Hidradenitis Suppurativa: Causes, Features, and Current Treatments
- PMID: 30519375
- PMCID: PMC6239161
Hidradenitis Suppurativa: Causes, Features, and Current Treatments
Abstract
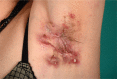
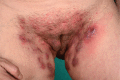
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), a relatively common and chronic inflammatory skin disorder. HS can have debilitating consequences if not diagnosed and treated appropriately. Clinically defined by recurrent, inflamed nodules in intertriginous regions (i.e., axillary, inguinal, and perianal areas), HS can cause intense pain and, in severe disease stages, lead to the formation of fistulas, sinus tracts, and extensive scarring. Postpubertal onset and female preponderance further characterize HS. Numerous pathogenic mechanisms have been proposed in HS, including immune dysregulation, genetics, smoking, and obesity; however, the exact etiology remains to be elucidated. The association of HS with inflammatory bowel disease, cardiovascular disease risk factors, and psychiatric disorders suggests HS is a systemic disease. HS significantly impairs quality of life in patients in excess versus other skin diseases. Unfortunately, experiences indicate long diagnostic delays, which in many cases might be due to disease unawareness among physicians. Increased knowledge of HS is therefore important in order to optimize disease management and ultimately improve the quality of life of patients.
Keywords: Hidradenitis suppurativa; inflammatory skin disease.
Conflict of interest statement
FUNDING:No funding was provided for this study. DISCLOSURES:The authors have no conflicts of interest relevant to the content of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Zouboulis CC, Desai N, Emtestam L et al. European S1 guideline for the treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa/acne inversa. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;29(4):619–444. - PubMed
-
- Jemec GBE, Kimball AB. Hidradenitis suppurativa: epidemiology and scope of the problem. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73(5 Suppl 1):S4–S7. - PubMed
-
- Miller IM, McAndrew RJ, Hamzavi I. Prevalence, risk factors, and comorbidities of hidradenitis suppurativa. Dermatol Clin. 2016;34(1):7–16. - PubMed
-
- Esmann S, Jemec GBE. Psychosocial impact of hidradenitis suppurativa: a qualitative study. Acta Derm Venereol. 2011;91(3):328–332. - PubMed
-
- Matusiak L, Bieniek A, Szepietowski JC. Psychophysical aspects of hidradenitis suppurativa. Acta Derm Venereol. 2010;90(3):264–268. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources