Osthole sensitizes with radiotherapy to suppress tumorigenesis of human nasopharyngeal carcinoma in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 30519095
- PMCID: PMC6233473
- DOI: 10.2147/CMAR.S182798
Osthole sensitizes with radiotherapy to suppress tumorigenesis of human nasopharyngeal carcinoma in vitro and in vivo
Retraction in
-
Osthole Sensitizes with Radiotherapy to Suppress Tumorigenesis of Human Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma in vitro and in vivo [Retraction].Cancer Manag Res. 2023 Mar 24;15:319-320. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S412641. eCollection 2023. Cancer Manag Res. 2023. PMID: 36998312 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Radiotherapy is one of the most comment and useful treatment for nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC), but the radioresistance remains a major obstacle. Osthole, a natural coumarin derivative, has been shown to have anti-tumor and anti-inflammatory activity. However, the relationship between osthole and NPC treatment, especially for radiotherapy, is still elusive.
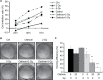
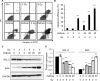
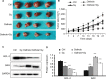
Methods: Osthole with or without X ray radiotherapy treated with CNE2 cells, a human EC cell line. Cell viability, proliferation, migration and apoptosis were measured by MTT, colony formation, Annexin V/PI double staining, Transwell assay, respectively. NPC tumor models were established on BALB/c nude mice by subcutaneously injection of CNE2 cells and the effect of osthole and radiotherapy on tumor growth in vivo was studied.
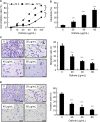
Results: We found that in a dose-dependent manner, osthole could individually, and synergistically with radiotherapy, reduce NPC cell (CNE2) viability, proliferation, migration, and invasion, and induce apoptosis, respectively. This effect of anti-tumor growth and induction of apoptosis was further confirmed in mice induced by subcutaneously injection with CNE2 cells and following treated with osthole or/and radiation.
Conclusion: Osthole increases the effect of radiotherapy on anti-human nasopharyngeal cancer.
Keywords: apoptosis; human nasopharyngeal carcinoma; osthole; proliferation; radiotherapy; tumorigenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Growth inhibition and apoptosis induced by osthole, a natural coumarin, in hepatocellular carcinoma.PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e37865. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0037865. Epub 2012 May 25. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22662241 Free PMC article.
-
In Vivo and In Vitro Effects of ATM/ATR Signaling Pathway on Proliferation, Apoptosis, and Radiosensitivity of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Cells.Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2017 Aug;32(6):193-203. doi: 10.1089/cbr.2017.2212. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2017. PMID: 28820634
-
Knockdown of annexin VII enhances nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell radiosensitivity in vivo and in vitro.Cancer Biomark. 2020;28(2):129-139. doi: 10.3233/CBM-190739. Cancer Biomark. 2020. PMID: 31958076
-
Downregulation of EB virus miR-BART4 inhibits proliferation and aggressiveness while promoting radiosensitivity of nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Dec;108:741-751. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.08.146. Epub 2018 Sep 21. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 30248542
-
Osthole induces human nasopharyngeal cancer cells apoptosis through Fas-Fas ligand and mitochondrial pathway.Environ Toxicol. 2018 Apr;33(4):446-453. doi: 10.1002/tox.22530. Epub 2018 Jan 10. Environ Toxicol. 2018. PMID: 29319219
Cited by
-
Environmental Cadmium Exposure Promotes the Development, Progression and Chemoradioresistance of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Feb 18;10:792933. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.792933. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35252173 Free PMC article.
-
ECRG4 acts as a tumor suppressor in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by suppressing the AKT/GSK3β/β-catenin signaling pathway.Cytotechnology. 2022 Apr;74(2):231-243. doi: 10.1007/s10616-022-00520-8. Epub 2022 Jan 27. Cytotechnology. 2022. PMID: 35464163 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Chinese Herbal Medicine Therapy on Overall and Cancer Related Mortality in Patients With Advanced Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma in Taiwan.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jan 29;11:607413. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.607413. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33708119 Free PMC article.
-
Osthole increases the radiosensitivity of hepatoma cells by inhibiting GSK-3β/AMPK/mTOR pathway-controlled glycolysis.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023 Apr;396(4):683-692. doi: 10.1007/s00210-022-02347-8. Epub 2022 Nov 29. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36445387
-
The NRF2/KEAP1 Pathway Modulates Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Cell Radiosensitivity via ROS Elimination.Onco Targets Ther. 2020 Sep 11;13:9113-9122. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S260169. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. PMID: 32982300 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chua MLK, Wee JTS, Hui EP, Chan ATC. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Lancet. 2016;387(10022):1012–1024. - PubMed
-
- Lo KW, To KF, Huang DP. Focus on nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Cell. 2004;5(5):423–428. - PubMed
-
- Lee AW, Ma BB, Ng WT, Chan AT. Management of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: current practice and future perspective. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33(29):3356–3364. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

