Validation of the 2017 European LeukemiaNet classification for acute myeloid leukemia with NPM1 and FLT3-internal tandem duplication genotypes
- PMID: 30521114
- PMCID: PMC6561101
- DOI: 10.1002/cncr.31885
Validation of the 2017 European LeukemiaNet classification for acute myeloid leukemia with NPM1 and FLT3-internal tandem duplication genotypes
Abstract
Background: The revised 2017 European LeukemiaNet (ELN) classification (ELN-2017) of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) divides patients into 3 prognostic risk categories, with additional factors such as the fms-like tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3)-internal tandem duplication (ITD) allele ratio (AR) considered for risk stratification. To the best of the authors' knowledge, the prognostic usefulness of ELN-2017 in comparison with ELN-2010 in younger patients with AML has not been validated to date.
Methods: The authors performed a retrospective study on patients aged <60 years who received idarubicin plus cytarabine (IA)-based induction chemotherapy for newly diagnosed AML.
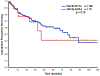
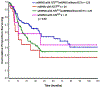
Results: According to ELN-2017 criteria, the number of patients in the favorable (Fav), intermediate (Int), and adverse (Adv) risk categories was 192 patients (27%), 331 patients (46%), and 192 patients (27%), respectively. Overall survival probabilities at 5 years in the Fav, Int, and Adv groups were 57%, 37%, and 18%, respectively. In comparison, the 5-year overall survival probabilities in the Fav (169 patients), intermediate (IR)-1 (80 patients), IR-2 (306 patients), and Adv (160 patients) ELN-2010 categories were 59%, 32%, 40%, and 14%, respectively. Although ELN-2010 historically distinguishes prognosis into IR-1 and IR-2 categories in younger patients, this difference was nullified in the current study cohort. When comparing patients with a low FLT3-ITD AR with those with a high FLT3-ITD AR, no significant differences in survival were noted among patients with nucleophosmin 1 (NPM1)-mutated AML (P = .28) or wild-type NPM1 (P = .35), and in those treated with IA alone (P = .79) or those treated with IA and a FLT3 inhibitor (P = .10).
Conclusions: The ELN-2017 more accurately distinguishes prognosis in patients with newly diagnosed AML. The lack of prognostic significance for the FLT3-ITD AR needs further evaluation in different treatment settings.
Keywords: European LeukemiaNet; acute myeloid leukemia; allele ratio; prognosis; validation; younger.
© 2018 American Cancer Society.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST DISCLOSURES
The authors made no disclosures.
Figures

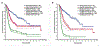
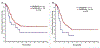

References
-
- Estey E, Dohner H. Acute myeloid leukaemia. Lancet. 2006;368:1894–1907. - PubMed
-
- Grimwade D, Walker H, Oliver F, et al. The importance of diagnostic cytogenetics on outcome in AML: analysis of 1,612 patients entered into the MRC AML 10 trial. The Medical Research Council Adult and Children’s Leukaemia Working Parties. Blood. 1998;92:2322–2333. - PubMed
-
- Grimwade D, Hills RK, Moorman AV, et al. ; National Cancer Research Institute Adult Leukaemia Working Group. Refinement of cytogenetic classification in acute myeloid leukemia: determination of prognostic significance of rare recurring chromosomal abnormalities among 5876 younger adult patients treated in the United Kingdom Medical Research Council trials. Blood. 2010;116:354–365. - PubMed
-
- Byrd JC, Mrozek K, Dodge RK, et al. ; Cancer and Leukemia Group B (CALGB 8461). Pretreatment cytogenetic abnormalities are predictive of induction success, cumulative incidence of relapse, and overall survival in adult patients with de novo acute myeloid leukemia: results from Cancer and Leukemia Group B (CALGB 8461). Blood. 2002;100:4325–4336. - PubMed
-
- Dohner H, Estey EH, Amadori S, et al. ; European LeukemiaNet. Diagnosis and management of acute myeloid leukemia in adults: recommendations from an international expert panel, on behalf of the European LeukemiaNet. Blood. 2010;115:453–474. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

