IFN response have been difficult to define in vivo. Signaling through type I IFN receptors leads to interferon-stimulated response element (ISRE)-dependent gene expression and an antiviral state. As an alternative to tracking IFN, we used an ISRE-dependent reporter mouse to define the cell types, localization, and kinetics of IFN responding cells during influenza virus infection. We find that measurable IFN responses are largely limited to hematopoietic cells, which show a high sensitivity to IFN. Inflammatory monocytes display high basal IFN responses, which are enhanced upon infection and correlate with infection of these cells. We find that inflammatory monocyte development is independent of IFN signaling; however, IFN is critical for chemokine production and recruitment following infection. The data reveal a role for inflammatory monocytes in both basal IFN responses and responses to infection.
Keywords: influenza; innate immunity; interferon; monocytes.
Copyright © 2018 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


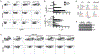
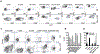
References
-
- Asano A, Jin HK, and Watanabe T (2003). Mouse Mx2 gene: organization, mRNA expression and the role of the interferon-response promoter in its regulation. Gene 306, 105–113. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

