Hypertension and chronic kidney disease affect long-term outcomes in patients with stable coronary artery disease receiving percutaneous coronary intervention
- PMID: 30518771
- PMCID: PMC6281739
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-35982-4
Hypertension and chronic kidney disease affect long-term outcomes in patients with stable coronary artery disease receiving percutaneous coronary intervention
Abstract
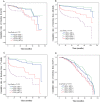
Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) is commonly used for patients with coronary artery disease (CAD). However, the effects of chronic kidney disease (CKD) and hypertension (HT) on long-term outcomes in patients with stable CAD receiving PCI are still unclear. A total of 1,676 patients treated with PCI were prospectively enrolled and divided into 4 groups according to the presence or absence of HT or CKD. General characteristics, clinical medications, risk factors, angiographic findings, and long-term outcomes were analyzed. Patients with CKD had the highest rate of all-cause and cardiovascular (CV) mortality (both P < 0.01). Patients with CKD alone had the lowest event-free rate of all-cause and CV deaths (both P < 0.001). Based on Cox proportional hazard model, patients with CKD alone had the highest risk of all-cause death (HR:2.86, 95% CI:1.73-4.75) and CV death (HR: 3.57,95% CI:2.01-6.33); while patients with both CKD and HT had the highest risk of repeat PCI (HR: 1.42, 95% CI:1.09-1.85).We found that in stable CAD patients after undergoing PCI, those with CKD alone had the highest long-term mortality. Comorbid CKD appears to increase risk in patient with HT, whereas comorbid HT doesn't seem to increase risk in patients with CKD.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Mathew V, et al. Outcomes in patients with diabetes mellitus undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention in the current era: a report from the Prevention of REStenosis with Tranilast and its Outcomes (PRESTO) trial. Circulation. 2004;109:476–480. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000109693.64957.20. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Laskey WK, et al. Comparison of in-hospital and one-year outcomes in patients with and without diabetes mellitus undergoing percutaneous catheter intervention (from the National, Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Dynamic Registry) Am. J. Cardiol. 2002;90:1062–1067. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9149(02)02770-4. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

