Clinical observation of the effect of prophylaxis on allodynia in patients with migraine
- PMID: 30519076
- PMCID: PMC6233946
- DOI: 10.2147/JPR.S172976
Clinical observation of the effect of prophylaxis on allodynia in patients with migraine
Abstract
Objective: The clinical characteristics of migraine with and without allodynia were compared to evaluate the risk factors of cutaneous allodynia in migraine. The effects of prophylactic therapy on allodynia in patients with migraine were assessed based on the change in pain threshold after therapy.
Patients and methods: A total of 71 patients with migraine admitted to the Department of Neurology of Shandong Provincial Hospital were recruited in this study. The included patients were aged 18-70 years and did not present positive symptoms according to the nervous system examination. The variation in cutaneous allodynia was assessed for the role of classic prophylactic therapy in migraine-related allodynia, also termed as central sensitization (CS). Patients with migraine were randomized into two groups (topiramate and flunarizine groups), and the effect of drugs was evaluated by the change in cutaneous pain threshold between the two groups. Fifty-five patients were tested for pain threshold due to instrument failure. Pressure allodynia was measured with a force gage, and pricking was measured with Electronic von Frey Anesthesiometer. The pain threshold was measured every 3 months for 6 months. The variations in pain threshold after treatment were compared using t-test and χ 2 test.
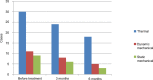
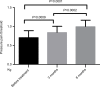
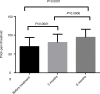
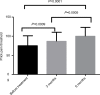
Results: Allodynia was seen in 70.4% of the patients; of these, 76.3% were females. Female gender, duration of illness, and frequency of migraine attacks per month were significantly associated with allodynia. The rate of allodynia and frequency of headache declined significantly, the number of patients with allodynia was reduced, and the pain threshold improved dramatically after treatment. The composite adverse events were low after treatment with topiramate and flunarizine.
Conclusion: Allodynia was observed, especially in females who experienced frequent migraine attacks for a prolonged period. Gender, duration of illness, and number of migraine attacks per month were the major predictors of allodynia. Topiramate and flunarizine administered orally for a short duration can effectively improve the pain threshold and CS of patients with migraine, and efficiently relieve allodynia.
Keywords: allodynia; central sensitization; flunarizine; migraine; prophylaxis; topiramate.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Topiramate as an adjunctive treatment in migraine prophylaxis.Headache. 2003 Nov-Dec;43(10):1080-4. doi: 10.1046/j.1526-4610.2003.03209.x. Headache. 2003. PMID: 14629243 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of pregabalin on central sensitization in patients with migraine.Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2015 Apr;53(4):277-83. doi: 10.5414/CP202205. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2015. PMID: 25669613
-
Cutaneous allodynia in patients with episodic migraine.Neurol Sci. 2013 Aug;34(8):1397-402. doi: 10.1007/s10072-012-1249-9. Epub 2012 Nov 23. Neurol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23179186
-
Central sensitisation and cutaneous allodynia in migraine: implications for treatment.CNS Drugs. 2004;18(6):337-42. doi: 10.2165/00023210-200418060-00001. CNS Drugs. 2004. PMID: 15089101 Review.
-
Topiramate prophylaxis and response to triptan treatment for acute migraine.Headache. 2006 Oct;46(9):1424-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1526-4610.2006.00531.x. Headache. 2006. PMID: 17040339 Review.
Cited by
-
Risk Factors and Consequences of Cutaneous Allodynia among Individuals with Migraine: A Scoping Review.Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2025 Jul 22;29(1):102. doi: 10.1007/s11916-025-01417-9. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2025. PMID: 40694183 Review. No abstract available.
-
Prevalence and characteristics of cutaneous allodynia in probable migraine.Sci Rep. 2021 Jan 28;11(1):2467. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-82080-z. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33510340 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Ultrasound-Guided Combined Greater Occipital Nerve Block at the C2 Level with Trapezius Trigger Point Injection and Supraorbital-Supratrochlear Nerve Block: More Effective on Allodynia and Disability in Chronic Migraine.Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 2023 Nov-Dec;26(6):943-951. doi: 10.4103/aian.aian_677_23. Epub 2023 Dec 15. Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 2023. PMID: 38229643 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lipton RB, Stewart WF, Diamond S, Diamond ML, Reed M. Prevalence and burden of migraine in the United States: data from the American Migraine Study II. Headache. 2001;41(7):646–657. - PubMed
-
- Stewart W, Lipton R, Celentano D, et al. Prevalence of migraine headache in the United States: relation to age, income, race, and other sociodemographic factors. JAMA. 1991;267:64–69. - PubMed
-
- Bigal ME, Lipton RB. The epidemiology, burden, and comorbidities of migraine. Neurol Clin. 2009;27(2):321–334. - PubMed
-
- Burton WN, Conti DJ, Chen CY, Schultz AB, Edington DW. The economic burden of lost productivity due to migraine headache: a specific worksite analysis. J Occup Environ Med. 2002;44(6):523–529. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

