Fenestrations control resting-state block of a voltage-gated sodium channel
- PMID: 30518562
- PMCID: PMC6304959
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1814928115
Fenestrations control resting-state block of a voltage-gated sodium channel
Abstract
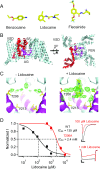
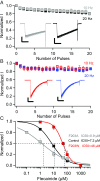
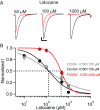
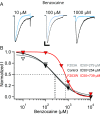
Potency of drug action is usually determined by binding to a specific receptor site on target proteins. In contrast to this conventional paradigm, we show here that potency of local anesthetics (LAs) and antiarrhythmic drugs (AADs) that block sodium channels is controlled by fenestrations that allow drug access to the receptor site directly from the membrane phase. Voltage-gated sodium channels initiate action potentials in nerve and cardiac muscle, where their hyperactivity causes pain and cardiac arrhythmia, respectively. LAs and AADs selectively block sodium channels in rapidly firing nerve and muscle cells to relieve these conditions. The structure of the ancestral bacterial sodium channel NaVAb, which is also blocked by LAs and AADs, revealed fenestrations connecting the lipid phase of the membrane to the central cavity of the pore. We cocrystallized lidocaine and flecainide with NavAb, which revealed strong drug-dependent electron density in the central cavity of the pore. Mutation of the contact residue T206 greatly reduced drug potency, confirming this site as the receptor for LAs and AADs. Strikingly, mutations of the fenestration cap residue F203 changed fenestration size and had graded effects on resting-state block by flecainide, lidocaine, and benzocaine, the potencies of which were altered from 51- to 2.6-fold in order of their molecular size. These results show that conserved fenestrations in the pores of sodium channels are crucial pharmacologically and determine the level of resting-state block by widely used drugs. Fine-tuning drug access through fenestrations provides an unexpected avenue for structure-based design of ion-channel-blocking drugs.
Keywords: antiarrhythmic drugs; fenestration; local anesthetics; sodium channel; voltage-gating.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Hille B. Ionic Channels of Excitable Membranes. 3rd Ed Sinauer Associates Inc.; Sunderland, MA: 2001.
-
- Catterall WA. From ionic currents to molecular mechanisms: The structure and function of voltage-gated sodium channels. Neuron. 2000;26:13–25. - PubMed
-
- Catterall WA. Sodium channels, inherited epilepsy, and antiepileptic drugs. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2014;54:317–338. - PubMed
-
- Dib-Hajj SD, Cummins TR, Black JA, Waxman SG. Sodium channels in normal and pathological pain. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2010;33:325–347. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

