Visualization of Exo- and Endocytosis of AMPA Receptors During Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity Around Postsynaptic-Like Membrane Formed on Glass Surface
- PMID: 30519162
- PMCID: PMC6258823
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2018.00442
Visualization of Exo- and Endocytosis of AMPA Receptors During Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity Around Postsynaptic-Like Membrane Formed on Glass Surface
Abstract
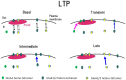
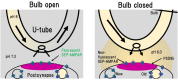
Regulation of exo- and endocytosis of α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA)-type glutamate receptor (AMPAR) plays a critical role in the expression of synaptic plasticity such as long-term potentiation (LTP) and long-term depression (LTD) at excitatory central synapses. Enhanced AMPAR exocytosis or endocytosis has been suggested to contribute to LTP or LTD, respectively. However, several unsettled fundamental questions have remained about AMPAR exo- and endocytosis in the basal condition and during synaptic plasticity: (1) Does the size of each exo- or endocytosis event, and/or do the frequencies of these events change during LTP or LTD? If they change, what are the time courses of the respective changes? (2) Where does the exo- or endocytosis preferentially occur in each condition: inside or in the vicinity of postsynaptic membrane, or in the extrasynaptic membrane? (3) Do different types of AMPAR, such as GluA1 homo-tetramer, GluA1/2 hetero-tetramer and GluA2/3 hetero-tetramer, show distinct exo- and endocytosis changes? To address these questions, we developed new methods to observe individual events of AMPAR exo- or endocytosis with a high signal to noise (SN) ratio in a culture preparation using total internal reflection fluorescence microscopy (TIRFM). In these studies, hippocampal neurons were cultured on a neurexin (NRX)-coated glass coverslip, which induced formation of postsynaptic-like membrane (PSLM) directly on the glass surface. Then, a super-ecliptic pHluorin (SEP)-tagged AMPAR subunit such as GluA1 (GluA1-SEP) was expressed in neurons and its fluorescence changes during LTP induced by high frequency electrical field stimulation were observed with TIRFM, which showed different time courses of exocytosis changes of GluA1-, GluA2-, or GluA3-SEP in and around PSLM. In addition, a new method to detect individual endocytosis events of AMPAR was developed by combining TIFRM observation of GluA-SEP around PSLM with a rapid extracellular pH exchange method using a U-tube. Recent results on exo- and endocytosis changes of GluA-SEP during N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA)-induced LTD suggested that suppression of AMPAR exocytosis rather than enhancement of AMPAR endocytosis primarily contributes to LTD expression, although the NMDA application transiently enhances clathrin-dependent endocytosis of GluA1-containing AMPAR.
Keywords: AMPA receptor; LTD; LTP; endocytosis; exocytosis; hippocampus; live-cell imaging; total internal reflection fluorescence microscopy.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Suppression of AMPA Receptor Exocytosis Contributes to Hippocampal LTD.J Neurosci. 2018 Jun 13;38(24):5523-5537. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3210-17.2018. Epub 2018 May 21. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29899033 Free PMC article.
-
Detection and characterization of individual endocytosis of AMPA-type glutamate receptor around postsynaptic membrane.Genes Cells. 2017 Jun;22(6):583-590. doi: 10.1111/gtc.12493. Epub 2017 May 5. Genes Cells. 2017. PMID: 28474392
-
Visualization of subunit-specific delivery of glutamate receptors to postsynaptic membrane during hippocampal long-term potentiation.Cell Rep. 2012 Apr 19;1(4):291-8. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2012.02.004. Epub 2012 Mar 22. Cell Rep. 2012. PMID: 22832222
-
Regulation of neuronal PKA signaling through AKAP targeting dynamics.Eur J Cell Biol. 2006 Jul;85(7):627-33. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2006.01.010. Epub 2006 Feb 28. Eur J Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16504338 Review.
-
The AMPA Receptor Code of Synaptic Plasticity.Neuron. 2018 Oct 24;100(2):314-329. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2018.10.018. Neuron. 2018. PMID: 30359599 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Rumex acetosa L. enhance learning and cognitive function by modulating NMDA receptor and BDNF pathways in vitro and in vivo.Metab Brain Dis. 2025 Apr 17;40(5):185. doi: 10.1007/s11011-025-01608-8. Metab Brain Dis. 2025. PMID: 40244509
-
AMPA Receptors: A Key Piece in the Puzzle of Memory Retrieval.Front Hum Neurosci. 2021 Sep 21;15:729051. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2021.729051. eCollection 2021. Front Hum Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34621161 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AMPA Receptor Expression Requirement During Long-Term Memory Retrieval and Its Association with mTORC1 Signaling.Mol Neurobiol. 2021 Apr;58(4):1711-1722. doi: 10.1007/s12035-020-02215-7. Epub 2020 Nov 26. Mol Neurobiol. 2021. PMID: 33244735

