Inside Plectosphaerellaceae
- PMID: 30518989
- PMCID: PMC6276054
- DOI: 10.1016/j.simyco.2018.10.005
Inside Plectosphaerellaceae
Abstract
The family Plectosphaerellaceae (Glomerellales, Sordariomycetes) includes numerous plant pathogenic genera and soil-borne fungal species. Ten genera are currently accepted, including several taxa that occupy an unresolved position within the family. To address this issue, a multilocus sequence analysis was carried out using partial gene sequences from the 28S large subunit nrRNA gene (LSU), the internal transcribed spacer (ITS) regions of the nrDNA region, including the 5.8S nrRNA gene, the translation elongation factor 1-alpha (TEF1-α), tryptophan synthase (TS), actin (ACT) and the RNA polymerase II second largest subunit (RPB2), based on a large set of isolates mainly from the CBS collection. Results of the molecular data combined with a detailed morphological study resolved 22 genera in the family, of which 12 are newly described. Additionally, 15 new species and 10 new combinations are proposed. An epitype and neotype are also introduced for Stachylidium bicolor and Plectosphaerella cucumerina, respectively.
Keywords: Acremonium; B. nepalense (W. Gams) Giraldo López & Crous; B. terrestre Giraldo López & Crous; Brunneochlamydosporium Giraldo López & Crous; Brunneochlamydosporium cibotii (J.F.H. Beyma) Giraldo López & Crous; Brunneochlamydosporium macroclavatum Giraldo López & Crous; Chlamydosporiella Giraldo López & Crous; Chlamydosporiella restricta (J.F.H. Beyma) Giraldo López & Crous; Furcasterigmium Giraldo López & Crous; Furcasterigmium furcatum (W. Gams) Giraldo López & Crous; Fuscohypha Giraldo López & Crous; Fuscohypha expansa Giraldo López & Crous; G. catenata Giraldo López & Crous; G. serrae (Maffei) Giraldo López & Crous; Gibellulopsis aquatica Giraldo López & Crous; Gibellulopsis fusca (Thirum. & Sukapure) Giraldo López & Crous; L. phaseoli Giraldo López & Crous; Lectera humicola Giraldo López & Crous; M. elettariae Giraldo López & Crous; Musicillium tropicale Giraldo López & Crous; Musidium Giraldo López & Crous; Musidium stromaticum (W. Gams & R.H. Stover) Giraldo López & Crous; New taxa; Nigrocephalum Giraldo López & Crous; Nigrocephalum collariferum (Weisenb. & R. Kirschner) Giraldo López & Crous; Paragibellulopsis Giraldo López & Crous; Paragibellulopsis chrysanthemi (Hirooka et al.) Giraldo López & Crous; Paramusicillium Giraldo López & Crous; Paramusicillium asperulatum Giraldo López & Crous; Phialoparvum Giraldo López & Crous; Phialoparvum bifurcatum Giraldo López & Crous; Phylogeny; Plant pathogens; Plectosphaerella; Plectosphaerella humicola Giraldo López & Crous; Sayamraella Giraldo López & Crous; Sayamraella subulata Giraldo López & Crous; Sodiomyces alcalophilus (Okada) Giraldo López & Crous; Sodiomyces alkalinus Grum-Grzhim., Debets & Bilanenko; Soil fungi; Stachylidium bicolor Link; Summerbellia Giraldo López & Crous; Summerbellia oligotrophica Giraldo López & Crous; Taxonomy; Theobromium Giraldo López & Crous; Theobromium fuscum Giraldo López & Crous; Venturia cucumerina Lindf.
Figures





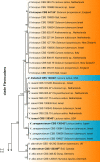






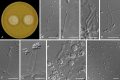
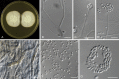

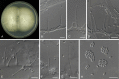

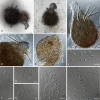
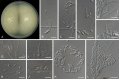
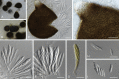

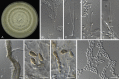

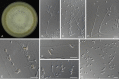
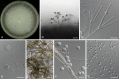
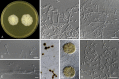


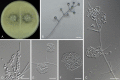
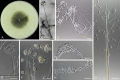



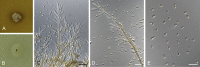
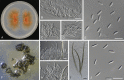
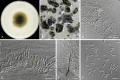

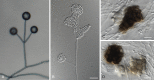
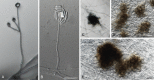
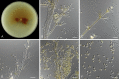
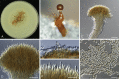
References
-
- Barron G.L. Waverly Press; Baltimore, USA: 1968. Genera of Hyphomycetes from soil.
-
- Batista A.C., Maia H da Silva. Uma nova doença fúngica de peixe ornamental. Anais da Sociedade de Biologia de Pernambuco. 1959;16:153–159.
-
- Bilanenko E., Sorokin D., Ivanova M. Heleococcum alkalinum, a new alkali-tolerant ascomycete from saline soda soils. Mycotaxon. 2005;91:497–507.
-
- Cannon P., Buddie A.G., Bridge P.D. Lectera, a new genus of the Plectosphaerellaceae for the legume pathogen Volutella colletotrichoides. MycoKeys. 2012;3:23–36.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
