Exfoliative cytology for diagnosing basal cell carcinoma and other skin cancers in adults
- PMID: 30521689
- PMCID: PMC6517175
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD013187
Exfoliative cytology for diagnosing basal cell carcinoma and other skin cancers in adults
Abstract
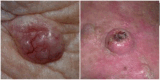
Background: Early accurate detection of all skin cancer types is essential to guide appropriate management, reduce morbidity and improve survival. Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is usually localised to the skin but has potential to infiltrate and damage surrounding tissue, while cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC) and melanoma have a much higher potential to metastasise and ultimately lead to death. Exfoliative cytology is a non-invasive test that uses the Tzanck smear technique to identify disease by examining the structure of cells obtained from scraped samples. This simple procedure is a less invasive diagnostic test than a skin biopsy, and for BCC it has the potential to provide an immediate diagnosis that avoids an additional clinic visit to receive skin biopsy results. This may benefit patients scheduled for either Mohs micrographic surgery or non-surgical treatments such as radiotherapy. A cytology scrape can never give the same information as a skin biopsy, however, so it is important to better understand in which skin cancer situations it may be helpful.
Objectives: To determine the diagnostic accuracy of exfoliative cytology for detecting basal cell carcinoma (BCC) in adults, and to compare its accuracy with that of standard diagnostic practice (visual inspection with or without dermoscopy). Secondary objectives were: to determine the diagnostic accuracy of exfoliative cytology for detecting cSCC, invasive melanoma and atypical intraepidermal melanocytic variants, and any other skin cancer; and for each of these secondary conditions to compare the accuracy of exfoliative cytology with visual inspection with or without dermoscopy in direct test comparisons; and to determine the effect of observer experience.
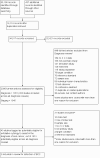
Search methods: We undertook a comprehensive search of the following databases from inception up to August 2016: Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials; MEDLINE; Embase; CINAHL; CPCI; Zetoc; Science Citation Index; US National Institutes of Health Ongoing Trials Register; NIHR Clinical Research Network Portfolio Database; and the World Health Organization International Clinical Trials Registry Platform. We also studied the reference lists of published systematic review articles.
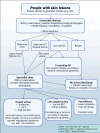
Selection criteria: Studies evaluating exfoliative cytology in adults with lesions suspicious for BCC, cSCC or melanoma, compared with a reference standard of histological confirmation.
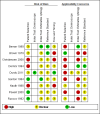
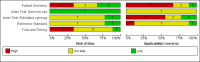
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently extracted all data using a standardised data extraction and quality assessment form (based on QUADAS-2). Where possible we estimated summary sensitivities and specificities using the bivariate hierarchical model.
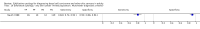
Main results: We synthesised the results of nine studies contributing a total of 1655 lesions to our analysis, including 1120 BCCs (14 datasets), 41 cSCCs (amongst 401 lesions in 2 datasets), and 10 melanomas (amongst 200 lesions in 1 dataset). Three of these datasets (one each for BCC, melanoma and any malignant condition) were derived from one study that also performed a direct comparison with dermoscopy. Studies were of moderate to poor quality, providing inadequate descriptions of participant selection, thresholds used to make cytological and histological diagnoses, and blinding. Reporting of participants' prior referral pathways was particularly poor, as were descriptions of the cytodiagnostic criteria used to make diagnoses. No studies evaluated the use of exfoliative cytology as a primary diagnostic test for detecting BCC or other skin cancers in lesions suspicious for skin cancer. Pooled data from seven studies using standard cytomorphological criteria (but various stain methods) to detect BCC in participants with a high clinical suspicion of BCC estimated the sensitivity and specificity of exfoliative cytology as 97.5% (95% CI 94.5% to 98.9%) and 90.1% (95% CI 81.1% to 95.1%). respectively. When applied to a hypothetical population of 1000 clinically suspected BCC lesions with a median observed BCC prevalence of 86%, exfoliative cytology would miss 21 BCCs and would lead to 14 false positive diagnoses of BCC. No false positive cases were histologically confirmed to be melanoma. Insufficient data are available to make summary statements regarding the accuracy of exfoliative cytology to detect melanoma or cSCC, or its accuracy compared to dermoscopy.
Authors' conclusions: The utility of exfoliative cytology for the primary diagnosis of skin cancer is unknown, as all included studies focused on the use of this technique for confirming strongly suspected clinical diagnoses. For the confirmation of BCC in lesions with a high clinical suspicion, there is evidence of high sensitivity and specificity. Since decisions to treat low-risk BCCs are unlikely in practice to require diagnostic confirmation given that clinical suspicion is already high, exfoliative cytology might be most useful for cases of BCC where the treatments being contemplated require a tissue diagnosis (e.g. radiotherapy). The small number of included studies, poor reporting and varying methodological quality prevent us from drawing strong conclusions to guide clinical practice. Despite insufficient data on the use of cytology for cSCC or melanoma, it is unlikely that cytology would be useful in these scenarios since preservation of the architecture of the whole lesion that would be available from a biopsy provides crucial diagnostic information. Given the paucity of good quality data, appropriately designed prospective comparative studies may be required to evaluate both the diagnostic value of exfoliative cytology by comparison to dermoscopy, and its confirmatory value in adequately reported populations with a high probability of BCC scheduled for further treatment requiring a tissue diagnosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Lavinia Ferrante di Ruffano: none known. Jac Dinnes: none known. Naomi Chuchu: none known. Susan E Bayliss: none known. Yemisi Takwoingi: none known. Clare Davenport: none known. Rubeta N Matin: "my institution received a grant for a Barco NV commercially sponsored study to evaluate digital dermoscopy in the skin cancer clinic. My institution also received Oxfordshire Health Services Research Charitable Funds for carrying out a study of feasibility of using the Skin Cancer Quality of Life Impact Tool (SCQOLIT) in non melanoma skin cancer. I have received royalties for the Oxford Handbook of Medical Dermatology (Oxford University Press) and payment from the UK Photopheresis Society for a lecture on cutaneous graft versus host disease (October 2017). I have received payment from Public Health England for the "Be Clear on Cancer" skin cancer report. I have no conflicts of interest to declare that directly relate to the publication of this work." Colette O'Sullivan: none known. Derek Roskell: none known. Jonathan J Deeks: none known. Hywel C Williams is the director of the NIHR HTA Programme. HTA is part of the NIHR, which also supports the NIHR systematic reviews programme from which this work is funded.
Figures





















References
References to studies included in this review
Berner 1999 {published data only}
-
- Berner A, Soler A, Warloe T. Skin scrape cytology in the diagnosis of nodular basal cell carcinoma for treatment by photodynamic therapy. Acta Dermato‐venereologica 1999;79(2):147‐9. [PUBMED: 10228637] - PubMed
Brown 1979 {published data only}
Christensen 2008 {published data only}
-
- Christensen E, Bofin A, Guðmundsdóttir I, Skogvoll E. Cytological diagnosis of basal cell carcinoma and actinic keratosis, using Papanicolaou and May–Grunwald–Giemsa stained cutaneous tissue smear. Cytopathology 2008;19(5):316‐22. [DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2303.2007.00483.x; PUBMED: 17916094] - DOI - PubMed
Derrick 1994 {published data only}
-
- Derrick EK, Smith R, Melcher DH, Morrison EA, Kirkham N, Darley CR. The use of cytology in the diagnosis of basal cell carcinoma. British Journal of Dermatology 1994;130(5):561‐3. [PUBMED: 8204464] - PubMed
Durdu 2011 {published data only}
-
- Durdu M, Baba M, Seckin D. Dermatoscopy versus Tzanck smear test: a comparison of the value of two tests in the diagnosis of pigmented skin lesions. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2011;65(5):972‐82. [ER4:15465910; PUBMED: 21565420] - PubMed
Gordon 1984 {published data only}
-
- Gordon LA, Orell SR. Evaluation of cytodiagnosis of cutaneous basal cell carcinoma. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 1984;11(6):1082‐6. [ER4:21450608; PUBMED: 6512053] - PubMed
Nauth 1988 {published data only}
-
- Nauth HF, Gizycki‐Nienhaus B. Cytodiagnosis of benign, precancerous and malignant skin changes. Zeitschrift fur Hautkrankheiten 1988;63(5):430‐8. [ER4:21450629; PUBMED: 3407259] - PubMed
Powell 2000 {published data only}
-
- Powell CR, Menon G, Harris AJ. Cytological examination or basal cell carcinoma ‐ a useful tool for diagnosis?. British Journal of Dermatology 2000;143(Suppl 57):71.
Ruocco 1992 {published data only}
-
- Ruocco V. Reliability of cytodiagnosis in basalioma [Attendibilità della diagnosi citologica di basalioma]. Giornale Italiano di Dermatologia e Venereologia 1992;127(1‐2):23‐9. [EMBASE: 22118929; ER4:21450638]
References to studies excluded from this review
Baba 2010 {published data only}
-
- Baba M, Durdu M, Seckin D. A useful alternative approach for the treatment of well‐demarcated Basal cell carcinoma: surgical excision and margin control with Tzanck smear test. Dermatologic Surgery 2010;36(5):659‐64. - PubMed
Bakis 2004 {published data only}
-
- Bakis S, Irwig L, Wood G, Wong D. Exfoliative cytology as a diagnostic test for basal cell carcinoma: a meta‐analysis. British Journal of Dermatology 2004;150(5):829‐36. [PUBMED: 15149493] - PubMed
Barton 1996 {published data only}
-
- Barton K, Curling OM, Paridaens AD, Hungerford JL. The role of cytology in the diagnosis of periocular basal cell carcinomas. Ophthalmic Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 1996;12(3):190‐195. [ER4:21450594] - PubMed
Berardi 1992 {published data only}
-
- Berardi P, Arcangeli F. The tape stripping toluidine blue (TSTB) method in the diagnosis of malignant melanoma: an investigator‐blind study. Melanoma Research 1992;2(2):93‐9. - PubMed
Bilen 2000 {published data only}
-
- Bilen N, Dal H, Kaur AC. Scraping cytology in the diagnosis of malignant squamous neoplasms of the skin. Acta Cytologica 2000;44(1):101‐3. - PubMed
Bocking 1987 {published data only}
-
- Böcking A, Schunck K, Auffermann W. Exfoliative–cytologic diagnosis of basal–cell–carcinoma, with the use of DNA image cytometry as a diagnostic aid. Acta Cytologica 1987;31(2):143‐9. - PubMed
David 1971 {published data only}
-
- David M, Esanu J G, Filip Z, Glavan II. Cytodiagnosis as an examination technic in the diagnosis of eye neoplasms. Klinische Monatsblatter fur Augenheilkunde 1971;158(5):633‐45. - PubMed
Eryilmaz 2014 {published data only}
-
- Eryilmaz A, Durdu M, Baba M, Yildirim FE. Diagnostic reliability of the Tzanck smear in dermatologic diseases. International Journal of Dermatology 2014;53(2):178‐86. - PubMed
Hajdu 1973 {published data only}
-
- Hajdu SI, Savino A. Cytologic diagnosis of malignant melanoma. Acta Cytologica 1973;17(4):320‐7. - PubMed
Hatvani 1974 {published data only}
-
- Hatvani I, Jako J. Contribution to cytodiagnosis of malignant melanoma. Klinische Monatsblatter fur Augenheilkunde 1974;165(3):452‐7. - PubMed
Hering 1970 {published data only}
-
- Hering H. Value of cytodiagnosis in malignant melanoma. Dermatologische Monatsschrift 1970;156(5):385‐91. - PubMed
Jakasa 1976 {published data only}
-
- Jakasa V, Popovic S, Nola P, Maricic Z, Mihajlovic L. Cytologic diagnosis of malignant melanoma. Lijecnicki Vjesnik 1976;98(6):323‐7. - PubMed
Korabiec 1977 {published data only}
-
- Korabiec M. Value of cytological studies in the diagnosis of skin neoplasms. Annales Academiae Medicae Stetinensis 1977;23:351‐68. - PubMed
Melek 1970 {published data only}
-
- Melek M, Jahoda E. The value of smear technic for cytologic diagnosis of malignant tumors. Osterreichische Zeitschrift fur Erforschung und Bekampfung der Krebskrankheit 1970;25(5):325‐41. - PubMed
Norris 2008 {published data only}
-
- Norris P. Cytological diagnosis of basal cell carcinoma and actinic keratosis, using Papanicolaou and May‐Grunwald‐Giemsa stained cutaneous tissue smear. Cytopathology 2008;19(5):333‐4; author reply 334. - PubMed
Oram 1997 {published data only}
-
- Oram Y, Turhan O, Aydin NE. Diagnostic value of cytology in basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas. International Journal of Dermatology 1997;36(2):156‐7. [PUBMED: 9109022] - PubMed
Ozden 2013 {published data only}
-
- Ozden MG, Maier T, Bek Y, Ruzicka T, Berking C. Cytodiagnosis of erosive melanoma and basal cell carcinoma of the skin using cutaneous tissue smear. Clinical & Experimental Dermatology 2013;38(3):251‐61. - PubMed
Rojo 1998 {published data only}
-
- García Rojo B, García Solano Jo, Sánchez Sánchez C, Montalbán Romero S, Ortega VV, Pérez‐Guillermo M. On the limited value of fine‐needle aspiration for the diagnosis of benign melanocytic proliferations of the skin. Diagnostic Cytopathology 1998;19(6):441‐5. - PubMed
Scanagatta 1981 {published data only}
-
- Scanagatta A. Cytological diagnosis of basal cell carcinoma. Rivista di Patologia Clinica e Sperimentale 1981;21:89‐93.
Schmid‐Wendtner 1999 {published data only}
-
- Schmid‐Wendtner MH, Worle B, Volkenandt M. Rapid diagnosis of clinically atypical basal cell carcinoma by cytomorphology. British Journal of Dermatology 1999;141(4):761‐2. - PubMed
Sharifi 2007 {published data only}
-
- Sharifi N, Yazdanpanah MJ. Cytodiagnosis of cutaneous basal and squamous cell carcinoma. Iranian Journal of Pathology 2007;97(2):97‐9.
Spinowitz 1986 {published data only}
-
- Spinowitz A, Goldsmith BA. Evaluation of cytodiagnosis of cutaneous basal cell carcinoma. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 1986;14(5 Pt 1):843‐4. - PubMed
Strokowska 1981 {published data only}
-
- Strokowska M. Cytological studies of basocellular epithelioma. Przeglad Dermatologiczny 1981;68(1):17‐25. - PubMed
Tzanck 1951 {published data only}
-
- Tzanck A, Aron‐Brunetiere R, Melki G. Cytodiagnosis of malignant melanomas. Acta Unio Internationalis Contra Cancrum 1951;7(4):722‐6. - PubMed
Urbach 1957 {published data only}
-
- Urbach F, Burke EM, Traenkle HL. Cytodiagnosis of cutaneous malignancy. AMA Archives of Dermatology 1957;76(3):343‐50. - PubMed
Vakhturova 1995 {published data only}
-
- Vakhturova ZM, Sadnikova NA, Levina SI, Chibezova AA. Possibilities of the cytological method in intraoperative diagnosis of pigmented tumors of the skin [Vozmozhnosti tsitologicheskogo metoda issledovaniia pri intraoperatsionnoi diagnostike nekotorykh pigmentnykh opukholei kozhi]. Klinicheskaia Laboratornaia Diagnostika 1995;5:4‐6. [PUBMED: 7582776] - PubMed
Vega‐Memije 2000 {published data only}
-
- Vega‐Memije E, Larios NM, Waxtein LM, Dominguez‐Soto L. Cytodiagnosis of cutaneous basal and squamous cell carcinoma. International Journal of Dermatology 2000;39(2):116‐20. - PubMed
Veselovskaia 1984 {published data only}
-
- Veselovskaia LP, Semavin IE, Timofeev BIa, Mikhailova NA, Gerasimova OB. Cytomorphological characteristics of basalioma based on data from outpatient observations [Tsitomorfologicheskie osobennosti bazaliomy na materiale ambulatornogo nabliudeniia]. Laboratornoe Delo 1984;4:209‐11. [PUBMED: 6202938] - PubMed
Viglioglia 1955 {published data only}
-
- Viglioglia PA, Viglioglia J. Immediate cytodiagnosis in dermatology. Prensa Medica Argentina 1955;42(45):3422‐30. - PubMed
von Gizycki‐Nienhaus 1992 {published data only}
-
- Gizycki‐Nienhaus B, Kaudewitz P. Cytologic aspects of the differential diagnosis of basalioma. Hautarzt 1992;43(10):629‐33. - PubMed
Yu 2005 {published data only}
-
- Yu XM, Wang WD, Zhang CH, Huang SF. Cytopathological scrape examination of superficial lesions of skin and mucosal membrane‐‐a cytological and histological comparative study of 148 cases. Chung‐Hua Ping Li Hsueh Tsa Chih [Chinese Journal of Pathology] 2005;34(10):637‐40. - PubMed
Additional references
ACIM 2017
-
- Australian Cancer Database. Melanoma of the skin for Australia (ICD10 C43). Australian Institute of Health and Welfare (AIHW) 2017 Australian Cancer Incidence and Mortality (ACIM) books (www.aihw.gov.au/acim‐books/). Canberra: Australian Institute of Health and Welfare, 2017.
Alam 2001
-
- Alam M, Ratner D. Cutaneous squamous‐cell carcinoma. New England Journal of Medicine 2001;344(13):975‐83. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Argenziano 1998
-
- Argenziano G, Fabbrocini G, Carli P, Giorgi V, Sammarco E, Delfino M. Epiluminescence microscopy for the diagnosis of doubtful melanocytic skin lesions. Comparison of the ABCD rule of dermatoscopy and a new 7‐point checklist based on pattern analysis. Archives of Dermatology 1998;134(12):1563‐70. [PUBMED: 9875194] - PubMed
Argenziano 2012
-
- Argenziano G, Albertini G, Castagnetti F, Pace B, Lernia V, Longo C, et al. Early diagnosis of melanoma: what is the impact of dermoscopy?. Dermatologic Therapy 2012;25(5):403‐9. [PUBMED: 23046019] - PubMed
Arits 2013
-
- Arits AH, Mosterd K, Essers BA, Spoorenberg E, Sommer A, Rooij MJ, et al. Photodynamic therapy versus topical imiquimod versus topical fluorouracil for treatment of superficial basal‐cell carcinoma: a single blind, non‐inferiority, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncology 2013;14(7):647‐54. [DOI: 10.1016/S1470-2045(13)70143-8; PUBMED: 23683751] - DOI - PubMed
Arnold 2014
-
- Arnold M, Holterhues C, Hollestein LM, Coebergh JW, Nijsten T, Pukkala E, et al. Trends in incidence and predictions of cutaneous melanoma across Europe up to 2015. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology : JEADV 2014;28(9):1170‐8. [PUBMED: 23962170] - PubMed
Baena 2017
-
- Baena A, Guevara E, Almonte M, Arias‐Stella J, Sasieni P, Sanchez GI. Factors related to inter‐observer reproducibility of conventional Pap smear cytology: a multilevel analysis of smear and laboratory characteristics. Cytopathology 2017;28(3):192‐202. [PUBMED: 28029192] - PubMed
Balch 2001
-
- Balch CM, Soong SJ, Gershenwald JE, Thompson JF, Reintgen DS, Cascinelli N, et al. Prognostic factors analysis of 17,600 melanoma patients: validation of the American Joint Committee on Cancer melanoma staging system. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2001;19(16):3622‐34. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Balch 2009
Baldursson 1993
-
- Baldursson B, Sigurgeirsson B, Lindelof B. Leg ulcers and squamous cell carcinoma. An epidemiological study and a review of the literature. Acta Dermato‐Venereologica 1993;73(3):171‐4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Barr 1984
-
- Barr RJ. Cutaneous cytology. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 1984;10(2 Pt 1):163‐80. [PUBMED: 6201514] - PubMed
Bath‐Hextall 2007a
-
- Bath‐Hextall F, Leonardi‐Bee J, Smith C, Meal A, Hubbard R. Trends in incidence of skin basal cell carcinoma. Additional evidence from a UK primary care database study. International Journal of Cancer 2007;121(9):2105‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Bath‐Hextall 2007b
Bath‐Hextall 2014
-
- Bath‐Hextall F, Ozolins M, Armstrong SJ, Colver GB, Perkins W, Miller PS, et al. Surgical excision versus imiquimod 5% cream for nodular and superficial basal‐cell carcinoma (SINS): a multicentre, non‐inferiority, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncology 2014;15(1):96‐105. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Batra 2002
-
- Batra RS, Kelley LC. A risk scale for predicting extensive subclinical spread of nonmelanoma skin cancer. Dermatologic Surgery 2002;28(2):107‐12; discussion 112. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Belbasis 2016
-
- Belbasis L, Stefanaki I, Stratigos AJ, Evangelou E. Non‐genetic risk factors for cutaneous melanoma and keratinocyte skin cancers: an umbrella review of meta‐analyses. Journal of Dermatological Science 2016;84(3):330‐9. [PUBMED: 27663092] - PubMed
Boring 1994
-
- Boring CC, Squires TS, Tong T, Montgomery S. Cancer statistics, 1994. CA: a Cancer Journal for Clinicians 1994;44(1):7‐26. [PUBMED: 8281473] - PubMed
Bossuyt 2015
Braun 2005
-
- Braun RP, Rabinovitz HS, Oliviero M, Kopf AW, Saurat JH. Dermoscopy of pigmented skin lesions. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2005;52(1):109‐21. [PUBMED: 15627088] - PubMed
Cancer Research UK 2017
-
- Cancer Research UK. Skin cancer statistics. www.cancerresearchuk.org/health‐professional/cancer‐statistics/statistic.... (accessed prior to 19 July 2017).
Canti 1984
-
- Canti G. Rapid cytologic diagnosis of skin lesions. In: Koss LG, Coleman DV editor(s). Advances in Clinical Cytology. New York: Masson Publishing, 1984:243‐66.
CCAAC Network 2008
-
- Cancer Council Australia & Australian Cancer Network. Basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma (and related lesions) ‐ a guide to clinical management in Australia. www.cancer.org.au/content/pdf/HealthProfessionals/ClinicalGuidelines/Bas.... Sydney: Cancer Council Australia & Australian Cancer Network, 2008 (accessed 19 May 2015).
Chandra 2009
-
- Chandra A, Cross P, Denton K, Giles T, Hemming D, Payne C, et al. The BSCC Code of Practice – exfoliative cytopathology (excluding gynaecological cytopathology). Cytopathology 2009;20(4):211‐23. [PUBMED: 19659955] - PubMed
Cho 2014
Chowdri 1996
-
- Chowdri NA, Darzi MA. Postburn scar carcinomas in Kashmiris. Burns 1996;22(6):477‐82. [PUBMED: 8884010] - PubMed
Chuchu 2018a
Chuchu 2018b
Dabski 1986
-
- Dabski K, Stoll HL Jr, Milgrom H. Squamous cell carcinoma complicating late chronic discoid lupus erythematosus. Journal of Surgical Oncology 1986;32(4):233‐7. [PUBMED: 3736067] - PubMed
Deeks 2005
-
- Deeks JJ, Macaskill P, Irwig L. The performance of tests of publication bias and other sample size effects in systematic reviews of diagnostic test accuracy was assessed. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2005;58(9):882‐93. [PUBMED: 16085191] - PubMed
Dinnes 2018a
Dinnes 2018b
Dinnes 2018c
Dinnes 2018d
Dinnes 2018e
Dinnes 2018f
Drew 2017
Drucker 2017
-
- Drucker A, Adam GP, Langberg V, Gazula A, Smith B, Moustafa F, et al. Treatments for Basal Cell and Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Skin. Comparative Effectiveness Reviews, No. 199. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US), 2017. - PubMed
Edwards 2016
Erdmann 2013
-
- Erdmann F, Lortet‐Tieulent J, Schuz J, Zeeb H, Greinert R, Breitbart EW, et al. International trends in the incidence of malignant melanoma 1953‐2008‐‐are recent generations at higher or lower risk?. International Journal of Cancer 2013;132(2):385‐400. [PUBMED: 22532371] - PubMed
Esteva 2017
EUCAN 2012
-
- EUCAN, International Agency for Research on Cancer. Malignant melanoma of skin: estimated incidence, mortality & prevalence for both sexes, 2012. eco.iarc.fr/eucan/Cancer.aspx?Cancer=20. International Agency for Research on Cancer, (accessed 29 July 2015).
Farmer 1996
-
- Farmer ER, Gonin R, Hanna MP. Discordance in the histopathologic diagnosis of melanoma and melanocytic nevi between expert pathologists. Human Pathology 1996;27(6):528‐31. [PUBMED: 8666360] - PubMed
Fasching 1989
-
- Fasching MC, Meland NB, Woods JE, Wolff BG. Recurrent squamous‐cell carcinoma arising in pilonidal sinus tract‐‐multiple flap reconstructions. Report of a case. Diseases of the Colon & Rectum 1989;32(2):153‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Ferlay 2015
-
- Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. International Journal of Cancer 2015;136(5):E359‐86. [PUBMED: 25220842] - PubMed
Ferrante di Ruffano 2018a
Ferrante di Ruffano 2018b
-
- Ferrante di Ruffano L, Takwoingi Y, Dinnes J, Chuchu N, Bayliss SE, Davenport C, et al. Computer‐assisted diagnosis techniques (dermoscopy and spectroscopy‐based) for diagnosing skin cancer in adults. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2018, Issue 12. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD013186] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Ferrara 2009
Firnhaber 2012
-
- Firnhaber JM. Diagnosis and treatment of basal cell and squamous cell carcinoma. American Family Physician 2012;86(2):161‐8. [PUBMED: 22962928] - PubMed
Fitzpatrick 1975
-
- Fitzpatrick TB. Soleil et peau. Journal de Médecine Esthétique 1975;2:33‐4.
Flohill 2013
Fortuno‐Mar 2013
-
- Fortuno–Mar A. Cytology. In: Baldi A, Pasquali P, Spugnini E editor(s). Skin Cancer. Current Clinical Pathology. New York: Humana Press, 2014:213‐9. [DOI: 10.1007/978-1-4614-7357-2_12] - DOI
Friedman 1985
-
- Friedman HI, Cooper PH, Wanebo HJ. Prognostic and therapeutic use of microstaging of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma of the trunk and extremities. Cancer 1985;56(5):1099‐105. [PUBMED: 4016700] - PubMed
Garbe 2016
-
- Garbe C, Peris K, Hauschild A, Saiag P, Middleton M, Bastholt L, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of melanoma. European consensus‐based interdisciplinary guideline ‐ update 2016. European Journal of Cancer 2016;63:201‐17. [PUBMED: 27367293] - PubMed
Garcia 2009
-
- Garcia C, Poletti E, Crowson AN. Basosquamous carcinoma. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2009;60(1):137‐43. [PUBMED: 19103364] - PubMed
Gershenwald 2017
-
- Gershenwald JE, Scolyer RA, Hess KR, Sondak VK, Long GV, Ross MI, et al. Melanoma staging: evidence‐based changes in the American Joint Committee on Cancer eighth edition cancer staging manual. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians 2017;67(6):472‐92. [DOI: 10.3322/caac.21409; PUBMED: 29028110] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Gordon 2013
-
- Gordon R. Skin cancer: an overview of epidemiology and risk factors. Seminars in Oncology Nursing 2013;29(3):160‐9. [PUBMED: 23958214] - PubMed
Gorlin 2004
-
- Gorlin RJ. Nevoid basal cell carcinoma (Gorlin) syndrome. Genetics in Medicine 2004;6(6):530‐9. [PUBMED: 15545751] - PubMed
Grachtchouk 2011
Griffin 2016
Griffiths 2005
-
- Griffiths RW, Suvarna SK, Stone J. Do basal cell carcinomas recur after complete conventional surgical excision?. British Journal of Plastic Surgery 2005;58(6):795‐805. [PUBMED: 16086990] - PubMed
Haenssle 2010
-
- Haenssle HA, Korpas B, Hansen‐Hagge C, Buhl T, Kaune KM, Rosenberger A, et al. Seven‐point checklist for dermatoscopy: performance during 10 years of prospective surveillance of patients at increased melanoma risk. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2010;62(5):785‐93. [PUBMED: 20226567] - PubMed
Hartevelt 1990
-
- Hartevelt MM, Bavinck JN, Kootte AM, Vermeer BJ, Vandenbroucke JP. Incidence of skin cancer after renal transplantation in the Netherlands. Transplantation 1990;49(3):506‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Hauschild 2014
-
- Hauschild A, Chen SC, Weichenthal M, Blum A, King HC, Goldsmith J, et al. To excise or not: impact of MelaFind on German dermatologists' decisions to biopsy atypical lesions. Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft 2014;12(7):606‐14. [PUBMED: 24944011] - PubMed
Hoorens 2016
-
- Hoorens I, Vossaert K, Pil L, Boone B, Schepper S, Ongenae K, et al. Total‐body examination vs lesion‐directed skin cancer screening. JAMA Dermatology 2016;152(1):27‐34. [PUBMED: 26466155] - PubMed
HPA and MelNet NZ 2014
-
- Health Promotion Agency and the Melanoma Network of New Zealand (MelNet). New Zealand Skin Cancer Primary Prevention and Early Detection Strategy 2014 to 2017. www.sunsmart.org.nz//sites/default/files/documents/NZ%20Skin%20Cancer%20.... Cancer Society of New Zealand, (accessed 29 May 2018).
Jensen 1999
-
- Jensen P, Hansen S, Moller B, Leivestad T, Pfeffer P, Geiran O, et al. Skin cancer in kidney and heart transplant recipients and different long‐term immunosuppressive therapy regimens. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 1999;40(2 Pt 1):177‐86. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kao 1986
-
- Kao GF. Carcinoma arising in Bowen's disease. Archives of Dermatology 1986;122(10):1124‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Karimkhani 2015
-
- Karimkhani C, Boyers LN, Dellavalle RP, Weinstock MA. It's time for "keratinocyte carcinoma" to replace the term "nonmelanoma skin cancer". Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2015;72(1):186‐7. [PUBMED: 25497921] - PubMed
Kasprzak 2015
Kelleners‐Smeets 2017
-
- Kelleners‐Smeets NW, Mosterd K, Nelemans PJ. Treatment of low‐risk basal cell carcinoma. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2017;137(3):539‐40. [PUBMED: 28235442] - PubMed
Kim 2014
-
- Kim DD, Tang JY, Ioannidis JP. Network geometry shows evidence sequestration for medical vs. surgical practices: treatments for basal cell carcinoma. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2014;67(4):391‐400. [PUBMED: 24491794] - PubMed
Kittler 2002
-
- Kittler H, Pehamberger H, Wolff K, Binder M. Diagnostic accuracy of dermoscopy. Lancet Oncology 2002;3(3):159‐65. Review. [PUBMED: 11902502] - PubMed
Lansbury 2010
Lansbury 2013
Lear 1997
Lear 2012
-
- Lear JT. Oral hedgehog‐pathway inhibitors for basal‐cell carcinoma. New England Journal of Medicine 2012;366(23):2225‐6. [PUBMED: 22670909] - PubMed
Linos 2009
Lister 1997
-
- Lister RK, Black MM, Calonje E, Burnand KG. Squamous cell carcinoma arising in chronic lymphoedema. British Journal of Dermatology 1997;136(3):384‐7. [PUBMED: 9115922] - PubMed
Lo 1991
-
- Lo JS, Snow SN, Reizner GT, Mohs FE, Larson PO, Hruza GJ. Metastatic basal cell carcinoma: report of twelve cases with a review of the literature. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 1991;24(5 Pt 1):715‐9. [PUBMED: 1869642] - PubMed
Lomas 2012
-
- Lomas A, Leonardi‐Bee J, Bath‐Hextall F. A systematic review of worldwide incidence of nonmelanoma skin cancer. British Journal of Dermatology 2012;166(5):1069‐80. [PUBMED: 22251204] - PubMed
Macaskill 2013
-
- Macaskill P, Gatsonis C, Deeks JJ, Harbord RM, Takwoingi Y. Chapter 10: Analysing and presenting results. In: Deeks JJ, Bossuyt PM, Gatsonis C (editors), Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Diagnostic Test Accuracy Version 1.0.0. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2013. Available from: srdta.cochrane.org. The Cochrane Collaboration.
Madan 2010
-
- Madan V, Lear JT, Szeimies RM. Non‐melanoma skin cancer. Lancet 2010;375(9715):673‐85. [PUBMED: 20171403] - PubMed
Maia 1995
-
- Maia M, Proenca NG, Moraes JC. Risk factors for basal cell carcinoma: a case‐control study. Revista de Saude Publica 1995;29(1):27‐37. [PUBMED: 8525311] - PubMed
Maloney 1996
-
- Maloney ME. Arsenic in dermatology. Dermatologic Surgery 1996;22(3):301‐4. [PUBMED: 8599743] - PubMed
Malvehy 2014
-
- Malvehy J, Hauschild A, Curiel‐Lewandrowski C, Mohr P, Hofmann‐Wellenhof R, Motley R, et al. Clinical performance of the Nevisense system in cutaneous melanoma detection: an international, multicentre, prospective and blinded clinical trial on efficacy and safety. British Journal of Dermatology 2014;171(5):1099‐107. [PUBMED: 24841846] - PMC - PubMed
Marsden 2010
-
- Marsden JR, Newton‐Bishop JA, Burrows L, Cook M, Corrie PG, Cox NH, et al. BAD Guidelines: revised UK guidelines for the management of cutaneous melanoma 2010. British Journal of Dermatology 2010;163(2):238‐56. [PUBMED: 20608932] - PubMed
McCormack 1997
-
- McCormack CJ, Kelly JW, Dorevitch AP. Differences in age and body site distribution of the histological subtypes of basal cell carcinoma. A possible indicator of differing causes. Archives of Dermatology 1997;133(5):593‐6. [PUBMED: 9158412] - PubMed
McCusker 2014
-
- McCusker M, Basset‐Seguin N, Dummer R, Lewis K, Schadendorf D, Sekulic A, et al. Metastatic basal cell carcinoma: prognosis dependent on anatomic site and spread of disease. European Journal of Cancer 2014;50(4):774‐83. [PUBMED: 24412051] - PubMed
Mistry 2011
Moncrieff 2002
-
- Moncrieff M, Cotton S, Claridge E, Hall P. Spectrophotometric intracutaneous analysis: a new technique for imaging pigmented skin lesions. British Journal of Dermatology 2002;146(3):448‐57. [PUBMED: 11952545] - PubMed
Monheit 2011
-
- Monheit G, Cognetta AB, Ferris L, Rabinovitz H, Gross K, Martini M, et al. The performance of MelaFind: a prospective multicenter study. Archives of Dermatology 2011;147(2):188‐94. [PUBMED: 20956633] - PubMed
Motley 2009
-
- Motley RJ, Preston PW, Lawrence CM. Multi‐professional guidelines for the management of the patient with primary cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. www.bsds.org.uk/uploads/pdfs/SCCguide2009.pdf (accessed 15 November 2017).
Murali 2009
-
- Murali R, Loughman NT, McKenzie PR, Watson GF, Thompson JF, Scolyer RA. Cytological features of melanoma in exfoliative fluid specimens. Journal of Clinical Pathology 2009;62(7):638‐43. [PUBMED: 19561232] - PubMed
Musah 2013
-
- Musah A, Gibson JE, Leonardi‐Bee J, Cave MR, Ander EL, Bath‐Hextall F. Regional variations of basal cell carcinoma incidence in the U.K. using the Health Improvement Network database (2004‐10). British Journal of Dermatology 2013;169(5):1093‐9. [PUBMED: 23701520] - PubMed
Nart 2015
-
- Nart IF, Armayones SG, Medina FV, Orti MB, Orpinell XB. Basal cell carcinoma treated with ingenol mebutate. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2015;5(Suppl 1):AB180.
Newcombe 1998
-
- Newcombe RG. Two‐sided confidence intervals for the single proportion: comparison of seven methods. Statistics in Medicine 1998;17(8):857‐72. - PubMed
NICE 2010
-
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. NICE guidance on cancer services. Improving outcomes for people with skin tumours including melanoma (update): the management of low‐risk basal cell carcinomas in the community. www.nice.org.uk/guidance/csg8/resources/improving‐outcomes‐for‐people‐wi.... NICE, (accessed 27 November 2017).
NICE 2015a
-
- National Collaborating Centre for Cancer. Melanoma: assessment and management. www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng14. London: National Institute for Health and Care Excellence, (accessed prior to 19 July 2017).
NICE 2015b
-
- National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. Suspected cancer: recognition and referral [NG12]. www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng12. London: National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence, (accessed prior to 5 December 2017).
Norman 2009
-
- Norman G, Barraclough K, Dolovich L, Price D. Iterative diagnosis. BMJ 2009;339:b3490. [PUBMED: 19773326] - PubMed
O'Gorman 2014
-
- O'Gorman SM, Murphy GM. Photosensitizing medications and photocarcinogenesis. Photodermatology, Photoimmunology & Photomedicine 2014;30(1):8‐14. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Pasquali 2018
Rajpara 2009
-
- Rajpara SM, Botello AP, Townend J, Ormerod AD. Systematic review of dermoscopy and digital dermoscopy/artificial intelligence for the diagnosis of melanoma. British Journal of Dermatology 2009;161(3):591‐604. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Randle 1996
-
- Randle HW. Basal cell carcinoma. Identification and treatment of the high‐risk patient. Dermatologic Surgery 1996;22(3):255‐61. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
RevMan 2014 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Roozeboom 2012
-
- Roozeboom MH, Arits AH, Nelemans PJ, Kelleners‐Smeets NW. Overall treatment success after treatment of primary superficial basal cell carcinoma: a systematic review and meta‐analysis of randomized and nonrandomized trials. British Journal of Dermatology 2012;167(4):733‐56. - PubMed
Roozeboom 2016
-
- Roozeboom MH, Arits AH, Mosterd K, Sommer A, Essers BA, Rooij MJ, et al. Three‐year follow‐up results of photodynamic therapy vs. imiquimod vs. fluorouracil for treatment of superficial basal cell carcinoma: a single‐blind, noninferiority, randomized controlled trial. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2016;136(8):1568‐74. [PUBMED: 27113429] - PubMed
Rowe 1992
-
- Rowe DE, Carroll RJ, Day CL Jr. Prognostic factors for local recurrence, metastasis, and survival rates in squamous cell carcinoma of the skin, ear, and lip. Implications for treatment modality selection. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 1992;26(6):976‐90. [PUBMED: 1607418] - PubMed
Rozeman 2017
Ruocco 2011
-
- Ruocco E, Brunetti G, Vecchio M, Ruocco V. The practical use of cytology for diagnosis in dermatology. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology & Venereology 2011;25(2):125‐9. [PUBMED: 20553359] - PubMed
Russell 1999
-
- Russell EB, Carrington PR, Smoller BR. Basal cell carcinoma: a comparison of shave biopsy versus punch biopsy techniques in subtype diagnosis. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 1999;41(1):69‐71. [PUBMED: 10411414] - PubMed
Rutjes 2005
-
- Rutjes AW, Reitsma JB, Vandenbroucke JP, Glas AS, Bossuyt PM. Case‐control and two‐gate designs in diagnostic accuracy studies. Clinical Chemistry 2005;51(8):1335‐41. [PUBMED: 15961549] - PubMed
Shoo 2010
-
- Shoo BA, Sagebiel RW, Kashani‐Sabet M. Discordance in the histopathologic diagnosis of melanoma at a melanoma referral center. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2010;62(5):751‐6. [PUBMED: 20303612] - PubMed
Siegel 2015
-
- Siegel R, Miller K, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2015. CA: a Cancer Journal for Clinicians 2015;65(1):5‐29. [PUBMED: 25559415] - PubMed
SIGN 2014
-
- Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network (SIGN). Management of primary cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. www.sign.ac.uk/sign‐140‐management‐of‐primary‐cutaneous‐squamous‐cell‐ca... (accessed prior to 19 June 2018).
SIGN 2017
-
- Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network. Cutaneous melanoma. www.sign.ac.uk/sign‐146‐melanoma.html. Scotland: SIGN, (accessed prior to 19 July 2017).
Sladden 2009
Slater 2014a
-
- Slater D, Walsh M. Standards and datasets for reporting cancers: Dataset for the histological reporting of primary cutaneous malignant melanoma and regional lymph nodes, May 2014. www.rcpath.org/Resources/RCPath/Migrated%20Resources/Documents/G/G125_Da.... London: Royal College of Pathologists, (accessed 29 July 2015).
Slater 2014b
-
- Slater D, Walsh M, on behalf of the RCPath Working Group on Cancer Services. Dataset for the histological reporting of primary cutaneous basal cell carcinoma. Standards and datasets for reporting cancers, May 2014. www.rcpath.org/asset/53688094‐791E‐4AAA‐82CEC42C3CB65E35/. London: Royal College of Pathologists, (accessed 15 November 2017).
Slater 2014c
-
- Slater D, Walsh M, on behalf of the RCPath Working Group on Cancer Services. Dataset for the histological reporting of primary invasive cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma and regional lymph nodes. Standards and datasets for reporting cancers, May 2014. www.rcpath.org/asset/9C1D8F71‐5D3B‐4508‐8E6200F11E1F4A39/ (accessed 15 November 2017).
Smeets 2004
-
- Smeets NW, Krekels GA, Ostertag JU, Essers BA, Dirksen CD, Nieman FH, et al. Surgical excision vs Mohs' micrographic surgery for basal‐cell carcinoma of the face: randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2004;364(9447):1766‐72. [PUBMED: 15541449] - PubMed
Sober 1979
-
- Sober AJ, Fitzpatrick TB, Mihm MC, Wise TG, Pearson BJ, Clark WH, et al. Early recognition of cutaneous melanoma. JAMA 1979;242(25):2795‐9. [PUBMED: 501893] - PubMed
Stratigos 2015
-
- Stratigos A, Garbe C, Lebbe C, Malvehy J, Marmol V, Pehamberger H, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of invasive squamous cell carcinoma of the skin: European consensus‐based interdisciplinary guideline. European Journal of Cancer 2015;51(14):1989‐2007. [PUBMED: 26219687] - PubMed
Takwoingi 2013
-
- Takwoingi Y, Leeflang MM, Deeks JJ. Empirical evidence of the importance of comparative studies of diagnostic test accuracy. Annals of Internal Medicine 2013;158(7):544‐54. [PUBMED: 23546566] - PubMed
Telfer 2008
-
- Telfer NR, Colver GB, Morton CA, British Association of Dermatologists. Guidelines for the management of basal cell carcinoma. British Journal of Dermatology 2008;159(1):35‐48. [PUBMED: 18593385] - PubMed
Tzank 1949
-
- Tzanck A. Immediate cytodiagnostics in dermatology [Le cytodiagnostic immediate en dermatologie]. Bulletin De La Societe Francaise De Dermatologie Et De Syphiligraphie 1949;7:68‐76.
van Loo 2014
-
- Loo E, Mosterd K, Krekels GA, Roozeboom MH, Ostertag JU, Dirksen CD, et al. Surgical excision versus Mohs' micrographic surgery for basal cell carcinoma of the face: A randomised clinical trial with 10 year follow‐up. European Journal of Cancer 2014;50(17):3011‐20. - PubMed
Vega‐Memije 2000
-
- Vega‐Memije E, Loris NM, Waxtein LM, Dominguez‐Soto L. Cytodiagnosis of cutaneous basal and squamous cell carcinoma. International Journal of Dermatology 2000;39(2):116‐20. [PUBMED: 10692060] - PubMed
Verkouteren 2017
Walker 2006
-
- Walker P, Hill D. Surgical treatment of basal cell carcinomas using standard postoperative histological assessment. Australasian Journal of Dermatology 2006;47(1):1‐12. [PUBMED: 16405477] - PubMed
Wallace 2000
-
- Wallace VP, Bamber JC, Crawford DC, Ott RJ, Mortimer PS. Classification of reflectance spectra from pigmented skin lesions, a comparison of multivariate discriminant analysis and artificial neural networks. Physics in Medicine & Biology 2000;45(10):2859‐71. [DOI: 10.1088/0031-9155/45/10/309] - DOI - PubMed
Wallace 2000a
Walter 2012
Wells 2012
-
- Wells R, Gutkowicz‐Krusin D, Veledar E, Toledano A, Chen SC. Comparison of diagnostic and management sensitivity to melanoma between dermatologists and MelaFind: a pilot study. Archives of Dermatology 2012;148(9):1083‐4. [PUBMED: 22986873] - PubMed
Whiting 2011
-
- Whiting PF, Rutjes AW, Westwood ME, Mallett S, Deeks JJ, Reitsma JB, et al. QUADAS‐2: a revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Annals of Internal Medicine 2011;155(8):529‐36. [PUBMED: 22007046] - PubMed
WHO 2003
-
- World Health Organization. INTERSUN: The Global UV Project. A guide and compendium. www.who.int/uv/publications/en/Intersunguide.pdf. Geneva: World Health Organisation, 2003 (accessed 20 May 2015).
Williams 2017
-
- Williams HC, Bath‐Hextall F, Ozolins M, Armstrong SJ, Colver GB, Perkins W, et al. Surgery versus imiquimod for nodular and superficial basal cell carcinoma (SINS) study group. Surgery versus 5% imiquimod for nodular and superficial basal cell carcinoma: 5‐year results of the SINS randomized controlled trial. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2017;137(3):614‐9. [PUBMED: 27932240] - PubMed
Zak‐Prelich 2004
-
- Zak‐Prelich M, Narbutt J, Sysa‐Jedrzejowska A. Environmental risk factors predisposing to the development of basal cell carcinoma. Dermatologic Surgery 2004;30(2 Pt 2):248‐52. [PUBMED: 14871217] - PubMed
Zalaudek 2008
-
- Zalaudek I, Giacomel J, Cabo H, Stefani A, Ferrara G, Hofmann‐Wellenhof R, et al. Entodermoscopy: a new tool for diagnosing skin infections and infestations. Dermatology 2008;216(1):14‐23. [PUBMED: 18032894] - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Dinnes 2015a
-
- Dinnes J, Matin RN, Moreau JF, Patel L, Chan SA, Chuchu N, et al. Tests to assist in the diagnosis of cutaneous melanoma in adults: a generic protocol. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2015, Issue 10. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD011902] - DOI
Dinnes 2015b
-
- Dinnes J, Wong KY, Gulati A, Chuchu N, Leonardi‐Bee J, Bayliss SE, et al. Tests to assist in the diagnosis of keratinocyte skin cancers in adults: a generic protocol. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2015, Issue 10. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD011901] - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

