Structural and Functional Insights into Human Nuclear Cyclophilins
- PMID: 30518120
- PMCID: PMC6315705
- DOI: 10.3390/biom8040161
Structural and Functional Insights into Human Nuclear Cyclophilins
Abstract
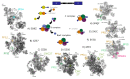
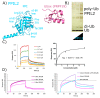
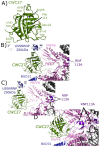
The peptidyl prolyl isomerases (PPI) of the cyclophilin type are distributed throughout human cells, including eight found solely in the nucleus. Nuclear cyclophilins are involved in complexes that regulate chromatin modification, transcription, and pre-mRNA splicing. This review collects what is known about the eight human nuclear cyclophilins: peptidyl prolyl isomerase H (PPIH), peptidyl prolyl isomerase E (PPIE), peptidyl prolyl isomerase-like 1 (PPIL1), peptidyl prolyl isomerase-like 2 (PPIL2), peptidyl prolyl isomerase-like 3 (PPIL3), peptidyl prolyl isomerase G (PPIG), spliceosome-associated protein CWC27 homolog (CWC27), and peptidyl prolyl isomerase domain and WD repeat-containing protein 1 (PPWD1). Each "spliceophilin" is evaluated in relation to the spliceosomal complex in which it has been studied, and current work studying the biological roles of these cyclophilins in the nucleus are discussed. The eight human splicing complexes available in the Protein Data Bank (PDB) are analyzed from the viewpoint of the human spliceophilins. Future directions in structural and cellular biology, and the importance of developing spliceophilin-specific inhibitors, are considered.
Keywords: NMR; X-ray crystallography; alternative splicing; nuclear cyclophilins; peptidyl prolyl isomerases; spliceophilins; spliceosomes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures









References
-
- Davis T.L., Walker J.R., Campagna-Slater V., Finerty P.J., Paramanathan R., Bernstein G., MacKenzie F., Tempel W., Ouyang H., Lee W.H., et al. Structural and biochemical characterization of the human cyclophilin family of peptidyl-prolyl isomerases. PLoS Boil. 2010;8:e1000439. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000439. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

