Reflectance confocal microscopy for diagnosing keratinocyte skin cancers in adults
- PMID: 30521687
- PMCID: PMC6516892
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD013191
Reflectance confocal microscopy for diagnosing keratinocyte skin cancers in adults
Abstract
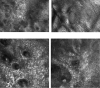
Background: Early accurate detection of all skin cancer types is important to guide appropriate management and improve morbidity and survival. Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is usually a localised skin cancer but with potential to infiltrate and damage surrounding tissue, whereas cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC) and melanoma are higher risk skin cancers with the potential to metastasise and ultimately lead to death. When used in conjunction with clinical or dermoscopic suspicion of malignancy, or both, reflectance confocal microscopy (RCM) may help to identify cancers eligible for non-surgical treatment without the need for a diagnostic biopsy, particularly in people with suspected BCC. Any potential benefit must be balanced against the risk of any misdiagnoses.
Objectives: To determine the diagnostic accuracy of RCM for the detection of BCC, cSCC, or any skin cancer in adults with any suspicious lesion and lesions that are difficult to diagnose (equivocal); and to compare its accuracy with that of usual practice (visual inspection or dermoscopy, or both).
Search methods: We undertook a comprehensive search of the following databases from inception to August 2016: Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials; MEDLINE; Embase; CINAHL; CPCI; Zetoc; Science Citation Index; US National Institutes of Health Ongoing Trials Register; NIHR Clinical Research Network Portfolio Database; and the World Health Organization International Clinical Trials Registry Platform. We studied reference lists and published systematic review articles.
Selection criteria: Studies of any design that evaluated the accuracy of RCM alone, or RCM in comparison to visual inspection or dermoscopy, or both, in adults with lesions suspicious for skin cancer compared with a reference standard of either histological confirmation or clinical follow-up, or both.
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently extracted data using a standardised data extraction and quality assessment form (based on QUADAS-2). We contacted authors of included studies where information related to the target condition or diagnostic threshold were missing. We estimated summary sensitivities and specificities using the bivariate hierarchical model. For computation of likely numbers of true-positive, false-positive, false-negative, and true-negative findings in the 'Summary of findings' tables, we applied summary sensitivity and specificity estimates to lower quartile, median and upper quartiles of the prevalence observed in the study groups. We also investigated the impact of observer experience.
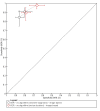
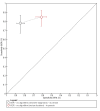
Main results: The review included 10 studies reporting on 11 study cohorts. All 11 cohorts reported data for the detection of BCC, including 2037 lesions (464 with BCC); and four cohorts reported data for the detection of cSCC, including 834 lesions (71 with cSCC). Only one study also reported data for the detection of BCC or cSCC using dermoscopy, limiting comparisons between RCM and dermoscopy. Studies were at high or unclear risk of bias across almost all methodological quality domains, and were of high or unclear concern regarding applicability of the evidence. Selective participant recruitment, unclear blinding of the reference test, and exclusions due to image quality or technical difficulties were observed. It was unclear whether studies were representative of populations eligible for testing with RCM, and test interpretation was often undertaken using images, remotely from the participant and the interpreter blinded to clinical information that would normally be available in practice.Meta-analysis found RCM to be more sensitive but less specific for the detection of BCC in studies of participants with equivocal lesions (sensitivity 94%, 95% confidence interval (CI) 79% to 98%; specificity 85%, 95% CI 72% to 92%; 3 studies) compared to studies that included any suspicious lesion (sensitivity 76%, 95% CI 45% to 92%; specificity 95%, 95% CI 66% to 99%; 4 studies), although CIs were wide. At the median prevalence of disease of 12.5% observed in studies including any suspicious lesion, applying these results to a hypothetical population of 1000 lesions results in 30 BCCs missed with 44 false-positive results (lesions misdiagnosed as BCCs). At the median prevalence of disease of 15% observed in studies of equivocal lesions, nine BCCs would be missed with 128 false-positive results in a population of 1000 lesions. Across both sets of studies, up to 15% of these false-positive lesions were observed to be melanomas mistaken for BCCs. There was some suggestion of higher sensitivities in studies with more experienced observers. Summary sensitivity and specificity could not be estimated for the detection of cSCC due to paucity of data.
Authors' conclusions: There is insufficient evidence for the use of RCM for the diagnosis of BCC or cSCC in either population group. A possible role for RCM in clinical practice is as a tool to avoid diagnostic biopsies in lesions with a relatively high clinical suspicion of BCC. The potential for, and consequences of, misclassification of other skin cancers such as melanoma as BCCs requires further research. Importantly, data are lacking that compare RCM to standard clinical practice (with or without dermoscopy).
Conflict of interest statement
JD: nothing to declare. JJD: nothing to declare. NC: nothing to declare. DS: nothing to declare. SB: nothing to declare. YT: nothing to declare. CD: nothing to declare. LP: nothing to declare. RM: "my institution received a grant for a BARCO NV commercially sponsored study to evaluate digital dermoscopy in the skin cancer clinic and Oxfordshire Health Services Research Charitable Funds for carrying out a study of feasibility of using the SCQOLIT tool in non‐melanoma skin cancer; I have received payment from the UK Photopheresis Society for a lecture on cutaneous graft versus host disease October 2017; and royalties for
Figures











References
References to studies included in this review
Castro 2015 {published data only}
-
- Castro RP, Stephens A, Fraga‐Braghiroli NA, Oliviero MC, Rezze GG, Rabinovitz H, et al. Accuracy of in vivo confocal microscopy for diagnosis of basal cell carcinoma: a comparative study between handheld and wide‐probe confocal imaging. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology 2015;29(6):1164‐9. [DOI: 10.1111/jdv.12780; ER4:20569441; PUBMED: 25338750] - DOI - PubMed
Curchin 2011 {published data only}
-
- Curchin CE, Wurm EM, Lambie DLj, Longo C, Pellacani G, Soyer HP. First experiences using reflectance confocal microscopy on equivocal skin lesions in Queensland. Australasian Journal of Dermatology 2011;52(2):89‐97. [ER4:15465900; PUBMED: 21605091] - PubMed
Farnetani 2015 {published data only}
-
- Farnetani F, Scope A, Braun RP, Gonzalez S, Guitera P, Malvehy J, et al. Skin cancer diagnosis with reflectance confocal microscopy: reproducibility of feature recognition and accuracy of diagnosis. JAMA Dermatology 2015;151(10):1075‐80. [ER4:25233569; PUBMED: 25993262] - PubMed
Guitera 2012 {published data only}
-
- Guitera P, Menzies SW, Longo C, Cesinaro AM, Scolyer RA, Pellacani G. In vivo confocal microscopy for diagnosis of melanoma and basal cell carcinoma using a two‐step method: analysis of 710 consecutive clinically equivocal cases. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2012;132(10):2386‐94. [ER4:15465942; PUBMED: 22718115] - PubMed
Incel 2015 {published data only}
-
- Incel P, Gurel MS, Erdemir AV. Vascular patterns of nonpigmented tumoral skin lesions: confocal perspectives. Skin Research & Technology 2015;21(3):333‐9. [PUBMED: 25345376] - PubMed
Longo 2013 {published data only}
-
- Longo C, Farnetani F, Ciardo S, Cesinaro AM, Moscarella E, Ponti G, et al. Is confocal microscopy a valuable tool in diagnosing nodular lesions? A study of 140 cases. British Journal of Dermatology 2013;169(1):58‐67. [ER4:15465992; PUBMED: 23374159] - PubMed
Nori 2004 {published data only}
-
- Nori S, Rius‐Diaz F, Cuevas J, Goldgeier M, Jaen P, Torres A, et al. Sensitivity and specificity of reflectance‐mode confocal microscopy for in vivo diagnosis of basal cell carcinoma: a multicenter study. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2004;51(6):923‐30. [ER4:15466027; PUBMED: 15583584] - PubMed
Pellacani 2014a (cons) {published data only}
-
- Pellacani G, Pepe P, Casari A, Longo C. Reflectance confocal microscopy as a second‐level examination in skin oncology improves diagnostic accuracy and saves unnecessary excisions: a longitudinal prospective study. British Journal of Dermatology 2014;171(5):1044‐51. [PUBMED: 24891083] - PubMed
Pellacani 2014b (doc) {published data only}
-
- Pellacani G, Pepe P, Casari A, Longo C. Reflectance confocal microscopy as a second‐level examination in skin oncology improves diagnostic accuracy and saves unnecessary excisions: a longitudinal prospective study. British Journal of Dermatology 2014;171(5):1044‐51. [PUBMED: 24891083] - PubMed
Rao 2013 {published data only}
-
- Rao BK, Mateus R, Wassef C, Pellacani G. In vivo confocal microscopy in clinical practice: comparison of bedside diagnostic accuracy of a trained physician and distant diagnosis of an expert reader. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2013;69(6):e295‐300. [ER4:15466076; PUBMED: 24035553] - PubMed
Witkowski 2016 {published data only}
-
- Witkowski AM, Ludzik J, DeCarvalho N, Ciardo S, Longo C, DiNardo A, et al. Non‐invasive diagnosis of pink basal cell carcinoma: how much can we rely on dermoscopy and reflectance confocal microscopy?. Skin Research & Technology 2016;22(2):230‐7. [ER4:25012281; PUBMED: 26338448] - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Agero 2006 {published data only}
-
- Agero AL, Busam KJ, Benvenuto‐Andrade C, Scope A, Gill M, Marghoob AA, et al. Reflectance confocal microscopy of pigmented basal cell carcinoma. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2006;54(4):638‐43. - PubMed
Ahlgrimm‐Siess 2010 {published data only}
-
- Ahlgrimm‐Siess V, Cao T, Oliviero M, Hofmann‐Wellenhof R, Rabinovitz HS, Scope A. The vasculature of nonmelanocytic skin tumors in reflectance confocal microscopy: vascular features of basal cell carcinoma. Archives of Dermatology 2010;146(3):353‐4. - PubMed
Ahlgrimm‐Siess 2011 {published data only}
-
- Ahlgrimm‐Siess V, Cao T, Oliviero M, Hofmann‐Wellenhof R, Rabinovitz HS, Scope A. The vasculature of nonmelanocytic skin tumors on reflectance confocal microscopy: vascular features of squamous cell carcinoma in situ. Archives of Dermatology 2011;147(2):264. - PubMed
Alarcon 2014 {published data only}
-
- Alarcon I, Carrera C, Turegano P, Malvehy J, Puig S. Basal cell carcinoma with spontaneous regression: added value of reflectance confocal microscopy when the dermoscopic diagnosis is uncertain. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2014;71(1):e7‐9. - PubMed
Amjadi 2011 {published data only}
-
- Amjadi M, Coventry BJ, Greenwood JE. Reflectance confocal microscopy in the diagnosis of non‐melanoma skin cancer and benign lesions versus normal skin: a blinded prospective trial. Internet Journal of Plastic Surgery 2011;7(2):1‐6. [ER4:21450593]
Bassoli 2012 {published data only}
-
- Bassoli S, Rabinovitz HS, Pellacani G, Porges L, Oliviero MC, Braun RP, et al. Reflectance confocal microscopy criteria of lichen planus‐like keratosis. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology & Venereology 2012;26(5):578‐90. - PubMed
Benati 2015 {published data only}
-
- Benati E, Argenziano G, Kyrgidis A, Moscarella E, Ciardo S, Bassoli S, et al. Melanoma and naevi with a globular pattern: confocal microscopy as an aid for diagnostic differentiation. British Journal of Dermatology 2015;173(5):1232‐8. - PubMed
Braga 2009 {published data only}
-
- Braga JC, Scope A, Klaz I, Mecca P, Gonzalez S, Rabinovitz H, et al. The significance of reflectance confocal microscopy in the assessment of solitary pink skin lesions. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2009;61(2):230‐41. - PubMed
Carrera 2015 {published data only}
-
- Carrera C. High‐risk melanoma patients: can unnecessary naevi biopsies be avoided?. British Journal of Dermatology 2015;172(2):313‐5. - PubMed
de Carvalho 2015 {published data only}
-
- Carvalho N, Farnetani F, Ciardo S, Ruini C, Witkowski AM, Longo C, et al. Reflectance confocal microscopy correlates of dermoscopic patterns of facial lesions help to discriminate lentigo maligna from pigmented nonmelanocytic macules. British Journal of Dermatology 2015;173(1):128‐33. - PubMed
de Carvalho 2016 {published data only}
-
- Carvalho N, Guida S, Spagnol AL, Cesinaro AM, Farnetani F, Bonamonte D, et al. Pink melanocytic and non‐melanocytic lesions: how reflectance confocal microscopy can help in differential diagnosis. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology & Venereology 2016;30(6):1026‐9. - PubMed
Edwards 2016 {published data only}
Eichert 2010 {published data only}
-
- Eichert S, Mohrle M, Breuninger H, Rocken M, Garbe C, Bauer J. Diagnosis of cutaneous tumors with in vivo confocal laser scanning microscopy. Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft 2010;8(6):400‐10. - PubMed
Ferrari 2015 {published data only}
-
- Ferrari B, Pupelli G, Farnetani F, Carvalho NT, Longo C, Reggiani C, et al. Dermoscopic difficult lesions: an objective evaluation of reflectance confocal microscopy impact for accurate diagnosis. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology : JEADV 2015;29(6):1135‐40. [DOI: 10.1111/jdv.12769; ER4:20569458; PUBMED: 25303304] - DOI - PubMed
Figueroa‐Silva 2016 {published data only}
-
- Figueroa‐Silva O, Cinotti E, Almeida Silva T, Moscarella E, Lallas A, Ciardo S, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of reflectance confocal microscopy for lesions typified by dermoscopic island. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology : JEADV 2016;30(9):1594‐8. [ER4:25012335; PUBMED: 27109574] - PubMed
Gareau 2009 {published data only}
Gerger 2005 {published data only}
-
- Gerger A, Koller S, Kern T, Massone C, Steiger K, Richtig E, et al. Diagnostic applicability of in vivo confocal laser scanning microscopy in melanocytic skin tumors. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2005;124(3):493‐8. - PubMed
Gerger 2006 {published data only}
-
- Gerger A, Kerl H, Samonigg H, Langsenlehner U, Krippl P, Smolle J. Sensitivity and specificity of confocal laser scanning microscopy for in vivo diagnosis of malignant skin tumors. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2006;126(Suppl 3):s114. - PubMed
Gerger 2008 {published data only}
-
- Gerger A, Wiltgen M, Langsenlehner U, Richtig E, Horn M, Weger W, et al. Diagnostic image analysis of malignant melanoma in in vivo confocal laser‐scanning microscopy: a preliminary study. Skin Research & Technology 2008;14(3):359‐63. - PubMed
Giambrone 2015 {published data only}
-
- Giambrone D, Alamgir M, Masud A, Bronsnick T, Rao B. The diagnostic accuracy of in vivo confocal microscopy in clinical practice. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2015;73(2):317‐9. - PubMed
Gill 2014 {published data only}
-
- Gill M, Longo C, Farnetani F, Cesinaro AM, Gonzalez S, Pellacani G. Non‐invasive in vivo dermatopathology: identification of reflectance confocal microscopic correlates to specific histological features seen in melanocytic neoplasms. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology & Venereology 2014;28(8):1069‐78. - PubMed
Gonzalez 2002 {published data only}
-
- Gonzalez S, Tannous Z. Real‐time in vivo confocal reflectance microscopy of basal cell carcinoma. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2002;47:869‐74. - PubMed
Gonzalez 2013 {published data only}
-
- Gonzalez S. Should reflectance confocal microscopy be the gold standard for basal cell carcinoma diagnosis?. Imaging in Medicine 2013;5(4):299‐301.
Guida 2015 {published data only}
-
- Guida S, Longo C, Casari A, Ciardo S, Manfredini M, Reggiani C, et al. Update on the use of confocal microscopy in melanoma and non‐melanoma skin cancer. Giornale Italiano di Dermatologia e Venereologia 2015;150(5):547‐63. - PubMed
Guitera 2009 {published data only}
-
- Guitera P, Pellacani G, Longo C, Seidenari S, Avramidis M, Menzies SW. In vivo reflectance confocal microscopy enhances secondary evaluation of melanocytic lesions. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2009;129(1):131‐8. [ER4:15465945; PUBMED: 18633444] - PubMed
Guitera 2010 {published data only}
-
- Guitera P, Pellacani G, Crotty KA, Scolyer RA, Li L‐X, Bassoli S, et al. The impact of in vivo reflectance confocal microscopy on the diagnostic accuracy of lentigo maligna and equivocal pigmented and nonpigmented macules of the face. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2010;130(8):2080‐91. - PubMed
Guitera 2013 {published data only}
-
- Guitera P, Moloney FJ, Menzies SW, Stretch JR, Quinn MJ, Hong A, et al. Improving management and patient care in lentigo maligna by mapping with in vivo confocal microscopy. JAMA Dermatology 2013;149(6):692‐8. - PubMed
Haenssle 2006 {published data only}
-
- Haenssle HA, Krueger U, Vente C, Thoms K‐M, Bertsch HP, Zutt M, et al. Results from an observational trial: digital epiluminescence microscopy follow‐up of atypical nevi increases the sensitivity and the chance of success of conventional dermoscopy in detecting melanoma. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2006;126(5):980‐5. - PubMed
Hennessy 2010 {published data only}
-
- Hennessy R, Jacques S, Pellacani G, Gareau D. Clinical feasibility of rapid confocal melanoma feature detection. Proceedings of the SPIE 2010;7548:75480Q.
Hofmann‐Wellenhof 2008 {published data only}
-
- Hofmann‐Wellenhof R, Langsenlehner U, Richtig E, Koller S, Weger W, Ahlgrimm‐Siess V, et al. In vivo confocal laser scanning microscopy of melanocytic skin tumours: diagnostic applicability using unselected tumour images. British Journal of Dermatology 2008;158(2):329‐33. - PubMed
Hoogedoorn 2014 {published data only}
-
- Hoogedoorn L, Peppelman M, Erp PE, Gerritsen MJ. The use of in vivo reflectance confocal microscopy in clinical practice: prospective differentiation of difficult to distinguish nodular basal cell carcinomas and intradermal nevi. Nederlands Tijdschrift voor Dermatologie en Venereologie 2014;24(1):48.
Hoogedoorn 2015 {published data only}
-
- Hoogedoorn L, Peppelman M, Blokx WA, Erp PE, Gerritsen M‐JP. Prospective differentiation of clinically difficult to distinguish nodular basal cell carcinomas and intradermal nevi by non‐invasive reflectance confocal microscopy: a case series study. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology 2015;29(2):330‐6. - PubMed
Humphrey 2006 {published data only}
-
- Humphrey S, Walsh NM, Delaney L, Propperova I, Langley RG. Prognostic significance of vascularity in cutaneous melanoma: pilot study using in vivo confocal scanning laser microscopy. Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery 2006;10(3):122‐7. - PubMed
Kadouch 2015a {published data only}
-
- Kadouch DJ, Schram ME, Leeflang MM, Limpens J, Spuls PI, Rie MA. In vivo confocal microscopy of basal cell carcinoma: a systematic review of diagnostic accuracy. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology & Venereology 2015;29(10):1890‐7. - PubMed
Kadouch 2015b {published data only}
-
- Kadouch DJ, Wolkerstorfer A, Elshot Y, Zupan‐Kajcovski B, Crijns MB, Starink MV, et al. Treatment of basal cell carcinoma using a one‐stop‐shop with reflectance confocal microscopy: study design and protocol of a randomized controlled multicenter trial. JMIR Research Protocols 2015;4(3):e109. - PMC - PubMed
Koller 2011 {published data only}
-
- Koller S, Wiltgen M, Ahlgrimm‐Siess V, Weger W, Hofmann‐Wellenhof R, Richtig E, et al. In vivo reflectance confocal microscopy: automated diagnostic image analysis of melanocytic skin tumours. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology : JEADV 2011;25(5):554‐8. [ER4:15465979; PUBMED: 20735518] - PubMed
Kose 2014 {published data only}
Langley 2001 {published data only}
-
- Langley RG, Rajadhyaksha M, Dwyer PJ, Sober AJ, Flotte TJ, Anderson RR. Confocal scanning laser microscopy of benign and malignant melanocytic skin lesions in vivo. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2001;45(3):365‐76. - PubMed
Langley 2006 {published data only}
-
- Langley RG, Burton E, Walsh N, Propperova I, Murray SJ. In vivo confocal scanning laser microscopy of benign lentigines: comparison to conventional histology and in vivo characteristics of lentigo maligna. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2006;55(1):88‐97. - PubMed
Langley 2007 {published data only}
-
- Langley RG, Walsh N, Sutherland AE, Propperova I, Delaney L, Morris SF, et al. The diagnostic accuracy of in vivo confocal scanning laser microscopy compared to dermoscopy of benign and malignant melanocytic lesions: a prospective study. Dermatology 2007;215(4):365‐72. [ER4:15465985; PUBMED: 17912001] - PubMed
Losi 2014 {published data only}
-
- Losi A, Longo C, Cesinaro AM, Benati E, Witkowski A, Guitera P, et al. Hyporeflective pagetoid cells: a new clue for amelanotic melanoma diagnosis by reflectance confocal microscopy. British Journal of Dermatology 2014;171(1):48‐54. - PubMed
Lovatto 2015 {published data only}
-
- Lovatto L, Carrera C, Salerni G, Alos L, Malvehy J, Puig S. In vivo reflectance confocal microscopy of equivocal melanocytic lesions detected by digital dermoscopy follow‐up. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology : JEADV 2015;29(10):1918‐25. [ER4:25012311; PUBMED: 25752663] - PubMed
Maier 2013 {published data only}
-
- Maier T, Sattler EC, Braun‐Falco M, Korting HC, Ruzicka T, Berking C. Reflectance confocal microscopy in the diagnosis of partially and completely amelanotic melanoma: report on seven cases. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology & Venereology 2013;27(1):e42‐52. - PubMed
Malvehy 2012 {published data only}
-
- Malvehy J, Hanke‐Martinez M, Costa J, Salerni G, Carrera C, Puig S. Semiology and pattern analysis in nonmelanocytic lesions. In: Hofmann‐Wellenhof R, Pellacani G, Malvehy J, Soyer HP editor(s). Reflectance Confocal Microscopy for Skin Diseases. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2012:239‐52.
Menge 2016 {published data only}
-
- Menge TD, Hibler BP, Cordova MA, Nehal KS, Rossi AM. Concordance of handheld reflectance confocal microscopy (RCM) with histopathology in the diagnosis of lentigo maligna (LM): a prospective study. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2016;74(6):1114‐20. - PubMed
Miller 2011 {published data only}
-
- Miller JH, Chrisler WB, Wang X, Sowa MB. Confocal microscopy for modeling electron microbeam irradiation of skin. Radiation & Environmental Biophysics 2011;50(3):365‐9. - PubMed
Nobre Moura 2011 {published data only}
-
- Nobre Moura F, Dalle S, Depaepe L, Durupt F, Balme B, Thomas L. Melanoma: early diagnosis using in vivo reflectance confocal microscopy. Clinical & Experimental Dermatology 2011;36(2):209‐11. - PubMed
Pellacani 2005 {published data only}
-
- Pellacani G, Cesinaro AM, Seidenari S. Reflectance‐mode confocal microscopy of pigmented skin lesions – improvement in melanoma diagnostic specificity. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2005;53(6):979‐85. - PubMed
Pellacani 2007 {published data only}
-
- Pellacani G, Guitera P, Longo C, Avramidis M, Seidenari S, Menzies S. The impact of in vivo reflectance confocal microscopy for the diagnostic accuracy of melanoma and equivocal melanocytic lesions. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2007;127(12):2759‐65. [ER4:15466047; PUBMED: 17657243] - PubMed
Pellacani 2008 {published data only}
-
- Pellacani G, Longo C, Malvehy J, Puig S, Carrera C, Segura S, et al. In vivo confocal microscopic and histopathologic correlations of dermoscopic features in 202 melanocytic lesions. Archives of Dermatology 2008;144(12):1597‐608. - PubMed
Pellacani 2009 {published data only}
-
- Pellacani G, Vinceti M, Bassoli S, Braun R, Gonzalez S, Guitera P, et al. Reflectance confocal microscopy and features of melanocytic lesions: an internet‐based study of the reproducibility of terminology. Archives of Dermatology 2009;145(10):1137‐43. - PubMed
Pellacani 2012 {published data only}
-
- Pellacani G, Farnetani F, Gonzalez S, Longo C, Cesinaro AM, Casari A, et al. In vivo confocal microscopy for detection and grading of dysplastic nevi: a pilot study. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2012;66(3):e109‐21. [ER4:15466043; PUBMED: 21742408] - PubMed
Peppelman 2013 {published data only}
-
- Peppelman M, Wolberink EA, Blokx WA, Kerkhof PC, Erp PE, Gerritsen MJ. In vivo diagnosis of basal cell carcinoma subtype by reflectance confocal microscopy. Dermatology 2013;227(3):255‐62. - PubMed
Peppelman 2015 {published data only}
-
- Peppelman M, Nguyen KP, Hoogedoorn L, Erp PE, Gerritsen MJ. Reflectance confocal microscopy: non‐invasive distinction between actinic keratosis and squamous cell carcinoma. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology & Venereology 2015;29(7):1302‐9. - PubMed
Peppelman 2016 {published data only}
Puig 2012 {published data only}
-
- Puig S, Giacomo TB, Serra D, Cabrini F, Alos L, Palou J, et al. Reflectance confocal microscopy of blue nevus. European Journal of Dermatology 2012;22(4):552‐3. - PubMed
Pupelli 2013 {published data only}
-
- Pupelli G, Longo C, Veneziano L, Cesinaro AM, Ferrara G, Piana S, et al. Small‐diameter melanocytic lesions: morphological analysis by means of in vivo confocal microscopy. British Journal of Dermatology 2013;168(5):1027‐33. [ER4:15466070; PUBMED: 23301553] - PubMed
Reggiani 2015 {published data only}
-
- Reggiani C, Manfredini M, Mandel VD, Farnetani F, Ciardo S, Bassoli S, et al. Update on non‐invasive imaging techniques in early diagnosis of non‐melanoma skin cancer. Giornale Italiano di Dermatologia e Venereologia 2015;150(4):393‐405. - PubMed
Rishpon 2009 {published data only}
-
- Rishpon A, Kim N, Scope A, Porges L, Oliviero MC, Braun RP, et al. Reflectance confocal microscopy criteria for squamous cell carcinomas and actinic keratoses. Archives of Dermatology 2009;145(7):766‐72. - PubMed
Röwert‐Huber 2007 {published data only}
-
- Röwert‐Huber J, Patel MJ, Forschner T, Ulrich C, Eberle J, Kerl H, et al. Actinic keratosis is an early in situ squamous cell carcinoma: a proposal for reclassification. British Journal of Dermatology 2007;156:8‐12. - PubMed
Salerni 2011 {published data only}
-
- Salerni G, Lovatto L, Carrera C, Palou J, Alos L, Puig‐Butille JA, et al. Correlation among dermoscopy, confocal reflectance microscopy, and histologic features of melanoma and basal cell carcinoma collision tumor. Dermatologic Surgery 2011;37(2):275‐9. - PubMed
Scope 2009 {published data only}
-
- Scope A, Mecca PS, Marghoob AA. skINsight lessons in reflectance confocal microscopy: rapid diagnosis of pigmented basal cell carcinoma. Archives of Dermatology 2009;145(1):106‐7. - PubMed
Scope 2014 {published data only}
Segura 2009 {published data only}
-
- Segura S, Puig S, Carrera C, Palou J, Malvehy J. Development of a two‐step method for the diagnosis of melanoma by reflectance confocal microscopy. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2009;61(2):216‐29. [ER4:20569494; PUBMED: 19406506] - PubMed
Soyer 2013 {published data only}
-
- Soyer HP, Prow TW. Reflectance confocal microscopy in the diagnosis of nodular skin lesions. British Journal of Dermatology 2013;169(1):4. - PubMed
Stanganelli 2015 {published data only}
-
- Stanganelli I, Longo C, Mazzoni L, Magi S, Medri M, Lanzanova G, et al. Integration of reflectance confocal microscopy in sequential dermoscopy follow‐up improves melanoma detection accuracy. British Journal of Dermatology 2015;172(2):365‐71. [ER4:20569496; PUBMED: 25154446] - PubMed
Steiner 1992 {published data only}
-
- Steiner A, Pehamberger H, Binder M, Wolff K. Pigmented Spitz nevi: improvement of the diagnostic accuracy by epiluminescence microscopy. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 1992;27(5 Pt 1):697‐701. - PubMed
Stephens 2013 {published data only}
-
- Stephens A, Fraga‐Braghiroli N, Oliviero M, Rabinovitz H, Scope A. Spoke wheel‐like structures in superficial basal cell carcinoma: a correlation between dermoscopy, histopathology, and reflective confocal microscopy. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2013;69(5):e219‐21. - PubMed
Stevenson 2013 {published data only}
Tannous 2009 {published data only}
-
- Tannous Z, Al‐Arashi M, Shah S, Yaroslavsky AN. Delineating melanoma using multimodal polarized light imaging. Lasers in Surgery & Medicine 2009;41(1):10‐6. - PubMed
Willard 2011 {published data only}
-
- Willard K, Warschaw KE, Swanson DL. Use of reflectance confocal microscopy to differentiate hidrocystoma from basal cell carcinoma. Dermatologic Surgery 2011;37(3):392‐4. - PubMed
Xiong 2016 {published data only}
-
- Xiong YD, Ma S, Li X, Zhong X, Duan C, Chen Q. A meta‐analysis of reflectance confocal microscopy for the diagnosis of malignant skin tumours. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology & Venereology 2016;30(8):1295‐302. - PubMed
Yelamos 2016 {published data only}
-
- Yelamos O, Nehal KS. Integrating clinical information, dermoscopy and reflectance confocal microscopy to improve the diagnostic accuracy and confidence of amelanotic and lightly pigmented melanomas. British Journal of Dermatology 2016;175(6):1147‐8. - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Borsari 2016 {published data only}
-
- Borsari S, Pampena R, Lallas A, Kyrgidis A, Moscarella E, Benati E, et al. Clinical indications for use of reflectance confocal microscopy for skin cancer diagnosis. JAMA Dermatology 2016;152(10):1093‐8. [PUBMED: 27580185] - PubMed
Guitera 2016 {published data only}
-
- Guitera P, Menzies SW, Argenziano G, Longo C, Losi A, Drummond M, et al. Dermoscopy and in vivo confocal microscopy are complementary techniques for diagnosis of difficult amelanotic and light‐coloured skin lesions. British Journal of Dermatology 2016;175(6):1311‐9. [PUBMED: 27177158 ] - PubMed
Jain 2017 {published data only}
-
- Jain M, Pulijal SV, Rajadhyaksha M. The bedside diagnostic accuracy of a novice reflectance confocal microscopy reader for skin cancer detection in vivo in real‐time: understanding challenges and potential pitfalls. Proceedings of SPIE. 2017; Vol. 10060. [DOI: 10.1117/12.2255685] - DOI
Ludzik 2016 {published data only}
-
- Ludzik J, Witkowski AM, Roterman‐Konieczna I, Bassoli S, Farnetani F, Pellacani G. Improving diagnostic accuracy of dermoscopically equivocal pink cutaneous lesions with reflectance confocal microscopy in telemedicine settings: double reader concordance evaluation of 316 cases. PloS One 2016;11(9):e0162495. [PUBMED: 27606812] - PMC - PubMed
Additional references
Alam 2001
-
- Alam M, Ratner D. Cutaneous squamous‐cell carcinoma. New England Journal of Medicine 2001;344(13):975‐83. [PUBMED: 11274625] - PubMed
Argenziano 1998
-
- Argenziano G, Fabbrocini G, Carli P, Giorgi V, Sammarco E, Delfino M. Epiluminescence microscopy for the diagnosis of doubtful melanocytic skin lesions. Comparison of the ABCD rule of dermatoscopy and a new 7‐point checklist based on pattern analysis. Archives of Dermatology 1998;134(12):1563‐70. [PUBMED: 9875194] - PubMed
Argenziano 2012
-
- Argenziano G, Albertini G, Castagnetti F, Pace B, Lernia V, Longo C, et al. Early diagnosis of melanoma: what is the impact of dermoscopy?. Dermatologic Therapy 2012;25(5):403‐9. [PUBMED: 23046019] - PubMed
Arits 2013
-
- Arits AH, Mosterd K, Essers BA, Spoorenberg E, Sommer A, Rooij MJ, et al. Photodynamic therapy versus topical imiquimod versus topical fluorouracil for treatment of superficial basal‐cell carcinoma: a single blind, non‐inferiority, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncology 2013;14(7):647‐54. [DOI: 10.1016/S1470-2045(13)70143-8; PUBMED: 23683751] - DOI - PubMed
Baldursson 1993
-
- Baldursson B, Sigurgeirsson B, Lindelof B. Leg ulcers and squamous cell carcinoma. An epidemiological study and a review of the literature. Acta Dermato‐Venereologica 1993;73(3):171‐4. [PUBMED: 8105611] - PubMed
Bath‐Hextall 2007a
-
- Bath‐Hextall F, Leonardi‐Bee J, Smith C, Meal A, Hubbard R. Trends in incidence of skin basal cell carcinoma. Additional evidence from a UK primary care database study. International Journal of Cancer 2007;121(9):2105‐8. [PUBMED: 17640064] - PubMed
Bath‐Hextall 2007b
Bath‐Hextall 2014
-
- Bath‐Hextall F, Ozolins M, Armstrong SJ, Colver GB, Perkins W, Miller PS, et al. Surgical excision versus imiquimod 5% cream for nodular and superficial basal‐cell carcinoma (SINS): a multicentre, non‐inferiority, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncology 2014;15(1):96‐105. [PUBMED: 24332516] - PubMed
Batra 2002
-
- Batra RS, Kelley LC. A risk scale for predicting extensive subclinical spread of nonmelanoma skin cancer. Dermatologic Surgery 2002;28(2):107‐12; discussion 112. [PUBMED: 11860418] - PubMed
Betti 2017
-
- Betti R, Moneghini L, Mapelli ET, Bulfamante G, Cerri A. Growth rate of different basal cell carcinoma subtypes. European Journal of Dermatology 2017;27(5):544‐5. [PUBMED: 29084641] - PubMed
Bossuyt 2015
Carter 2013
CCAAC Network 2008
-
- Cancer Council Australia & Australian Cancer Network. Basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma (and related lesions) – a guide to clinical management in Australia, 2008. www.cancer.org.au/content/pdf/HealthProfessionals/ClinicalGuidelines/Bas.... Sydney: Cancer Council Australia & Australian Cancer Network, (accessed 19 May 2015).
Chao 2013
-
- Chao D, London Cancer North and East. London cancer, guidelines for cutaneous malignant melanoma management August 2014. www.londoncancer.org/media/76373/london‐cancer‐melanoma‐guidelines‐2013‐.... London: London Cancer North and East Alliance, (accessed 25 February 2015).
Chowdri 1996
-
- Chowdri NA, Darzi MA. Postburn scar carcinomas in Kashmiris. Burns 1996;22(6):477‐82. [PUBMED: 8884010] - PubMed
Chu 2006
-
- Chu H, Cole S. Bivariate meta‐analysis for sensitivity and specificity with sparse data: a generalized linear mixed model approach (letter to the editor). Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2006;59(12):1331. [PUBMED: 17098577] - PubMed
Chuchu 2018a
Chuchu 2018b
Dabski 1986
-
- Dabski K, Stoll HL Jr, Milgrom H. Squamous cell carcinoma complicating late chronic discoid lupus erythematosus. Journal of Surgical Oncology 1986;32(4):233‐7. [PUBMED: 3736067] - PubMed
Deeks 2005
-
- Deeks JJ, Macaskill P, Irwig L. The performance of tests of publication bias and other sample size effects in systematic reviews of diagnostic test accuracy was assessed. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2005;58(9):882‐93. [PUBMED: 16085191] - PubMed
Deeks 2013
-
- Deeks JJ, Bossuyt PM, Gatsonis C, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Diagnostic Test Accuracy Version 1.0.0. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2013. Available from srdta.cochrane.org.
Dinnes 2018a
Dinnes 2018b
Dinnes 2018c
Drew 2017
Drucker 2017
-
- Drucker A, Adam GP, Langberg V, Gazula A, Smith B, Moustafa F, et al. Treatments for Basal Cell and Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Skin. Comparative Effectiveness Reviews, No. 199. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US), 2017. - PubMed
Efron 1983
-
- Efron B. Estimating the error rate of a prediction rule: improvement on cross‐validation. Journal of the American Statistical Association 1983;78(382):316‐31. [DOI: 10.1080/01621459.1983.10477973] - DOI
Esteva 2017
Fasching 1989
-
- Fasching MC, Meland NB, Woods JE, Wolff BG. Recurrent squamous‐cell carcinoma arising in pilonidal sinus tract – multiple flap reconstructions. Report of a case. Diseases of the Colon & Rectum 1989;32(2):153‐8. [PUBMED: 2914529] - PubMed
Ferrante di Ruffano 2018a
-
- Ferrante di Ruffano L, Takwoingi Y, Dinnes J, Chuchu N, Bayliss SE, Davenport C, et al. Computer‐assisted diagnosis techniques (dermoscopy and spectroscopy‐based) for diagnosing skin cancer in adults. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2018, Issue 12. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD013186] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Ferrante di Ruffano 2018b
Ferrante di Ruffano 2018c
Firnhaber 2012
-
- Firnhaber JM. Diagnosis and treatment of basal cell and squamous cell carcinoma. American Family Physician 2012;86(2):161‐8. [PUBMED: 22962928] - PubMed
Fitzpatrick 1975
-
- Fitzpatrick TB. Soleil et peau. Journal de Médecine Esthétique 1975;2:33‐4.
Flohil 2013
-
- Flohil SC, Leest RJ, Arends LR, Vries E, Nijsten T. Risk of subsequent cutaneous malignancy in patients with prior keratinocyte carcinoma: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. European Journal of Cancer 2013;49(10):2365‐75. [PUBMED: 23608733] - PubMed
Friedman 1985
-
- Friedman HI, Cooper PH, Wanebo HJ. Prognostic and therapeutic use of microstaging of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma of the trunk and extremities. Cancer 1985;56(5):1099‐105. [PUBMED: 4016700] - PubMed
Gambichler 2015
-
- Gambichler T, Schmid‐Wendtner MH, Plura I, Kampilafkos P, Stucker M, Berking C, et al. A multicentre pilot study investigating high‐definition optical coherence tomography in the differentiation of cutaneous melanoma and melanocytic naevi. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology & Venereology 2015;29(3):537‐41. [PUBMED: 25073788] - PubMed
Garcia 2009
-
- Garcia C, Poletti E, Crowson AN. Basosquamous carcinoma. Journal of the American Acadademy of Dermatology 2009;60(1):137‐43. [PUBMED: 19103364] - PubMed
Gerbert 2000
-
- Gerbert B, Bronstone A, Maurer T, Hofmann R, Berger T. Decision support software to help primary care physicians triage skin cancer: a pilot study. Archives of Dermatology 2000;136(2):187‐92. [PUBMED: 10677094] - PubMed
Gordon 2013
-
- Gordon R. Skin cancer: an overview of epidemiology and risk factors. Seminars in Oncology Nursing 2013;29(3):160‐9. [PUBMED: 23958214] - PubMed
Gorlin 2004
-
- Gorlin RJ. Nevoid basal cell carcinoma (Gorlin) syndrome. Genetics in Medicine 2004;6(6):530‐9. [PUBMED: 15545751] - PubMed
Grachtchouk 2011
Green 1988
-
- Green A, Leslie D, Weedon D. Diagnosis of skin cancer in the general population: clinical accuracy in the Nambour survey. Medical Journal of Australia 1988;148(9):447‐50. [PUBMED: 3283506] - PubMed
Griffin 2016
Griffiths 2005
-
- Griffiths RW, Suvarna SK, Stone J. Do basal cell carcinomas recur after complete conventional surgical excision?. British Journal of Plastic Surgery 2005;58(6):795‐805. [PUBMED: 16086990] - PubMed
Grob 1998
-
- Grob JJ, Bonerandi JJ. The 'ugly duckling' sign: identification of the common characteristics of nevi in an individual as a basis for melanoma screening. Archives of Dermatology 1998;134(1):103‐4. [PUBMED: 9449921] - PubMed
Guitera 2017
-
- Guitera P, Menzies S, Chamberlain A, Soyer P, Cancer Council Australia Melanoma Guidelines Working Party. What is the role of confocal microscopy in melanoma diagnosis?. www.wiki.cancer.org.au/australia/Guidelines:Melanoma/Confocal_microscopy (accessed prior to 28 November 2017).
Haenssle 2010
-
- Haenssle HA, Korpas B, Hansen‐Hagge C, Buhl T, Kaune KM, Rosenberger A, et al. Seven‐point checklist for dermatoscopy: performance during 10 years of prospective surveillance of patients at increased melanoma risk. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2010;62(5):785‐93. [PUBMED: 20226567] - PubMed
Harland 2000
-
- Harland CC, Kale SG, Jackson P, Mortimer PS, Bamber JC. Differentiation of common benign pigmented skin lesions from melanoma by high‐resolution ultrasound. British Journal of Dermatology 2000;143(2):281‐9. [PUBMED: 10951134] - PubMed
Hartevelt 1990
-
- Hartevelt MM, Bavinck JN, Kootte AM, Vermeer BJ, Vandenbroucke JP. Incidence of skin cancer after renal transplantation in The Netherlands. Transplantation 1990;49(3):506‐9. [PUBMED: 2316011] - PubMed
Hauschild 2014
-
- Hauschild A, Chen SC, Weichenthal M, Blum A, King HC, Goldsmith J, et al. To excise or not: impact of MelaFind on German dermatologists' decisions to biopsy atypical lesions. Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft 2014;12(7):606‐14. [PUBMED: 24944011] - PubMed
Hoorens 2016
-
- Hoorens I, Vossaert K, Pil L, Boone B, Schepper S, Ongenae K, et al. Total‐body examination vs lesion‐directed skin cancer screening. JAMA Dermatology 2016;152(1):27‐34. - PubMed
Jansen 2018
-
- Jansen MH, Mosterd K, Arits AH, Roozeboom MH, Sommer A, Essers BA, et al. Five‐year results of a randomized controlled trial comparing effectiveness of photodynamic therapy, topical imiquimod, and topical 5‐fluorouracil in patients with superficial basal cell carcinoma. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2018;138(3):527‐33. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jid.2017.09.033; PUBMED: 29045820] - DOI - PubMed
Jensen 1999
-
- Jensen P, Hansen S, Moller B, Leivestad T, Pfeffer P, Geiran O, et al. Skin cancer in kidney and heart transplant recipients and different long‐term immunosuppressive therapy regimens. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 1999;40(2 Pt 1):177‐86. [PUBMED: 10025742] - PubMed
Kao 1986
-
- Kao GF. Carcinoma arising in Bowen's disease. Archives of Dermatology 1986;122(10):1124‐6. [PUBMED: 3767398] - PubMed
Karimkhani 2015
-
- Karimkhani C, Boyers LN, Dellavalle RP, Weinstock MA. It's time for "keratinocyte carcinoma" to replace the term "nonmelanoma skin cancer". Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2015;72(1):186‐7. [PUBMED: 25497921] - PubMed
Kelleners‐Smeets 2017
-
- Kelleners‐Smeets NW, Mosterd K, Nelemans PJ. Treatment of low‐risk basal cell carcinoma. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2017;137(3):539‐40. [PUBMED: 28235442] - PubMed
Kim 2014
-
- Kim DD, Tang JY, Ioannidis JP. Network geometry shows evidence sequestration for medical vs. surgical practices: treatments for basal cell carcinoma. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2014;67(4):391‐400. [PUBMED: 24491794] - PubMed
Kittler 2002
-
- Kittler H, Pehamberger H, Wolff K, Binder M. Diagnostic accuracy of dermoscopy (review). Lancet Oncology 2002;3(3):159‐65. [PUBMED: 11902502] - PubMed
Kleinerman 2012
-
- Kleinerman R, Whang TB, Bard RL, Marmur ES. Ultrasound in dermatology: principles and applications. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2012;67(3):478‐87. [PUBMED: 22285673] - PubMed
Lansbury 2010
Lansbury 2013
Lear 1997
Lear 2012
-
- Lear JT. Oral hedgehog‐pathway inhibitors for basal‐cell carcinoma. New England Journal of Medicine 2012;366(23):2225‐6. [PUBMED: 22670909] - PubMed
Lederman 1985
-
- Lederman JS, Sober AJ. Does biopsy type influence survival in clinical stage I cutaneous melanoma?. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 1985;13(6):983‐7. [PUBMED: 4078105] - PubMed
Lees 1991
-
- Lees VC, Briggs JC. Effect of initial biopsy procedure on prognosis in stage I invasive cutaneous malignant melanoma: review of 1086 patients. British Journal of Surgery 1991;78(9):1108‐10. [PUBMED: 1933198] - PubMed
Lister 1997
-
- Lister RK, Black MM, Calonje E, Burnand KG. Squamous cell carcinoma arising in chronic lymphoedema. British Journal of Dermatology 1997;136(3):384‐7. [PUBMED: 9115922] - PubMed
Lo 1991
-
- Lo JS, Snow SN, Reizner GT, Mohs FE, Larson PO, Hruza GJ. Metastatic basal cell carcinoma: report of twelve cases with a review of the literature. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 1991;24(5 Pt 1):715‐9. [PUBMED: 1869642] - PubMed
Lomas 2012
-
- Lomas A, Leonardi‐Bee J, Bath‐Hextall F. A systematic review of worldwide incidence of nonmelanoma skin cancer. British Journal of Dermatology 2012;166(5):1069‐80. [PUBMED: 22251204] - PubMed
London Cancer Alliance 2013
-
- London Cancer Alliance. Guidelines for the treatment and referral of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) of the skin. www.londoncancer.org/media/76391/london‐cancer‐scc‐guidelines‐2013‐v1.0.pdf. London: London Cancer Alliance, (accessed prior to 25 May 2018).
Longo 2011
-
- Longo C, Rito C, Beretti F, Cesinaro AM, Piñeiro‐Maceira J, Seidenari S, et al. De novo melanoma and melanoma arising from pre‐existing nevus: in vivo morphologic differences as evaluated by confocal microscopy. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2011;65(3):604‐14. [PUBMED: 21715047] - PubMed
MacKie 1985
-
- MacKie RM, English J, Aitchison TC, Fitzsimons CP, Wilson P. The number and distribution of benign pigmented moles (melanocytic naevi) in a healthy British population. British Journal of Dermatology 1985;113(2):167‐74. [PUBMED: 4027184] - PubMed
MacKie 1990
Madan 2010
-
- Madan V, Lear JT, Szeimies RM. Non‐melanoma skin cancer. Lancet 2010;375(9715):673‐85. [PUBMED: 20171403] - PubMed
Maia 1995
-
- Maia M, Proenca NG, Moraes JC. Risk factors for basal cell carcinoma: a case‐control study. Revista de Saude Publica 1995;29(1):27‐37. [PUBMED: 8525311] - PubMed
Maloney 1996
-
- Maloney ME. Arsenic in dermatology. Dermatologic Surgery 1996;22(3):301‐4. [PUBMED: 8599743] - PubMed
Malvehy 2014
-
- Malvehy J, Hauschild A, Curiel‐Lewandrowski C, Mohr P, Hofmann‐Wellenhof R, Motley R, et al. Clinical performance of the Nevisense system in cutaneous melanoma detection: an international, multicentre, prospective and blinded clinical trial on efficacy and safety. British Journal of Dermatology 2014;171(5):1099‐107. [PUBMED: 24841846] - PMC - PubMed
Marsden 2010
-
- Marsden JR, Newton‐Bishop JA, Burrows L, Cook M, Corrie PG, Cox NH, et al. BAD guidelines: revised UK guidelines for the management of cutaneous melanoma 2010. British Journal of Dermatology 2010;163(2):238‐56. [PUBMED: 20608932] - PubMed
McCormack 1997
-
- McCormack CJ, Kelly JW, Dorevitch AP. Differences in age and body site distribution of the histological subtypes of basal cell carcinoma. A possible indicator of differing causes. Archives of Dermatology 1997;133(5):593‐6. [PUBMED: 9158412] - PubMed
McCusker 2014
-
- McCusker M, Basset‐Seguin N, Dummer R, Lewis K, Schadendorf D, Sekulic A, et al. Metastatic basal cell carcinoma: prognosis dependent on anatomic site and spread of disease. European Journal of Cancer 2014;50(4):774‐83. [PUBMED: 24412051] - PubMed
Moeckelmann 2018
-
- Moeckelmann N, Ebrahimi A, Dirven R, Liu J, Low TH, Gupta R, et al. Analysis and comparison of the 8th Edition American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) nodal staging system in cutaneous and oral squamous cell cancer of the head and neck. Annals of Surgical Oncology 2018;25(6):1730‐6. [DOI: 10.1245/s10434-018-6340-x; PUBMED: 29352431] - DOI - PubMed
Mogensen 2007
-
- Mogensen M, Jemec GB. Diagnosis of nonmelanoma skin cancer/keratinocyte carcinoma: a review of diagnostic accuracy of nonmelanoma skin cancer diagnostic tests and technologies.. Dermatologic Surgery 2007;33(10):1158‐74. [PUBMED: 17903149] - PubMed
Moncrieff 2002
-
- Moncrieff M, Cotton S, Claridge E, Hall P. Spectrophotometric intracutaneous analysis: a new technique for imaging pigmented skin lesions. British Journal of Dermatology 2002;146(3):448‐57. [PUBMED: 11952545] - PubMed
Monheit 2011
-
- Monheit G, Cognetta AB, Ferris L, Rabinovitz H, Gross K, Martini M, et al. The performance of MelaFind: a prospective multicenter study. Archives of Dermatology 2011;147(2):188‐94. [PUBMED: 20956633] - PubMed
Motley 2009
-
- Motley RJ, Preston PW, Lawrence CM. Multi‐professional guidelines for the management of the patient with primary cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. www.bad.org.uk/healthcare‐professionals/clinical‐standards/clinical‐guid... (accessed prior to 28 November 2017).
Murchie 2017
-
- Murchie P, Amalraj Raja E, Brewster DH, Iversen L, Lee AJ. Is initial excision of cutaneous melanoma by general practitioners (GPs) dangerous? Comparing patient outcomes following excision of melanoma by GPs or in hospital using national datasets and meta‐analysis. European Journal of Cancer 2017;86:373‐84. [PUBMED: 29100192] - PubMed
Musah 2013
-
- Musah A, Gibson JE, Leonardi‐Bee J, Cave MR, Ander EL, Bath‐Hextall F. Regional variations of basal cell carcinoma incidence in the U.K. using The Health Improvement Network database (2004‐10). British Journal of Dermatology 2013;169(5):1093‐9. [PUBMED: 23701520] - PubMed
Nart 2015
-
- Nart IF, Armayones SG, Medina FV, Orti MB, Orpinell XB. Basal cell carcinoma treated with ingenol mebutate. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2015;5(Suppl 1):AB180.
Nascimento 2014
-
- Nascimento MM, Shitara D, Enokihara MM, Yamada S, Pellacani G, Rezze GG. Inner gray halo, a novel dermoscopic feature for the diagnosis of pigmented actinic keratosis: clues for the differential diagnosis with lentigo maligna. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2014;71(4):708‐15. [PUBMED: 24947988] - PubMed
NICE 2010
-
- National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. NICE guidance on cancer services. Improving outcomes for people with skin tumours including melanoma (update). www.nice.org.uk/guidance/csgstim. NICE, (accessed 19 May 2015).
NICE 2015
-
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Suspected cancer: recognition and referral. www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng12. London: National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence, (accessed prior to 25 May 2018).
NICE 2017
-
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Vismodegib for treating basal cell carcinoma. www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ta489. London: NICE, (accessed prior to 25 May 2018).
Norman 2009
O'Gorman 2014
-
- O'Gorman SM, Murphy GM. Photosensitizing medications and photocarcinogenesis. Photodermatology, Photoimmunology & Photomedicine 2014;30(1):8‐14. [PUBMED: 24393207] - PubMed
Offidani 2002
-
- Offidani A, Simonetti O, Bernardini ML, Alpagut A, Cellini A, Bossi G. General practitioners' accuracy in diagnosing skin cancers. Dermatology 2002;205(2):127‐30. [PUBMED: 12218226] - PubMed
Olsen 2015
-
- Olsen J, Themstrup L, Jemec GB. Optical coherence tomography in dermatology. Giornale Italiano di Dermatologia e Venereologia 2015;150(5):603‐15. [PUBMED: 26129683] - PubMed
Pellacani 2014
-
- Pellacani G, Pepe P, Casari A, Longo C. Reflectance confocal microscopy as a second‐level examination in skin oncology improves diagnostic accuracy and saves unnecessary excisions: a longitudinal prospective study. British Journal of Dermatology 2014;171(5):1044‐51. [PUBMED: 24891083] - PubMed
Rajadhyaksha 1995
-
- Rajadhyaksha M, Grossman M, Esterowitz D, Webb RH, Anderson RR. In vivo confocal scanning laser microscopy of human skin: melanin provides strong contrast. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 1995;104(6):946‐52. [PUBMED: 7769264] - PubMed
Rajadhyaksha 2017
Rajpara 2009
-
- Rajpara SM, Botello AP, Townend J, Ormerod AD. Systematic review of dermoscopy and digital dermoscopy/artificial intelligence for the diagnosis of melanoma. British Journal of Dermatology 2009;161(3):591‐604. [PUBMED: 19302072] - PubMed
Randle 1996
-
- Randle HW. Basal cell carcinoma. Identification and treatment of the high‐risk patient. Dermatologic Surgery 1996;22(3):255‐61. [PUBMED: 8599737] - PubMed
Reitsma 2005
-
- Reitsma JB, Glas AS, Rutjes AW, Scholten RJ, Bossuyt PM, Zwinderman AH. Bivariate analysis of sensitivity and specificity produces informative summary measures in diagnostic reviews. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2005;58(10):982‐90. [PUBMED: 16168343] - PubMed
Review Manager 2014 [Computer program]
-
- Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Roozeboom 2012
-
- Roozeboom MH, Arits AH, Nelemans PJ, Kelleners‐Smeets NW. Overall treatment success after treatment of primary superficial basal cell carcinoma: a systematic review and meta‐analysis of randomized and nonrandomized trials. British Journal of Dermatology 2012;167(4):733‐56. [PUBMED: 22612571] - PubMed
Roozeboom 2016
-
- Roozeboom MH, Arits AH, Mosterd K, Sommer A, Essers BA, Rooij MJ, et al. Three‐year follow‐up results of photodynamic therapy vs. imiquimod vs. fluorouracil for treatment of superficial basal cell carcinoma: a single‐blind, noninferiority, randomized controlled trial. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2016;136(8):1568‐74. [PUBMED: 27113429] - PubMed
Royal College of Pathologists 2014
-
- Royal College of Pathologists. Standards and datasets for reporting cancers. Dataset for the histological reporting of primary invasive cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma and regional lymph nodes. www.rcpath.org/Resources/RCPath/Migrated%20Resources/Documents/G/G124_Da.... London: Royal College of Pathologists, (accessed 19 May 2015).
Rutjes 2005
-
- Rutjes AW, Reitsma JB, Vandenbroucke JP, Glas AS, Bossuyt PM. Case‐control and two‐gate designs in diagnostic accuracy studies. Clinical Chemistry 2005;51(8):1335‐41. [PUBMED: 15961549] - PubMed
Rutjes 2006
Sekulic 2012
Smeets 2004
-
- Smeets NW, Krekels GA, Ostertag JU, Essers BA, Dirksen CD, Nieman FH, et al. Surgical excision vs Mohs' micrographic surgery for basal‐cell carcinoma of the face: randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2004;364(9447):1766‐72. [PUBMED: 15541449] - PubMed
Sobarun 2015
-
- Sobarun P. Reflectance confocal microscopy. www.dermnetnz.org/topics/reflectance‐confocal‐microscopy/ (accessed 18 May 2017).
Sober 1979
-
- Sober AJ, Fitzpatrick TB, Mihm MC, Wise TG, Pearson BJ, Clark WH, et al. Early recognition of cutaneous melanoma. JAMA 1979;242(25):2795‐9. [PUBMED: 501893] - PubMed
Stratigos 2015
-
- Stratigos A, Garbe C, Lebbe C, Malvehy J, Marmol V, Pehamberger H, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of invasive squamous cell carcinoma of the skin: European consensus‐based interdisciplinary guideline. European Journal of Cancer 2015;51(14):1989‐2007. [PUBMED: 26219687] - PubMed
Takwoingi 2013
-
- Takwoingi Y, Leeflang MM, Deeks JJ. Empirical evidence of the importance of comparative studies of diagnostic test accuracy. Annals of Internal Medicine 2013;158(7):544‐54. [PUBMED: 23546566] - PubMed
Takwoingi 2017
Thomas 1998
-
- Thomas L, Tranchand P, Berard F, Secchi T, Colin C, Moulin G. Semiological value of ABCDE criteria in the diagnosis of cutaneous pigmented tumors. Dermatology 1998;197(1):11‐7. [PUBMED: 9693179] - PubMed
van Loo 2014
-
- Loo E, Mosterd K, Krekels GA, Roozeboom MH, Ostertag JU, Dirksen CD, et al. Surgical excision versus Mohs' micrographic surgery for basal cell carcinoma of the face: a randomised clinical trial with 10 year follow‐up. European Journal of Cancer 2014;50(17):3011‐20. [PUBMED: 25262378] - PubMed
Verkouteren 2017
Walker 2006
-
- Walker P, Hill D. Surgical treatment of basal cell carcinomas using standard postoperative histological assessment. Australasian Journal of Dermatology 2006;47(1):1‐12. [PUBMED: 16405477] - PubMed
Walter 2012
Wells 2012
-
- Wells R, Gutkowicz‐Krusin D, Veledar E, Toledano A, Chen SC. Comparison of diagnostic and management sensitivity to melanoma between dermatologists and MelaFind: a pilot study. Archives of Dermatology 2012;148(9):1083‐4. [PUBMED: 22986873] - PubMed
Whiting 2011
-
- Whiting PF, Rutjes AW, Westwood ME, Mallett S, Deeks JJ, Reitsma JB, et al. QUADAS‐2: a revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Annals of Internal Medicine 2011;155(8):529‐36. [PUBMED: 22007046] - PubMed
WHO 2003
-
- World Health Organization. INTERSUN: the Global UV Project. A guide and compendium. www.who.int/uv/publications/en/Intersunguide.pdf. Geneva: World Health Organisation, (accessed 20 May 2015).
Williams 2017
-
- Williams HC, Bath‐Hextall F, Ozolins M, Armstrong SJ, Colver GB, Perkins W, et al. Surgery versus 5% imiquimod for nodular and superficial basal cell carcinoma: 5‐year results of the SINS randomized controlled trial. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2017;137(3):614‐9. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jid.2016.10.019; PUBMED: 27932240] - DOI - PubMed
Wong 2017
Zak‐Prelich 2004
-
- Zak‐Prelich M, Narbutt J, Sysa‐Jedrzejowska A. Environmental risk factors predisposing to the development of basal cell carcinoma. Dermatologic Surgery 2004;30(2 Pt 2):248‐52. [PUBMED: 14871217] - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Dinnes 2015a
-
- Dinnes J, Wong KY, Gulati A, Chuchu N, Leonardi‐Bee J, Bayliss SE, et al. Tests to assist in the diagnosis of keratinocyte skin cancers in adults: a generic protocol. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2015, Issue 10. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD011901] - DOI
Dinnes 2015b
-
- Dinnes J, Matin RN, Moreau JF, Patel L, Chan SA, Wong KY, et al. Tests to assist in the diagnosis of cutaneous melanoma in adults: a generic protocol. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2015, Issue 10. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD011902] - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

