Effect of statins on fasting glucose in non-diabetic individuals: nationwide population-based health examination in Korea
- PMID: 30518364
- PMCID: PMC6280428
- DOI: 10.1186/s12933-018-0799-4
Effect of statins on fasting glucose in non-diabetic individuals: nationwide population-based health examination in Korea
Abstract
Background: Increasing evidence suggest that statin therapy has a diabetogenic effect. Individual types of statin may have a different effect on glucose metabolism. Using the repeated nationwide population-based health screening data in Korea, we investigated the longitudinal changes in fasting glucose level of non-diabetic individuals by use of statins.
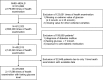
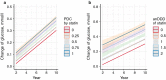
Methods: From the National Health Screening Cohort, we included 379,865 non-diabetic individuals who had ≥ 2 health screening examinations with fasting blood glucose level measured in 2002-2013. Using the prescription records of statins in the database, we calculated the proportion of days covered (PDC) and average number of defined daily doses per day (anDDD) by statins. We constructed multivariate linear mixed models to evaluate the effects of statins on the changes in fasting glucose (Δglu).
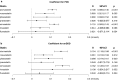
Results: High PDC by statins had a significant positive effect on Δglu (coefficient for PDC 0.093 mmol/L, standard error 0.007, p < 0.001). anDDD by statins was also positively associated with Δglu (coefficient for anDDD 0.119 mmol/L, standard error 0.009, p < 0.001). Unlike statins, the PDC by fibrate and ezetimibe were not significantly associated with Δglu. There was no significant interaction effect on Δglu between time interval and statin. Considering individual types of statins, use of atorvastatin, rosuvastatin, pitavastatin, and simvastatin were significantly associated with increase of Δglu. Pravastatin, lovastatin, and fluvastatin were also positively associated with Δglu, but were not statistically significant.
Conclusions: More adherent and intensive use of statins was significantly associated with an increase in fasting glucose of non-diabetic individuals. In subgroup analysis of individual statins, use of atorvastatin, rosuvastatin, pitavastatin and simvastatin had significant association with increase in fasting glucose. Pravastatin, lovastatin, and fluvastatin had non-significant trend toward an increased fasting glucose. Our findings suggest the medication class effect of statins inducing hyperglycemia.
Keywords: Diabetes mellitus; Glucose; Health examination; Statin.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Time-varying and dose-dependent effect of long-term statin use on risk of type 2 diabetes: a retrospective cohort study.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2020 May 16;19(1):67. doi: 10.1186/s12933-020-01037-0. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2020. PMID: 32416728 Free PMC article.
-
Statins and new-onset diabetes: a retrospective longitudinal cohort study.Clin Ther. 2012 Sep;34(9):1977-83. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2012.08.004. Epub 2012 Aug 30. Clin Ther. 2012. PMID: 22939164
-
Statin use and risk of new-onset diabetes: A meta-analysis of observational studies.Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2017 May;27(5):396-406. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2017.03.001. Epub 2017 Mar 10. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2017. PMID: 28416099 Review.
-
Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels and LDL-C goal attainment among elderly patients treated with rosuvastatin compared with other statins in routine clinical practice.Am J Geriatr Pharmacother. 2007 Sep;5(3):185-94. doi: 10.1016/j.amjopharm.2007.10.002. Am J Geriatr Pharmacother. 2007. PMID: 17996658
-
Do statins beneficially or adversely affect glucose homeostasis?Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2010 Sep;8(5):612-31. doi: 10.2174/157016110792006879. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20507274 Review.
Cited by
-
Combination therapy with pemafibrate (K-877) and pitavastatin improves vascular endothelial dysfunction in dahl/salt-sensitive rats fed a high-salt and high-fat diet.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2020 Sep 26;19(1):149. doi: 10.1186/s12933-020-01132-2. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2020. PMID: 32979918 Free PMC article.
-
CKD subpopulations defined by risk-factors: A longitudinal analysis of electronic health records.CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2021 Nov;10(11):1343-1356. doi: 10.1002/psp4.12695. Epub 2021 Sep 12. CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34510793 Free PMC article.
-
Modest effect of statins on fasting glucose in a longitudinal electronic health record based cohort.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2022 Jul 14;21(1):132. doi: 10.1186/s12933-022-01566-w. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2022. PMID: 35836181 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of Statin and Ezetimibe versus Statin Monotherapy on Cardiovascular Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Incidence among Adults with Impaired Fasting Glucose: a Propensity-Matched Nationwide Cohort Study.J Lipid Atheroscler. 2021 Sep;10(3):303-312. doi: 10.12997/jla.2021.10.3.303. Epub 2021 Jul 21. J Lipid Atheroscler. 2021. PMID: 34621701 Free PMC article.
-
Lower risk of subarachnoid haemorrhage in diabetes: a nationwide population-based cohort study.Stroke Vasc Neurol. 2021 Sep;6(3):402-409. doi: 10.1136/svn-2020-000601. Epub 2021 Feb 1. Stroke Vasc Neurol. 2021. PMID: 33526636 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

