Computer-assisted diagnosis techniques (dermoscopy and spectroscopy-based) for diagnosing skin cancer in adults
- PMID: 30521691
- PMCID: PMC6517147
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD013186
Computer-assisted diagnosis techniques (dermoscopy and spectroscopy-based) for diagnosing skin cancer in adults
Abstract
Background: Early accurate detection of all skin cancer types is essential to guide appropriate management and to improve morbidity and survival. Melanoma and cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC) are high-risk skin cancers which have the potential to metastasise and ultimately lead to death, whereas basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is usually localised with potential to infiltrate and damage surrounding tissue. Anxiety around missing early curable cases needs to be balanced against inappropriate referral and unnecessary excision of benign lesions. Computer-assisted diagnosis (CAD) systems use artificial intelligence to analyse lesion data and arrive at a diagnosis of skin cancer. When used in unreferred settings ('primary care'), CAD may assist general practitioners (GPs) or other clinicians to more appropriately triage high-risk lesions to secondary care. Used alongside clinical and dermoscopic suspicion of malignancy, CAD may reduce unnecessary excisions without missing melanoma cases.
Objectives: To determine the accuracy of CAD systems for diagnosing cutaneous invasive melanoma and atypical intraepidermal melanocytic variants, BCC or cSCC in adults, and to compare its accuracy with that of dermoscopy.
Search methods: We undertook a comprehensive search of the following databases from inception up to August 2016: Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL); MEDLINE; Embase; CINAHL; CPCI; Zetoc; Science Citation Index; US National Institutes of Health Ongoing Trials Register; NIHR Clinical Research Network Portfolio Database; and the World Health Organization International Clinical Trials Registry Platform. We studied reference lists and published systematic review articles.
Selection criteria: Studies of any design that evaluated CAD alone, or in comparison with dermoscopy, in adults with lesions suspicious for melanoma or BCC or cSCC, and compared with a reference standard of either histological confirmation or clinical follow-up.
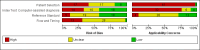
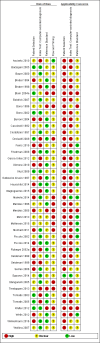
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently extracted all data using a standardised data extraction and quality assessment form (based on QUADAS-2). We contacted authors of included studies where information related to the target condition or diagnostic threshold were missing. We estimated summary sensitivities and specificities separately by type of CAD system, using the bivariate hierarchical model. We compared CAD with dermoscopy using (a) all available CAD data (indirect comparisons), and (b) studies providing paired data for both tests (direct comparisons). We tested the contribution of human decision-making to the accuracy of CAD diagnoses in a sensitivity analysis by removing studies that gave CAD results to clinicians to guide diagnostic decision-making.
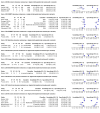
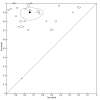
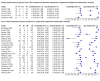
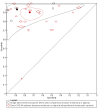
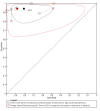
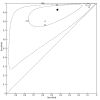
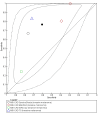
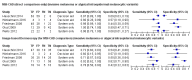
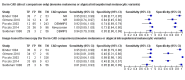
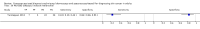
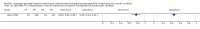
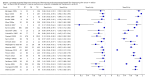
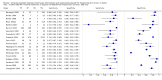
Main results: We included 42 studies, 24 evaluating digital dermoscopy-based CAD systems (Derm-CAD) in 23 study cohorts with 9602 lesions (1220 melanomas, at least 83 BCCs, 9 cSCCs), providing 32 datasets for Derm-CAD and seven for dermoscopy. Eighteen studies evaluated spectroscopy-based CAD (Spectro-CAD) in 16 study cohorts with 6336 lesions (934 melanomas, 163 BCC, 49 cSCCs), providing 32 datasets for Spectro-CAD and six for dermoscopy. These consisted of 15 studies using multispectral imaging (MSI), two studies using electrical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and one study using diffuse-reflectance spectroscopy. Studies were incompletely reported and at unclear to high risk of bias across all domains. Included studies inadequately address the review question, due to an abundance of low-quality studies, poor reporting, and recruitment of highly selected groups of participants.Across all CAD systems, we found considerable variation in the hardware and software technologies used, the types of classification algorithm employed, methods used to train the algorithms, and which lesion morphological features were extracted and analysed across all CAD systems, and even between studies evaluating CAD systems. Meta-analysis found CAD systems had high sensitivity for correct identification of cutaneous invasive melanoma and atypical intraepidermal melanocytic variants in highly selected populations, but with low and very variable specificity, particularly for Spectro-CAD systems. Pooled data from 22 studies estimated the sensitivity of Derm-CAD for the detection of melanoma as 90.1% (95% confidence interval (CI) 84.0% to 94.0%) and specificity as 74.3% (95% CI 63.6% to 82.7%). Pooled data from eight studies estimated the sensitivity of multispectral imaging CAD (MSI-CAD) as 92.9% (95% CI 83.7% to 97.1%) and specificity as 43.6% (95% CI 24.8% to 64.5%). When applied to a hypothetical population of 1000 lesions at the mean observed melanoma prevalence of 20%, Derm-CAD would miss 20 melanomas and would lead to 206 false-positive results for melanoma. MSI-CAD would miss 14 melanomas and would lead to 451 false diagnoses for melanoma. Preliminary findings suggest CAD systems are at least as sensitive as assessment of dermoscopic images for the diagnosis of invasive melanoma and atypical intraepidermal melanocytic variants. We are unable to make summary statements about the use of CAD in unreferred populations, or its accuracy in detecting keratinocyte cancers, or its use in any setting as a diagnostic aid, because of the paucity of studies.
Authors' conclusions: In highly selected patient populations all CAD types demonstrate high sensitivity, and could prove useful as a back-up for specialist diagnosis to assist in minimising the risk of missing melanomas. However, the evidence base is currently too poor to understand whether CAD system outputs translate to different clinical decision-making in practice. Insufficient data are available on the use of CAD in community settings, or for the detection of keratinocyte cancers. The evidence base for individual systems is too limited to draw conclusions on which might be preferred for practice. Prospective comparative studies are required that evaluate the use of already evaluated CAD systems as diagnostic aids, by comparison to face-to-face dermoscopy, and in participant populations that are representative of those in which the test would be used in practice.
Conflict of interest statement
Lavinia Ferrante di Ruffano: nothing to declare. Yemisi Takwoingi: nothing to declare. Jac Dinnes: nothing to declare. Naomi Chuchu: nothing to declare. Susan E Bayliss: nothing to declare. Clare Davenport: nothing to declare. Rubeta N Matin: "my institution received a grant for a Barco NV commercially sponsored study to evaluate digital dermoscopy in the skin cancer clinic. My institution also received Oxfordshire Health Services Research Charitable Funds for carrying out a study of feasibility of using the Skin Cancer Quality of Life Impact Tool (SCQOLIT) in non melanoma skin cancer. I have received royalties for the Oxford Handbook of Medical Dermatology (Oxford University Press). I have received payment from Public Health England for the "Be Clear on Cancer" skin cancer report. I have no conflicts of interest to declare that directly relate to the publication of this work." Kathie Godfrey: nothing to declare. Colette O'Sullivan: nothing to declare. Abha Gulati: nothing to declare. Sue Ann Chan: nothing to declare. Alana Durack: nothing to declare. Susan O'Connell: nothing to declare. Matthew D Gardiner: nothing to declare. Jeff Bamber: J Bamber has been a member of the advisory board of Michelson Diagnostics and has received payment from Cancer Research UK and the International Breast Ultrasound School and Queen Mary University of London for lectures given. He has received book royalties from John Wiley and Sons, and acknowledges funding from the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council, the NIHR Biomedical Research Centre and the Royal Marsden NHS Foundation Trust and Institute of Cancer Research, and the Cancer Research UK Imaging Centre Grant to the Institute of Cancer Research. There was no involvement of grant funders or other sponsors in the study whatsoever. J Bamber is the first named inventor on a patent jointly held by his institution (The Institute of Cancer Research) and The University of Bern. The priority date was 26 July 2012. The PCT publication date was 30 January 2014. A brief description of the invention is as follows: "A method of ultrasound and photoacoustic imaging in which image clutter is reduced, thus improving image quality and penetration depth, by using a localised vibration to tag true signals so as to discriminate them from false signals which occur from sources outside of the imaged region." Jonathan J Deeks: nothing to declare. Hywel C Williams: I am director of the NIHR HTA Programme. HTA is part of the NIHR which also supports the NIHR systematic reviews programme from which this work is funded.
Figures



































































References
References to studies included in this review
Ascierto 2010 {published data only}
Barzegari 2005 {published data only}
Bauer 2000 {published data only}
-
- Bauer P, Cristofolini P, Boi S, Burroni M, Dell'Eva G, Micciolo R, et al. Digital epiluminescence microscopy: usefulness in the differential diagnosis of cutaneous pigmentary lesions. A statistical comparison between visual and computer inspection. Melanoma Research 2000;10(4):345‐9. [ER4:15465861; PUBMED: 10985668] - PubMed
Binder 1994 {published data only}
-
- Binder M, Steiner A, Schwarz M, Knollmayer S, Wolff K, Pehamberger H. Application of an artificial neural network in epiluminescence microscopy pattern analysis of pigmented skin lesions: a pilot study. British Journal of Dermatology 1994;130(4):460‐5. [ER4:18375032; PUBMED: 8186110] - PubMed
Binder 1998 {published data only}
-
- Binder M, Kittler H, Seeber A, Steiner A, Pehamberger H, Wolff K. Epiluminescence microscopy‐based classification of pigmented skin lesions using computerized image analysis and an artificial neural network. Melanoma Research 1998;8(3):261‐6. [ER4:15465863; PUBMED: 9664148] - PubMed
Blum 2004a {published data only}
-
- Blum A, Luedtke H, Ellwanger U, Schwabe R, Rassner G, Garbe C. Digital image analysis for diagnosis of cutaneous melanoma. Development of a highly effective computer algorithm based on analysis of 837 melanocytic lesions. British Journal of Dermatology 2004;151(5):1029‐38. [ER4:15465866; PUBMED: 15541081] - PubMed
Boldrick 2007 {published data only}
-
- Boldrick JC, Layton CJ, Nguyen J, Swetter SM. Evaluation of digital dermoscopy in a pigmented lesion clinic: clinician versus computer assessment of malignancy risk. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2007;56(3):417‐21. [ER4:19728338; PUBMED: 17109995] - PubMed
Bono 1996 {published data only}
-
- Bono A, Tomatis S, Bartoli C, Cascinelli N, Clemente C, Cupeta C, et al. The invisible colours of melanoma. A telespectrophotometric diagnostic approach on pigmented skin lesions. European Journal of Cancer 1996;32(4):727‐9. [DOI: ; ER4:20569437] - PubMed
Bono 2002 {published data only}
-
- Bono A, Bartoli C, Cascinelli N, Lualdi M, Maurichi A, Moglia D, et al. Melanoma detection. A prospective study comparing diagnosis with the naked eye, dermatoscopy and telespectrophotometry. Dermatology 2002;205(4):362‐6. [ER4:15465870; PUBMED: 12444332] - PubMed
Burroni 2004 {published data only}
-
- Burroni M, Corona R, Dell'Eva G, Sera F, Bono R, Puddu P, et al. Melanoma computer‐assisted diagnosis: reliability and feasibility study. Clinical Cancer Research 2004;10(6):1881‐6. [ER4:15465878; PUBMED: 15041702] - PubMed
Cascinelli 1992 {published data only}
-
- Cascinelli N, Ferrario M, Bufalino R, Zurrida S, Galimberti V, Mascheroni L, et al. Results obtained by using a computerized image analysis system designed as an aid to diagnosis of cutaneous melanoma. Melanoma Research 1992;2(3):163‐70. [ER4:15465891; PUBMED: 1450670] - PubMed
Cristofolini 1997 {published data only}
-
- Cristofolini M, Bauer P, Boi S, Cristofolini P, Micciolo R, Sicher MC. Diagnosis of cutaneous melanoma: Accuracy of a computerized image analysis system (Skin View). Skin Research and Technology 1997;3(1):23‐7. [ER4:17941039; PUBMED: 27333169] - PubMed
Dreiseitl 2009 {published data only}
-
- Dreiseitl S, Binder M, Hable K, Kittler H. Computer versus human diagnosis of melanoma: evaluation of the feasibility of an automated diagnostic system in a prospective clinical trial. Melanoma Research 2009;19(3):180‐4. [ER4:15465907; PUBMED: 19369900] - PubMed
Ferris 2015 {published data only}
-
- Ferris LK, Harkes JA, Gilbert B, Winger DG, Golubets K, Akilov O, et al. Computer‐aided classification of melanocytic lesions using dermoscopic images. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2015;73(5):769‐76. [ER4:25012337; PUBMED: 26386631] - PubMed
Friedman 2008 {published data only}
-
- Friedman RJ, Gutkowicz‐Krusin D, Farber MJ, Warycha M, Schneider‐Kels L, Papastathis N, et al. The diagnostic performance of expert dermoscopists vs a computer‐vision system on small‐diameter melanomas. Archives of Dermatology 2008;144(4):476‐82. [ER4:15465921; PUBMED: 18427041] - PubMed
Garcia Uribe 2012 {published data only}
Gilmore 2010 {published data only}
-
- Gilmore S, Hofmann‐Wellenhof R, Soyer HP. A support vector machine for decision support in melanoma recognition. Experimental Dermatology 2010;19(9):830‐5. [ER4:15465935; PUBMED: 20629732] - PubMed
Glud 2009 {published data only}
-
- Glud M, Gniadecki R, Drzewiecki KT. Spectrophotometric intracutaneous analysis versus dermoscopy for the diagnosis of pigmented skin lesions: prospective, double‐blind study in a secondary reference centre. Melanoma Research 2009;19(3):176‐9. [ER4:18375045; PUBMED: 19319002] - PubMed
Gutkowicz Krusin 1997 {published data only}
-
- Gutkowicz‐Krusin D, Elbaum M, Szwaykowski P, Kopf AW. Can early malignant melanoma be differentiated from atypical melanocytic nevus by in vivo techniques? Part II. Automatic machine vision classification. Skin Research and Technology 1997;3(1):15‐22. [ER4:20569466; PUBMED: 27333168] - PubMed
Hauschild 2014 {published data only}
-
- Hauschild A, Chen SC, Weichenthal M, Blum A, King HC, Goldsmith J, et al. To excise or not: impact of MelaFind on German dermatologists' decisions to biopsy atypical lesions. Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft 2014;12(7):606‐14. [ER4:17941085; PUBMED: 24944011] - PubMed
Maglogiannis 2015 {published data only}
-
- Maglogiannis I, Delibasis KK. Enhancing classification accuracy utilizing globules and dots features in digital dermoscopy. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine 2015;118(2):124‐33. [ER4:25012309; PUBMED: 25540998] - PubMed
Malvehy 2014 {published data only}
-
- Malvehy J, Hauschild A, Curiel‐Lewandrowski C, Mohr P, Hofmann‐Wellenhof R, Motley R, et al. Clinical performance of the Nevisense system in cutaneous melanoma detection: An international, multicentre, prospective and blinded clinical trial on efficacy and safety. British Journal of Dermatology 2014;171(5):1099‐107. [PUBMED: 24841846] - PMC - PubMed
Menzies 1996 {published data only}
-
- Menzies SW, Ingvar C, Crotty KA, McCarthy WH. Frequency and morphologic characteristics of invasive melanomas lacking specific surface microscopic features. Archives of Dermatology 1996;132(10):1178‐82. [ER4:21450627; PUBMED: 8859028] - PubMed
Menzies 2005 {published data only}
-
- Menzies SW, Bischof L, Talbot H, Gutenev A, Avramidis M, Wong L, et al. The performance of SolarScan: an automated dermoscopy image analysis instrument for the diagnosis of primary melanoma.[Erratum appears in Arch Dermatol. 2006 May;142(5):558]. Archives of Dermatology 2005;141(11):1388‐96. [ER4:20569478; PUBMED: 16301386] - PubMed
Mohr 2013 {published data only}
-
- Mohr P, Birgersson U, Berking C, Henderson C, Trefzer U, Kemeny L, et al. Electrical impedance spectroscopy as a potential adjunct diagnostic tool for cutaneous melanoma. Skin Research and Technology 2013;19(2):75‐83. [PUBMED: 23350668] - PubMed
Mollersen 2015 {published data only}
-
- Mollersen K, Kirchesch H, Zortea M, Schopf TR, Hindberg K, Godtliebsen F. Computer‐aided decision support for melanoma detection applied on melanocytic and nonmelanocytic skin lesions: A comparison of two systems based on automatic analysis of dermoscopic images. BioMed Research International 2015;2015:579282. [ER4:25012302; PUBMED: 26693486] - PMC - PubMed
Monheit 2011 {published data only}
-
- Monheit G, Cognetta AB, Ferris L, Rabinovitz H, Gross K, Martini M, et al. The performance of MelaFind: a prospective multicenter study. Archives of Dermatology 2011;147(2):188‐94. [ER4:15466015; PUBMED: 20956633] - PubMed
Piccolo 2002 {published data only}
-
- Piccolo D, Ferrari A, Peris K, Diadone R, Ruggeri B, Chimenti S. Dermoscopic diagnosis by a trained clinician vs. a clinician with minimal dermoscopy training vs. computer‐assisted diagnosis of 341 pigmented skin lesions: a comparative study. British Journal of Dermatology 2002;147(3):481‐6. [ER4:15466057; PUBMED: 12207587] - PubMed
Piccolo 2014 {published data only}
-
- Piccolo D, Crisman G, Schoinas S, Altamura D, Peris K. Computer‐automated ABCD versus dermatologists with different degrees of experience in dermoscopy. European Journal of Dermatology 2014;24(4):477‐81. [ER4:17941089; PUBMED: 24721784] - PubMed
Rubegni 2002a {published data only}
-
- Rubegni P, Cevenini G, Burroni M, Perotti R, Dell'Eva G, Sbano P, et al. Automated diagnosis of pigmented skin lesions. International Journal of Cancer 2002;101(6):576‐80. [ER4:20569489; PUBMED: 12237900] - PubMed
Seidenari 1998 {published data only}
-
- Seidenari S, Pellacani G, Pepe P. Digital videomicroscopy improves diagnostic accuracy for melanoma. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 1998;39(2 Pt 1):175‐81. [ER4:15466116; PUBMED: 9704824] - PubMed
Seidenari 1999 {published data only}
-
- Seidenari S, Pellacani G, Giannetti A. Digital videomicroscopy and image analysis with automatic classification for detection of thin melanomas. Melanoma Research 1999;9(2):163‐71. [ER4:17940983; PUBMED: 10380939] - PubMed
Serrao 2006 {published data only}
-
- Serrao VV, Baptista J, Paris F, Lopes LC, Fidalgo A, Ferreira A. Digital dermoscopy. Review of 652 lesions analysed by the DANAOS system. Skin Cancer 2006;21(4):185‐98. [ER4:18375096]
Sgouros 2014 {published data only}
-
- Sgouros D, Lallas A, Julian Y, Rigopoulos D, Zalaudek I, Longo C, et al. Assessment of SIAscopy in the triage of suspicious skin tumours. Skin Research and Technology 2014;20(4):440‐4. [ER4:17941094; PUBMED: 24517201] - PubMed
Stanganelli 2005 {published data only}
-
- Stanganelli I, Brucale A, Calori L, Gori R, Lovato A, Magi S, et al. Computer‐aided diagnosis of melanocytic lesions. Anticancer Research 2005;25(6C):4577‐82. [ER4:15466126; PUBMED: 16334145] - PubMed
Terstappen 2013 {published data only}
-
- Terstappen K, Suurkula M, Hallberg H, Ericson MB, Wennberg AM. Poor correlation between spectrophotometric intracutaneous analysis and histopathology in melanoma and nonmelanoma lesions [Erratum appears in J Biomed Opt. 2013 Jun;18(6):069804]. Journal of Biomedical Optics 2013;18(6):061223. [ER4:15466138; PUBMED: 23296145] - PubMed
Tomatis 2003 {published data only}
-
- Tomatis S, Bono A, Bartoli C, Carrara M, Lualdi M, Tragni G, et al. Automated melanoma detection: multispectral imaging and neural network approach for classification. Medical Physics 2003;30(2):212‐21. [ER4:18375057; PUBMED: 12607839] - PubMed
Tomatis 2005 {published data only}
-
- Tomatis S, Carrara M, Bono A, Bartoli C, Lualdi M, Tragni G, et al. Automated melanoma detection with a novel multispectral imaging system: results of a prospective study. Physics in Medicine and Biology 2005;50(8):1675‐87. [ER4:17941003; PUBMED: 15815089] - PubMed
Walter 2012 {published data only}
Wells 2012 {published data only}
-
- Wells R, Gutkowicz‐Krusin D, Veledar E, Toledano A, Chen SC. Comparison of diagnostic and management sensitivity to melanoma between dermatologists and MelaFind: a pilot study. Archives of Dermatology 2012;148(9):1083‐4. [ER4:15466163; PUBMED: 22986873] - PubMed
Winkelmann 2016 {published data only}
-
- Winkelmann RR, Farberg AS, Tucker N, White R, Rigel DS. Enhancement of international dermatologists' pigmented skin lesion biopsy decisions following dermoscopy with subsequent integration of multispectral digital skin lesion analysis. Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology 2016;9(7):53‐5. [ER4:25701735; PUBMED: 27672411] - PMC - PubMed
Wollina 2007 {published data only}
-
- Wollina U, Burroni M, Torricelli R, Gilardi S, Dell'Eva G, Helm C, et al. Digital dermoscopy in clinical practise: a three‐centre analysis. Skin Research and Technology 2007;13(2):133‐42. [ER4:17941010; PUBMED: 17374053] - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Abbas 2010 {published data only}
-
- Abbas Q, Garcia IF, Rashid M. Automatic skin tumour border detection for digital dermoscopy using a new digital image analysis scheme. British Journal of Biomedical Science 2010;67(4):177‐83. - PubMed
Abbas 2011a {published data only}
-
- Abbas Q, Celebi ME, Fondon Garcia I, Rashid M. Lesion border detection in dermoscopy images using dynamic programming. Skin Research and Technology 2011;17(1):91‐100. [PUBMED: 21226876] - PubMed
Abbas 2011b {published data only}
-
- Abbas Q, Fondon I, Rashid M. Unsupervised skin lesions border detection via two‐dimensional image analysis. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine 2011;104(3):e1‐15. - PubMed
Abbas 2012 {published data only}
-
- Abbas Q, Celebi ME, Fondon I. Computer‐aided pattern classification system for dermoscopy images. Skin Research and Technology 2012;18(3):278‐89. - PubMed
Abbas 2013a {published data only}
-
- Abbas Q, Garcia IF, Emre Celebi M, Ahmad W, Mushtaq Q. Unified approach for lesion border detection based on mixture modeling and local entropy thresholding. Skin Research and Technology 2013;19(3):314‐9. - PubMed
Abbas 2013b {published data only}
-
- Abbas Q, Garcia IF, Emre Celebi M, Ahmad W, Mushtaq Q. A perceptually oriented method for contrast enhancement and segmentation of dermoscopy images. Skin Research and Technology 2013;19(1):e490‐7. - PubMed
Abuzaghleh 2015 {published data only}
Afonso 2012 {published data only}
-
- Afonso A, Silveira M. Hair detection in dermoscopic images using percolation. IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Magazine 2012;2012:4378‐81. [PUBMED: 23366897] - PubMed
Alfed 2015 {published data only}
Ali 2012 {published data only}
-
- Ali ARA, Deserno TM. A systematic review of automated melanoma detection in dermatoscopic images and its ground truth data. SPIE. Medical Imaging 2012: Image Perception, Observer Performance, and Technology Assessment. 29 February 2012; Vol. 8318. [DOI: 10.1117/12.912389] - DOI
Altamura 2008 {published data only}
-
- Altamura D, Avramidis M, Menzies SW. Assessment of the optimal interval for and sensitivity of short‐term sequential digital dermoscopy monitoring for the diagnosis of melanoma. Archives of Dermatology 2008;144(4):502‐6. - PubMed
Andreassi 1999 {published data only}
-
- Andreassi L, Perotti R, Rubegni P, Burroni M, Cevenini G, Biagioli M, et al. Digital dermoscopy analysis for the differentiation of atypical nevi and early melanoma: a new quantitative semiology. Archives of Dermatology 1999;135(12):1459‐65. - PubMed
Armengol 2011 {published data only}
-
- Armengol E. Classification of melanomas in situ using knowledge discovery with explained case‐based reasoning. Artificial Intelligence in Medicine 2011;51(2):93‐105. - PubMed
Arroyo 2011 {published data only}
-
- Arroyo JL, Zapirain BG, Zorrilla AM. Blue‐white veil and dark‐red patch of pigment pattern recognition in dermoscopic images using machine‐learning techniques. IEEE International Symposium on Signal Processing and Information Technology (ISSPIT), Bilbao. 2011:196‐201. [DOI: 10.1109/ISSPIT.2011.6151559] - DOI
Ballerini 2012 {published data only}
-
- Ballerini L, Fisher RB, Aldridge B, Rees J. Non‐melanoma skin lesion classification using colour image data in a hierarchical K‐NN classifier. 9th IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), Barcelona. 2012:358‐61. [DOI: 10.1109/ISBI.2012.6235558] - DOI
Barata 2012a {published data only}
-
- Barata C, Marques JS, Rozeira J. A system for the detection of pigment network in dermoscopy images using directional filters. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering 2012;59(10):2744‐54. - PubMed
Barata 2012b {published data only}
-
- Barata C, Marques JS, Rozeira J. A system for the automatic detection of pigment network. 9th IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), Barcelona. 2012:1651‐4. [DOI: 10.1109/ISBI.2012.6235894] - DOI
Barata 2013 {published data only}
-
- Barata C, Marques JS, Rozeira J. Evaluation of color based keypoints and features for the classification of melanomas using the bag‐of‐features model. Advances in Visual Computing. ISVC. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, 2013; Vol. 8033:40‐9. [DOI: 10.1007/978-3-642-41914-0_5] - DOI
Barata 2015a {published data only}
-
- Barata C, Celebi ME, Marques JS. Improving dermoscopy image classification using color constancy. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics 2015;19(3):1146‐52. - PubMed
Barata 2015b {published data only}
Barata 2015c {published data only}
Binder 2000 {published data only}
-
- Binder M, Kittler H, Dreiseitl S, Ganster H, Wolff K, Pehamberger H. Computer‐aided epiluminescence microscopy of pigmented skin lesions: the value of clinical data for the classification process. Melanoma Research 2000;10(6):556‐61. - PubMed
Bjerring 2001 {published data only}
-
- Bjerring P, Obitz ER, Cotton S. In vivo spectrophotometric evaluation of the skin tumours using a new skin chromophore imaging system SIAscope. Melanoma Research 2001;11:S180.
Blum 2004b {published data only}
-
- Blum A, Hofmann‐Wellenhof R, Luedtke H, Ellwanger U, Steins A, Roehm S, et al. Value of the clinical history for different users of dermoscopy compared with results of digital image analysis. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology : JEADV 2004;18(6):665‐9. [ER4:15465865; PUBMED: 15482291] - PubMed
Boden 2013 {published data only}
-
- Boden I, Nystrom J, Lundskog B, Zazo V, Geladi P, Lindholm‐Sethson B, et al. Non‐invasive identification of melanoma with near‐infrared and skin impedance spectroscopy. Skin Research and Technology 2013;19(1):e473‐8. - PubMed
Bono 1999 {published data only}
-
- Bono A, Tomatis S, Bartoli C, Tragni G, Radaelli G, Maurichi A, et al. The ABCD system of melanoma detection: a spectrophotometric analysis of the Asymmetry, Border, Color, and Dimension. Cancer 1999;85(1):72‐7. - PubMed
Borlu 2008 {published data only}
-
- Borlu M, Yüksel ME. Development of an image processing system for automatic melanoma diagnosis from dermoscopic images: preliminary study. Turkish Journal of Dermatology 2008;2(4):111‐5.
Brown 2000 {published data only}
-
- Brown N. Exploration of diagnostic techniques for malignant melanoma: an integrative review. Clinical Excellence for Nurse Practitioners 2000;4(5):263‐71. - PubMed
Carrara 2007 {published data only}
-
- Carrara M, Bono A, Bartoli C, Colombo A, Lualdi M, Moglia D, et al. Multispectral imaging and artificial neural network: mimicking the management decision of the clinician facing pigmented skin lesions. Physics in Medicine and Biology 2007;52(9):2599‐613. [ER4:20756747; PUBMED: 17440255] - PubMed
Celebi 2008 {published data only}
Chen 2003 {published data only}
Cheng 2012 {published data only}
-
- Cheng B, Stanley RJ, Stoecker WV, Hinton K. Automatic telangiectasia analysis in dermoscopy images using adaptive critic design. Skin Research and Technology 2012;18(4):389‐96. - PubMed
Cheng 2013 {published data only}
Christensen 2010 {published data only}
-
- Christensen JH, Soerensen MB, Linghui Z, Chen S, Jensen MO. Pre‐diagnostic digital imaging prediction model to discriminate between malignant melanoma and benign pigmented skin lesion. Skin Research and Technology 2010;16(1):98‐108. - PubMed
Claridge 1992 {published data only}
-
- Claridge E, Hall PN, Keefe M, Allen JP. Shape analysis for classification of malignant melanoma. Journal of Biomedical Engineering 1992;14(3):229‐34. - PubMed
Cukras 2013 {published data only}
-
- Cukras AR. On the comparison of diagnosis and management of melanoma between dermatologists and MelaFind. JAMA Dermatology 2013;149(5):622‐3. - PubMed
Day 2001 {published data only}
-
- Day GR, Barbour RH. Automated skin lesion screening ‐ A new approach. Melanoma Research 2001;11(1):31‐5. - PubMed
Debeir 1999 {published data only}
-
- Debeir O, Decaestecker C, Pasteels JL, Salmon I, Kiss R, Ham P. Computer‐assisted analysis of epiluminescence microscopy images of pigmented skin lesions. Cytometry 1999;37(4):255‐66. - PubMed
Di 2010 {published data only}
-
- Leo G, Paolillo A, Sommella P, Fabbrocini G. Automatic diagnosis of melanoma: a software system based on the 7‐point check‐list. 43rd Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences (HICSS). IEEE, 2010:2319‐28. [DOI: 10.1109/HICSS.2010.76] - DOI
Ding 2015 {published data only}
-
- Ding Y, John NW, Smith L, Sun J, Smith M. Combination of 3D skin surface texture features and 2D ABCD features for improved melanoma diagnosis. Medical & Biological Engineering & Computing 2015;53(10):961‐74. - PubMed
Dreiseitl 2005 {published data only}
-
- Dreiseitl S, Binder M. Do physicians value decision support? A look at the effect of decision support systems on physician opinion. Artificial Intelligence in Medicine 2005;33(1):25‐30. - PubMed
Durg 1993 {published data only}
-
- Durg A, Stoecker WV, Cookson JP, Umbaugh SE, Moss RH. Identification of variegated coloring in skin tumors: Neural network vs. rule‐based induction methods. IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Magazine 1993;12(3):71‐4.
Elbaum 2001 {published data only}
-
- Elbaum M, Kopf AW, Rabinovitz HS, Langley RG, Kamino H, Mihm MC Jr, et al. Automatic differentiation of melanoma from melanocytic nevi with multispectral digital dermoscopy: a feasibility study. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2001;44(2):207‐18. - PubMed
Emery 2010 {published data only}
Engin 2016 {published data only}
-
- Engin B, Kecici AS, Yilmaz S, Kutlubay Z, Serdaroglu S, Tuzun Y. Infrared imaging in diagnosis of dysplastic nevi and malignant melanoma. Turkiye Klinikleri Journal of Medical Sciences 2016;36(1):14‐21.
Ercal 1994 {published data only}
-
- Ercal F, Chawla A, Stoecker WV, Lee HC, Moss RH. Neural network diagnosis of malignant melanoma from color images. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering 1994;41(9):837‐45. - PubMed
Faal 2013 {published data only}
-
- Faal M, Miran Baygi MH, Kabir E. Improving the diagnostic accuracy of dysplastic and melanoma lesions using the decision template combination method. Skin Research and Technology 2013;19(1):e113‐22. - PubMed
Farina 2000 {published data only}
-
- Farina B, Bartoli C, Bono A, Colombo A, Lualdi M, Tragni G, et al. Multispectral imaging approach in the diagnosis of cutaneous melanoma: potentiality and limits. Physics in Medicine and Biology 2000;45(5):1243‐54. - PubMed
Ferris 2016 {published data only}
-
- Ferris LK, Satyanarayanan M. Reply to: "Computer‐aided classification of melanocytic lesions using dermoscopic images: Low reported accuracy for reader study on melanomas with low melanoma in situ to invasive melanoma ratio". Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2016;75(3):e121. - PubMed
Fidalgo 2003 {published data only}
-
- Fidalgo A, Caldas Lopes L, Macedo Ferreira A. Digital dermatoscopy: One‐year experience with the DANAOS system. Skin Cancer 2003;18(4):211‐8.
Fikrle 2007 {published data only}
-
- Fikrle T, Pizinger K. Digital computer analysis of dermatoscopical images of 260 melanocytic skin lesions; perimeter/area ratio for the differentiation between malignant melanomas and melanocytic nevi. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology 2007;21(1):48‐55. - PubMed
Fikrle 2013 {published data only}
-
- Fikrle T, Pizinger K, Szakos H, Panznerova P, Divisova B, Pavel S. Digital dermatoscopic follow‐up of 1027 melanocytic lesions in 121 patients at risk of malignant melanoma. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology 2013;27(2):180‐6. - PubMed
Fruhauf 2012 {published data only}
-
- Fruhauf J, Leinweber B, Fink‐Puches R, Ahlgrimm‐Siess V, Richtig E, Wolf IH, et al. Patient acceptance and diagnostic utility of automated digital image analysis of pigmented skin lesions. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology 2012;26(3):368‐72. - PubMed
Fueyo‐Casado 2009 {published data only}
-
- Fueyo‐Casado A, Vázquez‐López F, Sanchez‐Martin J, Garcia‐Garcia B, Pérez‐Oliva N. Evaluation of a program for the automatic dermoscopic diagnosis of melanoma in a general dermatology setting. Dermatologic Surgery 2009;35(2):257‐9; discussion 260‐2. - PubMed
Ganster 2001 {published data only}
-
- Ganster H, Pinz P, Rohrer R, Wildling E, Binder M, Kittler H. Automated melanoma recognition. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging 2001;20(3):233‐9. - PubMed
García 2014 {published data only}
-
- García Arroyo JL, García Zapirain B. Detection of pigment network in dermoscopy images using supervised machine learning and structural analysis. Computers in Biology and Medicine 2014;44:144‐57. - PubMed
Garcia‐Uribe 2004 {published data only}
-
- Garcia‐Uribe A, Kehtarnavaz N, Marquez G, Prieto V, Duvic M, Wang LV. Skin cancer detection by spectroscopic oblique‐incidence reflectometry: classification and physiological origins. Applied Optics 2004;43(13):2643‐50. - PubMed
Garcia‐Uribe 2010 {published data only}
-
- Garcia‐Uribe A, Zou J, Chang TH, Duvic M, Prieto V, Wang LV. Oblique‐incidence spatially resolved diffuse reflectance spectroscopic diagnosis of skin cancer. SPIE. Optical Diagnostics and Sensing X: Toward Point‐of‐Care Diagnostics. 26 February 2010; Vol. 7572:75720L. [DOI: 10.1117/12.842781] - DOI
Garnavi 2012 {published data only}
-
- Garnavi R, Aldeen M, Bailey J. Computer‐aided diagnosis of melanoma using border and wavelet‐based texture analysis. IEEE Transactions on Information Technology in Biomedicine 2012;16(6):1239‐52. - PubMed
Gerger 2003 {published data only}
-
- Gerger A, Pompl R, Smolle J, Stolz W. Automated epiluminescence microscopy‐‐tissue counter analysis using CART and 1‐NN in the diagnosis of melanoma. Skin Research and Technology 2003;9(2):105‐10. [ER4:15465930; PUBMED: 12709127] - PubMed
Glotsos 2015 {published data only}
-
- Glotsos D, Kostopoulos S, Lalissidou S, Sidiropoulos K, Asvestas P, Konstandinou C, et al. Design of a decision support system, trained on GPU, for assisting melanoma diagnosis in dermatoscopy images. 4th International Conference on Mathematical Modeling in Physical Sciences. 2015:012079. [DOI: 10.1088/1742-6596/633/1/012079] - DOI
Gniadecka 2004 {published data only}
-
- Gniadecka M, Philipsen PA, Sigurdsson S, Wessel S, Nielsen OF, Christensen DH, et al. Melanoma diagnosis by Raman spectroscopy and neural networks: structure alterations in proteins and lipids in intact cancer tissue. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2004;122(2):443‐9. - PubMed
Govindan 2007 {published data only}
-
- Govindan K, Smith J, Knowles L, Harvey A, Townsend P, Kenealy J. Assessment of nurse‐led screening of pigmented lesions using SIAscope. Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive & Aesthetic Surgery 2007;60(6):639‐45. - PubMed
Green 1991 {published data only}
-
- Green A, Martin N, McKenzie G, Pfitzner J, Quintarelli F, Thomas BW, et al. Computer image analysis of pigmented skin lesions. Melanoma Research 1991;1(4):231‐236. [PUBMED: 1823631] - PubMed
Green 1994 {published data only}
-
- Green A, Martin N, Pfitzner J, O'Rourke M, Knight N. Computer image analysis in the diagnosis of melanoma. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 1994;31(6):958‐64. - PubMed
Guerra‐Rosas 2015 {published data only}
Guillod 1996 {published data only}
-
- Guillod JF, Schmid Ph, Fischer S, Salomon D, Saurat JH. Detection and classification of pigmented skin lesions by dermatoscopic digital image processing. Dermatology 1996;193(2):169.
Gutkowicz‐Krusin 2000 {published data only}
-
- Gutkowicz‐Krusin D, Elbaum M, Jacobs A, Keem S, Kopf AW, Kamino H, et al. Precision of automatic measurements of pigmented skin lesion parameters with a MelaFind(™) multispectral digital dermatoscope. Melanoma Research 2000;10(6):563‐70. - PubMed
Hacioglu 2013 {published data only}
-
- Hacioglu S, Saricaoglu H, Baskan EB, Uner SI, Aydogan K, Tunali S. The value of spectrophotometric intracutaneous analysis in the noninvasive diagnosis of nonmelanoma skin cancers. Clinical and Experimental Dermatology 2013;38(5):464‐9. - PubMed
Haenssle 2004 {published data only}
-
- Haenssle HA, Vente C, Bertsch HP, Rupprecht R, Abuzahra F, Junghans V, et al. Results of a surveillance programme for patients at high risk of malignant melanoma using digital and conventional dermoscopy. European Journal of Cancer Prevention 2004;13(2):133‐8. - PubMed
Haenssle 2010 {published data only}
-
- Haenssle HA, Korpas B, Hansen‐Hagge C, Buhl T, Kaune KM, Johnsen S, et al. Selection of patients for long‐term surveillance with digital dermoscopy by assessment of melanoma risk factors. Archives of Dermatology 2010;146(3):257‐64. - PubMed
Haniffa 2007 {published data only}
-
- Haniffa MA, Lloyd JJ, Lawrence CM. The use of a spectrophotometric intracutaneous analysis device in the real‐time diagnosis of melanoma in the setting of a melanoma screening clinic. British Journal of Dermatology 2007;156(6):1350‐2. - PubMed
Hintz‐Madsen 2001 {published data only}
-
- Hintz‐Madsen M, Hansen LK, Larsen J, Drzewiecki KT. A probabilistic neural network framework for detection of malignant melanoma. In: Naguib RNG, Sherbet GV editor(s). Artificial Neural Networks in Cancer Diagnosis, Prognosis and Patient Management. CRC Press, 2001:141‐83.
Hoffmann 2003 {published data only}
-
- Hoffmann K, Gambichler T, Rick A, Kreutz M, Anschuetz M, Grunendick T, et al. Diagnostic and neural analysis of skin cancer (DANAOS). A multicentre study for collection and computer‐assisted analysis of data from pigmented skin lesions using digital dermoscopy. British Journal of Dermatology 2003;149(4):801‐9. - PubMed
Horsch 1997 {published data only}
-
- Horsch A, Stolz W, Neiss A, Abmayr W, Pompl R, Bernklau A, et al. Improving early recognition of malignant melanomas by digital image analysis in dermatoscopy. Studies in Health Technology and Informatics 1997;43(Pt B):531‐5. - PubMed
Huang 1996 {published data only}
-
- Huang CL, Wasti Q, Marghoob AA, Kopf AW, David M, Rao BK, et al. Border irregularity: Atypical moles versus melanoma. European Journal of Dermatology 1996;6(4):270‐3.
Ikuma 2013 {published data only}
-
- Ikuma Y, Iyatomi H. Production of the grounds for melanoma classification using adaptive fuzzy inference neural network. IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC). 2013:2570‐5. [DOI: 10.1109/SMC.2013.439] - DOI
Isasi 2011 {published data only}
-
- Isasi AG, Zapirain BG, Zorrilla AM. Melanomas non‐invasive diagnosis application based on the ABCD rule and pattern recognition image processing algorithms. Computers in Biology and Medicine 2011;41(9):742‐55. - PubMed
Iyatomi 2006 {published data only}
-
- Iyatomi H, Oka H, Saito M, Miyake A, Kimoto M, Yamagami J, et al. Quantitative assessment of tumour extraction from dermoscopy images and evaluation of computer‐based extraction methods for an automatic melanoma diagnostic system. Melanoma Research 2006;16(2):183‐90. - PubMed
Iyatomi 2008a {published data only}
Iyatomi 2008b {published data only}
-
- Iyatomi H, Oka H, Celebi ME, Hashimoto M, Hagiwara M, Tanaka M, et al. An improved Internet‐based melanoma screening system with dermatologist‐like tumor area extraction algorithm. Computerized Medical Imaging and Graphics 2008;32(7):566‐79. - PubMed
Iyatomi 2008c {published data only}
-
- Iyatomi H, Oka H, Celebi ME, Ogawa K, Argenziano G, Soyer HP, et al. Computer‐based classification of dermoscopy images of melanocytic lesions on acral volar skin. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2008;128(8):2049‐54. - PubMed
Iyatomi 2010a {published data only}
-
- Iyatomi H, Celebi ME, Schaefer G, Tanaka M. Automated color normalization for dermoscopy images. 17th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP). 2010:4357‐60. [DOI: 10.1109/ICIP.2010.5652370] - DOI
Iyatomi 2010b {published data only}
Iyatomi 2011 {published data only}
-
- Iyatomi H, Celebi ME, Schaefer G, Tanaka M. Automated color calibration method for dermoscopy images. Computerized Medical Imaging and Graphics 2011;35(2):89‐98. - PubMed
Jain 2015 {published data only}
-
- Jain S, Jagtap V, Pise N. Computer aided melanoma skin cancer detection using image processing. Procedia Computer Science 2015;48:735‐40. [DOI: 10.1016/j.procs.2015.04.209] - DOI
Jakovels 2013 {published data only}
-
- Jakovels D, Lihacova I, Kuzmina I, Spigulis J. Application of principal component analysis to multispectral imaging data for evaluation of pigmented skin lesions. SPIE. Biophotonics ‐ Riga 2013. 18 November 2013; Vol. 9032:903204. [DOI: 10.1117/12.2044383; ER4:25233597] - DOI
Jamora 2003 {published data only}
-
- Jamora MJ, Wainwright BD, Meehan SA, Bystryn JC. Improved identification of potentially dangerous pigmented skin lesions by computerized image analysis. Archives of Dermatology 2003;139(2):195‐8. - PubMed
Jaworek‐Korjakowska 2016a {published data only}
Jaworek‐Korjakowska 2016b {published data only}
Jeddi 2016 {published data only}
Kahofer 2002 {published data only}
-
- Kahofer P, Hofmann‐Wellenhof R, Smolle J. Tissue counter analysis of dermatoscopic images of melanocytic skin tumours: preliminary findings. Melanoma Research 2002;12(1):71‐5. - PubMed
Kaur 2015 {published data only}
Korotkov 2012 {published data only}
-
- Korotkov K, Garcia R. Computerized analysis of pigmented skin lesions: a review. Artificial Intelligence in Medicine 2012;56(2):69‐90. - PubMed
Kuzmina 2011 {published data only}
-
- Kuzmina I, Diebele I, Valeine L, Jakovels D, Kempele A, Kapostinsh J, et al. Multi‐spectral imaging analysis of pigmented and vascular skin lesions: results of a clinical trial. SPIE. Photonic Therapeutics and Diagnostics VII. 3 February 2011; Vol. 7883:788312.
Landau 1999 {published data only}
-
- Landau M, Matz H, Tur E, Dvir M, Brenner S. Computerized system to enhance the clinical diagnosis of pigmented cutaneous malignancies. International Journal of Dermatology 1999;38(6):443‐6. - PubMed
LeAnder 2010 {published data only}
-
- LeAnder R, Chindam P, Das M, Umbaugh SE. Differentiation of melanoma from benign mimics using the relative‐color method. Skin Research and Technology 2010;16(3):297‐304. - PubMed
Lefevre 2000 {published data only}
-
- Lefevre E, Colot O, Vannoorenberghe P, Brucq D. Knowledge modeling methods in the framework of evidence theory: an experimental comparison for melanoma detection. IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics. 2000; Vol. 4:2806‐11. [DOI: 10.1109/ICSMC.2000.884422] - DOI
Lihacova 2013 {published data only}
-
- Lihacova I, Derjabo A, Spigulis J. A multispectral imaging approach for diagnostics of skin pathologies. In: Deckert V, Ramanujam N editor(s). SPIE. Clinical and Biomedical Spectroscopy and Imaging III. Vol. 8798, Optical Society of America, 2013:87980X.
Liu 2012 {published data only}
-
- Liu Z, Sun J, Smith L, Smith M, Warr R. Distribution quantification on dermoscopy images for computer‐assisted diagnosis of cutaneous melanomas. Medical & Biological Engineering & Computing 2012;50(5):503‐13. - PubMed
Machado 2015 {published data only}
Maglogiannis 2004 {published data only}
Maglogiannis 2006 {published data only}
-
- Maglogiannis I, Zafiropoulos E, Kyranoudis C. Intelligent segmentation and classification of pigmented skin lesions in dermatological images. Advances in Artificial Intelligence, 4th Helenic Conference on AI, SETN 2006 May 18‐20; Heraklion, Crete, Greece. Springer, 2006:214‐23.
Manousaki 2006 {published data only}
-
- Manousaki AG, Manios AG, EI Tsompanaki, Panayiotides JG, Tsiftsis DD, Kostaki AK, et al. A simple digital image processing system to aid in melanoma diagnosis in an everyday melanocytic skin lesion unit. A preliminary report. International Journal of Dermatology 2006;45(4):8. [DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-4632.2006.02726.x] - DOI - PubMed
Marchesini 1992 {published data only}
-
- Marchesini R, Cascinelli N, Brambilla M, Clemente C, Mascheroni L, Pignoli E, et al. In vivo spectrophotometric evaluation of neoplastic and non‐neoplastic skin pigmented lesions. II: discriminant analysis between nevus and melanoma. Photochemistry and Photobiology 1992;55(4):515‐22. - PubMed
Masood 2013 {published data only}
-
- Masood A, Al Jumaily AA, Hoshyar AN, Masood O. Automated segmentation of skin lesions: modified Fuzzy C mean thresholding based level set method. 16th International Multi Topic Conference (INMIC). IEEE, 2013:201‐6. [DOI: 10.1109/INMIC.2013.6731350] - DOI
Menzies 1999 {published data only}
-
- Menzies SW. Automated epiluminescence microscopy: human vs machine in the diagnosis of melanoma. Archives of Dermatology 1999;135(12):1538‐40. - PubMed
Mete 2011 {published data only}
-
- Mete M, Kockara S, Aydin K. Fast density‐based lesion detection in dermoscopy images. Computerized Medical Imaging and Graphics 2011;35(2):128‐36. - PubMed
Mhaske 2013 {published data only}
-
- Mhaske HR, Phalke DA. Melanoma skin cancer detection and classification based on supervised and unsupervised learning. International Conference on Circuits, Controls and Communications (CCUBE). IEEE, 2013. [DOI: 10.1109/CCUBE.2013.6718539] - DOI
Moncrieff 2002 {published data only}
-
- Moncrieff M, Cotton S, Claridge E, Hall P. Spectrophotometric intracutaneous analysis: a new technique for imaging pigmented skin lesions. British Journal of Dermatology 2002;146(3):448‐57. - PubMed
Morrow 2010 {published data only}
-
- Morrow T. MelaFind improves chances for accurate melanoma diagnosis. Managed Care 2010;19(3):54‐5. - PubMed
Nagaoka 2012 {published data only}
-
- Nagaoka T, Nakamura A, Okutani H, Kiyohara Y, Sota T. A possible melanoma discrimination index based on hyperspectral data: a pilot study. Skin Research and Technology 2012;18(3):301‐10. - PubMed
Nagaoka 2013 {published data only}
-
- Nagaoka T, Nakamura A, Okutani H, Kiyohara Y, Koga H, Saida T, et al. Hyperspectroscopic screening of melanoma on acral volar skin. Skin Research and Technology 2013;19(1):e290‐6. - PubMed
Nagaoka 2015 {published data only}
-
- Nagaoka T, Kiyohara Y, Koga H, Nakamura A, Saida T, Sota T. Modification of a melanoma discrimination index derived from hyperspectral data: a clinical trial conducted in 2 centers between March 2011 and December 2013. Skin Research and Technology 2015;21(3):278‐83. - PubMed
Noroozi 2016 {published data only}
-
- Noroozi N, Zakerolhosseini A. Computer assisted diagnosis of basal cell carcinoma using Z‐transform features. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation 2016;40(Part A):128‐48. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jvcir.2016.06.014] - DOI
Oka 2004a {published data only}
-
- Oka H, Hashimoto M, Iyatomi H, Argenziano G, Soyer HP, Tanaka M. Internet‐based program for automatic discrimination of dermoscopic images between melanomas and Clark naevi. British Journal of Dermatology 2004;150(5):1041. - PubMed
Oka 2004b {published data only}
-
- Oka H, Tanaka M, Kobayashi S, Argenziano G, Soyer HP, Nishikawa T. Linear discriminant analysis of dermoscopic parameters for the differentiation of early melanomas from Clark naevi. Melanoma Research 2004;14(2):131‐4. - PubMed
Oka 2006 {published data only}
-
- Oka H, Iyatomi H, Hashimoto M, Tanaka M. Reply to 'Digital dermoscopy analysis and internet‐based program for discrimination of pigmented skin lesion dermoscopic images'. British Journal of Dermatology 2006;154(3):570‐1; author reply 571‐2. - PubMed
Pellacani 2004a {published data only}
-
- Pellacani G, Grana C, Cucchiara R, Seidenari S. Automated extraction and description of dark areas in surface microscopy melanocytic lesion images. Dermatology 2004;208(1):21‐6. - PubMed
Pellacani 2004b {published data only}
-
- Pellacani G, Grana C, Seidenari S. Automated description of colours in polarized‐light surface microscopy images of melanocytic lesions. Melanoma Research 2004;14(2):125‐30. - PubMed
Pellacani 2006 {published data only}
-
- Pellacani G, Grana C, Seidenari S. Algorithmic reproduction of asymmetry and border cut‐off parameters according to the ABCD rule for dermoscopy. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology 2006;20(10):1214‐9. - PubMed
Perrinaud 2007 {published data only}
-
- Perrinaud A, Gaide O, French LE, Saurat JH, Marghoob AA, Braun RP. Can automated dermoscopy image analysis instruments provide added benefit for the dermatologist? A study comparing the results of three systems. British Journal of Dermatology 2007;157(5):926‐33. - PubMed
Pompl 2000 {published data only}
-
- Pompl R, Bunk W, Horsch A, Stolz W, Abmayr W, Brauer W, et al. MELDOQ: A system to support the early detection of malignant melanoma through digital image processing [MELDOQ: Ein System zur Unterstützung der Früherkennung des malignen Melanoms durch digitale Bildverarbeitung]. In: Horsch A, Lehmann T editor(s). Bildverarbeitung für die Medizin 2000. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, 2000:234‐8. [DOI: 10.1007/978-3-642-59757-2_44] - DOI
Rajpara 2009 {published data only}
-
- Rajpara SM, Botello AP, Townend J, Ormerod AD. Systematic review of dermoscopy and digital dermoscopy/ artificial intelligence for the diagnosis of melanoma. British Journal of Dermatology 2009;161(3):591‐604. - PubMed
Rastgoo 2015 {published data only}
-
- Rastgoo M, Garcia R, Morel O, Marzani F. Automatic differentiation of melanoma from dysplastic nevi. Computerized Medical Imaging and Graphics 2015;43:44‐52. - PubMed
Rigel 2012 {published data only}
-
- Rigel DS, Roy M, Yoo J, Cockerell CJ, Robinson JK, White R. Impact of guidance from a computer‐assisted multispectral digital skin lesion analysis device on decision to biopsy lesions clinically suggestive of melanoma. Archives of Dermatology 2012;148(5):541‐3. [ER4:15466080; PUBMED: 22351788] - PubMed
Rosado 2003 {published data only}
-
- Rosado B, Menzies S, Harbauer A, Pehamberger H, Wolff K, Binder M, et al. Accuracy of computer diagnosis of melanoma: a quantitative meta‐analysis. Archives of Dermatology 2003;139(3):361‐7; discussion 366. - PubMed
Rubegni 2001a {published data only}
-
- Rubegni P, Cevenini G, Burroni M, Perotti R, Dell'Eua G, Andreassi L. Digital dermoscopy analysis of pigmented skin lesions: An important auxiliary for clinical decision and not for automatic diagnosis. Archives of Dermatology 2001;137(3):378.
Rubegni 2001b {published data only}
-
- Rubegni P, Ferrari A, Cevenini G, Piccolo D, Burroni M, Perotti R, et al. Differentiation between pigmented Spitz naevus and melanoma by digital dermoscopy and stepwise logistic discriminant analysis. Melanoma Research 2001;11(1):37‐44. - PubMed
Rubegni 2002b {published data only}
-
- Rubegni P, Burroni M, Cevenini G, Perotti R, Dell'Eva G, Barbini P, et al. Digital dermoscopy analysis and artificial neural network for the differentiation of clinically atypical pigmented skin lesions: a retrospective study. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2002;119(2):471‐4. - PubMed
Rubegni 2005 {published data only}
-
- Rubegni P, Burroni M, Andreassi A, Fimiani M. The role of dermoscopy and digital dermoscopy analysis in the diagnosis of pigmented skin lesions. Archives of Dermatology 2005;141(11):1444‐6. - PubMed
Rubegni 2010 {published data only}
-
- Rubegni P, Cevenini G, Burroni M, Bono R, Sbano P, Biagioli M, et al. Objective follow‐up of atypical melanocytic skin lesions: a retrospective study. Archives of Dermatological Research 2010;302(7):551‐60. - PubMed
Rubegni 2013 {published data only}
-
- Rubegni P, Cevenini G, Nami N, Argenziano G, Saida T, Burroni M, et al. A simple scoring system for the diagnosis of palmo‐plantar pigmented skin lesions by digital dermoscopy analysis. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology 2013;27(3):e312‐9. - PubMed
Sadeghi 2013 {published data only}
-
- Sadeghi M, Lee TK, McLean D, Lui H, Atkins MS. Detection and analysis of irregular streaks in dermoscopic images of skin lesions. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging 2013;32(5):849‐61. - PubMed
Safi 2011 {published data only}
-
- Safi A, Castaneda V, Lasser T, Mateus DC, Navab N. Manifold learning for dimensionality reduction and clustering of skin spectroscopy data. SPIE. Medical Imaging 2011: Computer‐Aided Diagnosis. 2011; Vol. 7963:79631A. [DOI: 10.1117/12.877952] - DOI
Salerni 2012 {published data only}
-
- Salerni G, Carrera C, Lovatto L, Marti‐Laborda RM, Isern G, Palou J, et al. Characterization of 1152 lesions excised over 10 years using total‐body photography and digital dermatoscopy in the surveillance of patients at high risk for melanoma. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2012;67(5):836‐45. - PubMed
Sboner 2001 {published data only}
-
- Sboner A, Blanzieri E, Eccher C, Bauer P, Cristofolini M, Zumiani G, et al. A knowledge based system for early melanoma diagnosis support. pdfs.semanticscholar.org/9e12/21c5904bbd310c932414de841d3b126e5579.pdf (accessed prior to 1 May 2018).
Sboner 2003 {published data only}
-
- Sboner A, Eccher C, Blanzieri E, Bauer P, Cristofolini M, Zumiani G, et al. A multiple classifier system for early melanoma diagnosis. Artificial Intelligence in Medicine 2003;27(1):29‐44. - PubMed
Sboner 2004 {published data only}
-
- Sboner A, Bauer P, Zumiani G, Eccher C, Blanzieri E, Forti S, et al. Clinical validation of an automated system for supporting the early diagnosis of melanoma. Skin Research and Technology 2004;10(3):184‐92. - PubMed
Schindewolf 1993 {published data only}
-
- Schindewolf T, Stolz W, Albert R, Abmayer W, Harms H. Comparison of classification rates for conventional and dermatoscopic images of malignant and benign melanocytic lesions using computerized colour image analysis. European Journal of Dermatology 1993;3(4):299‐303.
Schindewolf 1994 {published data only}
-
- Schindewolf T, Schiffner R, Stolz W, Albert R, Abmayr W, Harms H. Evaluation of different image acquisition techniques for a computer vision system in the diagnosis of malignant melanoma. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 1994;31(1):33‐41. - PubMed
Schmid‐Saugeon 2003 {published data only}
-
- Schmid‐Saugeon P, Guillod J, Thiran JP. Towards a computer‐assisted diagnosis system for pigmented skin lesions. Computerized Medical Imaging and Graphics 2003;27(1):65‐78. - PubMed
Schumacher 2016 {published data only}
-
- Schumacher B, Mishra NK, Dusza SW, Halpern AC, Stoecker WV. Computer‐aided classification of melanocytic lesions using dermoscopic images: Low reported accuracy for reader study on melanomas with low melanoma in situ to invasive melanoma ratio. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2016;75(3):e119‐20. - PubMed
Seidenari 1995 {published data only}
-
- Seidenari S, Burroni M, Dell'Eva G, Pepe P, Belletti B. Computerized evaluation of pigmented skin lesion images recorded by a videomicroscope: comparison between polarizing mode observation and oil/slide mode observation. Skin Research and Technology 1995;1(4):187‐91. - PubMed
Seidenari 2005 {published data only}
-
- Seidenari S, Pellacani G, Grana C. Pigment distribution in melanocytic lesion images: a digital parameter to be employed for computer‐assisted diagnosis. Skin Research and Technology 2005;11(4):236‐41. - PubMed
Seidenari 2007 {published data only}
-
- Seidenari S, Grana C, Pellacani G. Colour clusters for computer diagnosis of melanocytic lesions. Dermatology 2007;214(2):137‐43. - PubMed
Seidenari 2012 {published data only}
-
- Seidenari S, Ferrari C, Borsari S, Bassoli S, Cesinaro AM, Giusti F, et al. The dermoscopic variability of pigment network in melanoma in situ. Melanoma Research 2012;22(2):151‐7. - PubMed
Shakya 2012 {published data only}
-
- Shakya NM, LeAnder RW, Hinton KA, Stricklin SM, Rader RK, Hagerty J, et al. Discrimination of squamous cell carcinoma in situ from seborrheic keratosis by color analysis techniques requires information from scale, scale‐crust and surrounding areas in dermoscopy images. Computers in Biology and Medicine 2012;42(12):1165‐9. - PubMed
She 2007 {published data only}
-
- She Z, Liu Y, Damatoa A. Combination of features from skin pattern and ABCD analysis for lesion classification. Skin Research and Technology 2007;13(1):25‐33. - PubMed
She 2013 {published data only}
-
- She Z, Excell PS. Lesion classification using 3D skin surface tilt orientation. Skin Research and Technology 2013;19(1):e305‐11. - PubMed
Shimizu 2012 {published data only}
-
- Shimizu K, Iyatomi H, Norton KA, Celebi ME. Extension of automated melanoma screening for non‐melanocytic skin lesions. Mechatronics and Machine Vision in Practice (M2VIP), 19th International Conference. IEEE, 2012:16‐19.
Skrovseth 2010 {published data only}
-
- Skrovseth SO, Schopf TR, Thon K, Zortea M, Geilhufe M, Mollersen K, et al. A computer‐assisted diagnostic system for malignant melanomas. Applied Sciences in Biomedical and Communication Technologies (ISABEL), 3rd International Symposium 2010. IEEE, 2010. [DOI: ]
Smith 2000 {published data only}
-
- Smith Y, Weinberg A, Klauss S, Soffer D, Ingber A. Improving screening for melanoma by measuring similarity to pre‐classified images. Melanoma Research 2000;10(3):265‐72. - PubMed
Sober 1994 {published data only}
-
- Sober AJ, Burstein JM. Computerized digital image analysis: An aid for melanoma diagnosis. Journal of Dermatology 1994;21(11):885‐90. - PubMed
Stanganelli 1995 {published data only}
-
- Stanganelli I, Burroni M, Rafanelli S, Bucchi L. Intraobserver agreement in interpretation of digital epiluminescence microscopy. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 1995;33(4):584‐9. - PubMed
Stanley 2007 {published data only}
Stanley 2008 {published data only}
Stoecker 2005 {published data only}
Swanson 2010 {published data only}
-
- Swanson DL, Laman SD, Biryulina M, Ryzhikov G, Stamnes JJ, Hamre B, et al. Optical transfer diagnosis of pigmented lesions. Dermatologic Surgery 2010;36(12):1979‐86. - PubMed
Tehrani 2006 {published data only}
-
- Tehrani H, Walls J, Price G, Cotton S, Sassoon E, Hall P. A novel imaging technique as an adjunct to the in vivo diagnosis of nonmelanoma skin cancer. British Journal of Dermatology 2006;155(6):1177‐83. - PubMed
Terstappen 2007 {published data only}
-
- Terstappen K, Larko O, Wennberg AM. Pigmented basal cell carcinoma‐‐comparing the diagnostic methods of SIAscopy and dermoscopy. Acta Dermato‐Venereologica 2007;87(3):238‐42. - PubMed
Varol 2006 {published data only}
-
- Varol A. Erratum: The performance of SolarScan: An automated dermoscopy image analysis instrument for the diagnosis of primary melanoma (Archives (November 2005) 141, 1388‐96). Archives of Dermatology 2006;142(5):558. - PubMed
Vestergaard 2008 {published data only}
-
- Vestergaard ME, Menzies SW. Automated diagnostic instruments for cutaneous melanoma. Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery 2008;27(1):32‐6. - PubMed
Wallace 2000a {published data only}
-
- Wallace VP, Bamber JC, Crawford DC, Ott RJ, Mortimer PS. Classification of reflectance spectra from pigmented skin lesions, a comparison of multivariate discriminant analysis and artificial neural networks. Physics in Medicine and Biology 2000;45(10):2859‐71. - PubMed
Wallace 2000b {published data only}
-
- Wallace VP, Crawford DC, Mortimer PS, Ott RJ, Bamber JC. Spectrophotometric assessment of pigmented skin lesions: methods and feature selection for evaluation of diagnostic performance. Physics in Medicine and Biology 2000;45(3):735. - PubMed
Wallace 2002 {published data only}
-
- Wallace VP, Bamber JC, Ott RJ, Crawford DC, Mortimer PS. Monitoring pigmented skin lesions. SPIE. International Symposium on Biomedical Optics. Functional Monitoring and Drug‐Tissue Interaction. 2002; Vol. 4623. [DOI: 10.1117/12.469443] - DOI
Walter 2010 {published data only}
-
- Walter FM, Morris HC, Humphrys E, Hall PN, Kinmonth AL, Prevost AT, et al. Protocol for the MoleMate UK Trial: a randomised controlled trial of the MoleMate system in the management of pigmented skin lesions in primary care. BMC Family Practice 2010;11:36. [DOI: 10.1186/1471-2296-11-36] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Watson 2009 {published data only}
Wazaefi 2012 {published data only}
-
- Wazaefi Y, Paris S, Fertil B. Contribution of a classifier of skin lesions to the dermatologist's decision. 3rd International Conference on Image Processing Theory, Tools and Applications (IPTA). IEEE, 2012. [DOI: 10.1109/IPTA.2012.6469560] - DOI
Wells 2011 {published data only}
-
- Wells R. Comparison of diagnostic and biopsy/referral sensitivity to melanoma between dermatologists and MelaFind: A pilot survey study. Journal of Drugs in Dermatology 2011;10(9):1078.
Wilson 2013 {published data only}
-
- Wilson EC, Emery JD, Kinmonth AL, Prevost AT, Morris HC, Humphrys E, et al. The cost‐effectiveness of a novel SIAscopic diagnostic aid for the management of pigmented skin lesions in primary care: a decision‐analytic model. Value in Health 2013;16(2):356‐66. - PubMed
Winkelmann 2015a {published data only}
-
- Winkelmann RR, Hauschild A, Tucker N, White R, Rigel DS. The impact of multispectral digital skin lesion analysis on German dermatologist decisions to biopsy atypical pigmented lesions with clinical characteristics of melanoma. Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology 2015;8(10):27‐9. - PMC - PubMed
Winkelmann 2015b {published data only}
Winkelmann 2015c {published data only}
-
- Winkelmann RR, Tucker N, White R, Rigel DS. Pigmented skin lesion biopsies after computer‐assisted multispectral digital skin lesion Analysis. Journal of the American Osteopathic Association 2015;115(11):666‐9. - PubMed
Winkelmann 2015d {published data only}
Winkelmann 2016a {published data only}
-
- Winkelmann RR, Rigel DS, Ferris L, Sober A, Tucker N, Cockerell CJ. Correlation between the evaluation of pigmented lesions by a multi‐spectral digital skin lesion analysis device and the clinical and histological features of melanoma. Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology 2016;9(3):36‐8. - PMC - PubMed
Wood 2008 {published data only}
-
- Wood A, Morris H, Emery J, Hall PN, Cotton S, Prevost AT, et al. Evaluation of the MoleMate training program for assessment of suspicious pigmented lesions in primary care. Informatics in Primary Care 2008;16(1):41‐50. - PubMed
Yoo 2015 {published data only}
-
- Yoo J, Tucker N, White R, Rigel D. The impact of probability of melanoma information provided by a multispectral digital skin lesion analysis device (MSDSLA) on resident dermatologists' decisions to biopsy clinical atypical lesions. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2015;72(5 Suppl 1):AB177.
Zagrouba 2004 {published data only}
-
- Zagrouba E, Barhoumi W. A prelimary approach for the automated recognition of malignant melanoma. Image Analysis and Stereology Journal 2004;23(2):121‐35.
Zhou 2010a {published data only}
-
- Zhou H, Rehg JM, Chen M. Exemplar‐based segmentation of pigmented skin lesions from dermoscopy images. 7th IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging: From Nano to Macro. 2010:225‐8. [DOI: 10.1109/ISBI.2010.5490372] - DOI
Zhou 2010b {published data only}
-
- Zhou Y, Smith M, Smith L, Warr R. A new method describing border irregularity of pigmented lesions. Skin Research and Technology 2010;16(1):66‐76. - PubMed
Zortea 2014 {published data only}
-
- Zortea M, Schopf TR, Thon K, Geilhufe M, Hindberg K, Kirchesch H, et al. Performance of a dermoscopy‐based computer vision system for the diagnosis of pigmented skin lesions compared with visual evaluation by experienced dermatologists. Artificial Intelligence in Medicine 2014;60(1):13‐26. - PubMed
Zouridakis 2004 {published data only}
-
- Zouridakis G, Doshi M, Mullani N. Early diagnosis of skin cancer based on segmentation and measurement of vascularization and pigmentation in Nevoscope images. 26th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society. 2004; Vol. 1:1593‐6. - PubMed
Additional references
ACIM 2017
-
- Australian Cancer Database. Melanoma of the skin for Australia (ICD10 C43). Australian Institute of Health and Welfare (AIHW) 2017 Australian Cancer Incidence and Mortality (ACIM) books (www.aihw.gov.au/acim‐books/). Canberra: Australian Institute of Health and Welfare, 2017.
Alam 2001
-
- Alam M, Ratner D. Cutaneous squamous‐cell carcinoma (Review). New England Journal of Medicine 2001;344(13):975‐83. [PUBMED: 11274625] - PubMed
Altman 2009
-
- Altman DG, Vergouwe Y, Royston P, Moons KG. Prognosis and prognostic research: validating a prognostic model. BMJ 2009;338(7708):b605. [doi: 10.1136/bmj.b605; PUBMED: 19477892] - PubMed
Argenziano 1998
-
- Argenziano G, Fabbrocini G, Carli P, Giorgi V, Sammarco E, Delfino M. Epiluminescence microscopy for the diagnosis of doubtful melanocytic skin lesions. Comparison of the ABCD rule of dermatoscopy and a new 7‐point checklist based on pattern analysis. Archives of Dermatology 1998;134(12):1563‐70. [PUBMED: 9875194] - PubMed
Argenziano 2012
-
- Argenziano G, Albertini G, Castagnetti F, Pace B, Lernia V, Longo C, et al. Early diagnosis of melanoma: what is the impact of dermoscopy?. Dermatologic Therapy 2012;25(5):403‐9. [PUBMED: 23046019] - PubMed
Arits 2013
-
- Arits AH, Mosterd K, Essers BA, Spoorenberg E, Sommer A, Rooij MJ, et al. Photodynamic therapy versus topical imiquimod versus topical fluorouracil for treatment of superficial basal‐cell carcinoma: a single blind, non‐inferiority, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncology 2013;14(7):647‐54. [DOI: 10.1016/S1470-2045(13)70143-8] - DOI - PubMed
Arnold 2014
-
- Arnold M, Holterhues C, Hollestein LM, Coebergh JW, Nijsten T, Pukkala E, et al. Trends in incidence and predictions of cutaneous melanoma across Europe up to 2015. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology 2014;28(9):1170‐8. [PUBMED: 23962170] - PubMed
Balch 2001
-
- Balch CM, Buzaid AC, Soong SJ, Atkins MB, Cascinelli N, Coit DG, et al. Final version of the American Joint Committee on Cancer staging system for cutaneous melanoma. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2001;19(16):3635‐48. - PubMed
Baldursson 1993
-
- Baldursson B, Sigurgeirsson B, Lindelof B. Leg ulcers and squamous cell carcinoma. An epidemiological study and a review of the literature. Acta Dermato‐Venereologica 1993;73(3):171‐4. [PUBMED: 8105611] - PubMed
Bath‐Hextall 2007a
-
- Bath‐Hextall F, Leonardi‐Bee J, Smith C, Meal A, Hubbard R. Trends in incidence of skin basal cell carcinoma. Additional evidence from a UK primary care database study. International Journal of Cancer 2007;121(9):2105‐8. [PUBMED: 17640064] - PubMed
Bath‐Hextall 2007b
Bath‐Hextall 2014
-
- Bath‐Hextall F, Ozolins M, Armstrong SJ, Colver GB, Perkins W, Miller PS, et al. Surgical excision versus imiquimod 5% cream for nodular and superficial basal‐cell carcinoma (SINS): a multicentre, non‐inferiority, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncology 2014;15(1):96‐105. [PUBMED: 24332516] - PubMed
Batra 2002
-
- Batra RS, Kelley LC. A risk scale for predicting extensive subclinical spread of nonmelanoma skin cancer. Dermatologic Surgery 2002;28(2):107‐12; discussion 112. [PUBMED: 11860418] - PubMed
Belbasis 2016
-
- Belbasis L, Stefanaki I, Stratigos AJ, Evangelou E. Non‐genetic risk factors for cutaneous melanoma and keratinocyte skin cancers: An umbrella review of meta‐analyses. Journal of Dermatological Science 2016;84(3):330‐9. [PUBMED: 27663092] - PubMed
Binder 1995
-
- Binder M, Schwarz M, Winkler A, Steiner A, Kaider A, Wolff K, et al. Epiluminescence microscopy. A useful tool for the diagnosis of pigmented skin lesions for formally trained dermatologists. Archives of Dermatology 1995;131(3):286‐91. [PUBMED: 7887657] - PubMed
Boring 1994
-
- Boring CC, Squires TS, Tong T, Montgomery S. Cancer statistics, 1994. CA: a Cancer Journal for Clinicians 1994;44(1):7‐26. [PUBMED: 8281473] - PubMed
Bossuyt 2015
Cancer Research UK 2017
-
- Cancer Research UK. Skin cancer statistics. www.cancerresearchuk.org/health‐professional/cancer‐statistics/statistic... (accessed prior to 19 July 2017).
CCAAC Network 2008
-
- Cancer Council Australia & Australian Cancer Network. Basal Cell Carcinoma, Squamous Cell Carcinoma (and related lesions) ‐ a guide to clinical management in Australia. www.cancer.org.au/content/pdf/HealthProfessionals/ClinicalGuidelines/Bas.... Sydney: Cancer Council Australia & Australian Cancer Network, (accessed 19 May 2015).
Chao 2013
-
- Chao D, London Cancer North and East. London Cancer, Guidelines for Cutaneous Malignant Melanoma Management August 2014. www.londoncancer.org/media/76373/london‐cancer‐melanoma‐guidelines‐2013‐.... London: London Cancer North and East Alliance, (accessed 12 August 2018).
Cho 2014
Chowdri 1996
-
- Chowdri NA, Darzi MA. Postburn scar carcinomas in Kashmiris. Burns 1996;22(6):477‐82. [PUBMED: 8884010] - PubMed
Chu 2006
-
- Chu H, Cole SR. Bivariate meta‐analysis for sensitivity and specificity with sparse data: a generalized linear mixed model approach (comment). Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2006;59(12):1331‐2. [PUBMED: 17098577] - PubMed
Chuchu 2018a
Chuchu 2018b
Dabski 1986
-
- Dabski K, Stoll HL Jr, Milgrom H. Squamous cell carcinoma complicating late chronic discoid lupus erythematosus. Journal of Surgical Oncology 1986;32(4):233‐7. [PUBMED: 3736067] - PubMed
Dal Pozzo 1999
-
- Dal Pozzo V, Benelli C, Roscetti E. The seven features for melanoma: a new dermoscopic algorithm for the diagnosis of malignant melanoma. European Journal of Dermatology 1999;9(4):303‐8. [ER4:18375041; PUBMED: 10356410] - PubMed
Deeks 2005
-
- Deeks JJ, Macaskill P, Irwig L. The performance of tests of publication bias and other sample size effects in systematic reviews of diagnostic test accuracy was assessed. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2005;58(9):882‐93. [PUBMED: 16085191] - PubMed
Dinnes 2018a
Dinnes 2018b
Dinnes 2018c
Dinnes 2018d
Dinnes 2018e
Dinnes 2018f
Drew 2017
Drucker 2017
-
- Drucker A, Adam GP, Langberg V, Gazula A, Smith B, Moustafa F, et al. Treatments for Basal Cell and Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Skin. Comparative Effectiveness Reviews, No. 199. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US), 2017. - PubMed
Efron 1983
-
- Efron B. Estimating the error rate of a prediction rule: improvement on cross‐validation. Journal of the American Statistical Association 1983;78(382):316‐331. [DOI: 10.1080/01621459.1983.10477973] - DOI
Erdmann 2013
-
- Erdmann F, Lortet‐Tieulent J, Schuz J, Zeeb H, Greinert R, Breitbart EW, et al. International trends in the incidence of malignant melanoma 1953‐2008‐‐are recent generations at higher or lower risk?. International Journal of Cancer 2013;132(2):385‐400. [PUBMED: 22532371] - PubMed
Esteva 2017
EUCAN 2012
-
- EUCAN, International Agency for Research on Cancer. Malignant melanoma of skin: estimated incidence, mortality & prevalence for both sexes, 2012. eco.iarc.fr/eucan/Cancer.aspx?Cancer=20. International Agency for Research on Cancer, (accessed 29 July 2015).
Fasching 1989
-
- Fasching MC, Meland NB, Woods JE, Wolff BG. Recurrent squamous‐cell carcinoma arising in pilonidal sinus tract‐‐multiple flap reconstructions. Report of a case. Diseases of the Colon and Rectum 1989;32(2):153‐8. [PUBMED: 2914529] - PubMed
Ferlay 2015
-
- Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. International Journal of Cancer 2015;136(5):E359‐86. [PUBMED: 25220842] - PubMed
Ferrante di Ruffano 2018a
Ferrante di Ruffano 2018b
Firnhaber 2012
-
- Firnhaber JM. Diagnosis and treatment of basal cell and squamous cell carcinoma. American Family Physician 2012;86(2):161‐8. [PUBMED: 22962928] - PubMed
Fitzpatrick 1975
-
- Fitzpatrick TB. Soleil et peau. Journal de Médecine Esthétique 1975;2:33‐4.
Garbe 2016
-
- Garbe C, Peris K, Hauschild A, Saiag P, Middleton M, Bastholt L, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of melanoma. European consensus‐based interdisciplinary guideline ‐ Update 2016. European Journal of Cancer 2016;63:201‐17. [PUBMED: 27367293] - PubMed
Garcia 2009
-
- Garcia C, Poletti E, Crowson AN. Basosquamous carcinoma. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2009;60(1):137‐43. [PUBMED: 19103364] - PubMed
Gershenwald 2017
-
- Gershenwald JE, Scolyer RA, Hess KR, Sondak VK, Long GV, Ross MI, et al. Melanoma staging: Evidence‐based changes in the American Joint Committee on Cancer eighth edition cancer staging manual. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians 2017;67(6):472‐92. [DOI: 10.3322/caac.21409; PUBMED: 29028110] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Gordon 2013
-
- Gordon R. Skin cancer: an overview of epidemiology and risk factors. Seminars in Oncology Nursing 2013;29(3):160‐9. [PUBMED: 23958214] - PubMed
Gorlin 2004
-
- Gorlin RJ. Nevoid basal cell carcinoma (Gorlin) syndrome. Genetics in Medicine 2004;6(6):530‐9. [PUBMED: 15545751] - PubMed
Grachtchouk 2011
Griffin 2016
Griffiths 2005
-
- Griffiths RW, Suvarna SK, Stone J. Do basal cell carcinomas recur after complete conventional surgical excision?. British Journal of Plastic Surgery 2005;58(6):795‐805. [PUBMED: 16086990] - PubMed
Gutkowicz‐Krusin 2007
-
- Gutkowicz‐Krusin D, Elbaum M, Greenebaum M, Jacobs A. Systems and methods for the multispectral imaging and characterization of skin tissue. patents.google.com/patent/US6208749B1/en (accessed prior to 12 November 2018).
Han 2018
Hartevelt 1990
-
- Hartevelt MM, Bavinck JN, Kootte AM, Vermeer BJ, Vandenbroucke JP. Incidence of skin cancer after renal transplantation in The Netherlands. Transplantation 1990;49(3):506‐9. [PUBMED: 2316011] - PubMed
Hoorens 2016
-
- Hoorens I, Vossaert K, Pil L, Boone B, Schepper S, Ongenae K, et al. Total‐body examination vs lesion‐directed skin cancer screening. JAMA Dermatology 2016;152(1):27‐34. [PUBMED: 26466155] - PubMed
Horsch 2011
-
- Horsch A. Melanoma diagnosis. In: TM Deserno editor(s). Biomedical Image Processing. Berlin: Springer‐Verlag, 2011:307‐26.
HPA and MelNet NZ 2014
-
- Health Promotion Agency and the Melanoma Network of New Zealand (MelNet). New Zealand Skin Cancer Primary Prevention and Early Detection Strategy 2014 to 2017. www.sunsmart.org.nz//sites/default/files/documents/NZ%20Skin%20Cancer%20.... Cancer Society of New Zealand, (accessed 29 May 2018).
Jensen 1999
-
- Jensen P, Hansen S, Moller B, Leivestad T, Pfeffer P, Geiran O, et al. Skin cancer in kidney and heart transplant recipients and different long‐term immunosuppressive therapy regimens. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 1999;40(2 Pt 1):177‐86. [PUBMED: 10025742] - PubMed
Kao 1986
-
- Kao GF. Carcinoma arising in Bowen's disease. Archives of Dermatology 1986;122(10):1124‐6. [PUBMED: 3767398] - PubMed
Kasprzak 2015
Kelleners‐Smeets 2017
-
- Kelleners‐Smeets NW, Mosterd K, Nelemans PJ. Treatment of low‐risk basal cell carcinoma. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2017;137(3):539‐40. [PUBMED: 28235442] - PubMed
Kim 2014
-
- Kim DD, Tang JY, Ioannidis JP. Network geometry shows evidence sequestration for medical vs. surgical practices: treatments for basal cell carcinoma. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2014;67(4):391‐400. [PUBMED: 24491794] - PubMed
Kittler 2002
-
- Kittler H, Pehamberger H, Wolff K, Binder M. Diagnostic accuracy of dermoscopy (Review). Lancet Oncology 2002;3(3):159‐65. [PUBMED: 11902502] - PubMed
Lachs 1992
-
- Lachs MS, Nachamkin I, Edelstein PH, Goldman J, Feinstein AR, Schwartz JS. Spectrum bias in the evaluation of diagnostic tests: lessons from the rapid dipstick test for urinary tract infection. Annals of Internal Medicine 1992;117(2):135‐40. [PUBMED: 1605428] - PubMed
Lansbury 2010
Lansbury 2013
Lear 1997
-
- Lear JT, Smith AG, Heagerty AH, Bowers B, Jones PW, Gilford J, et al. Truncal site and detoxifying enzyme polymorphisms significantly reduce time to presentation of further primary cutaneous basal cell carcinoma. Carcinogenesis 1997;18(8):1499‐503. [PUBMED: 9276622] - PubMed
Lear 2012
-
- Lear JT. Oral hedgehog‐pathway inhibitors for basal‐cell carcinoma. New England Journal of Medicine 2012;366(23):2225‐6. [PUBMED: 22670909] - PubMed
Lederman 1985
-
- Lederman JS, Sober AJ. Does biopsy type influence survival in clinical stage I cutaneous melanoma?. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 1985;13(6):983‐7. [PUBMED: 4078105] - PubMed
Leeflang 2013
Lees 1991
-
- Lees VC, Briggs JC. Effect of initial biopsy procedure on prognosis in stage I invasive cutaneous malignant melanoma: review of1086 patients. British Journal of Surgery 1991;78(9):1108‐10. [PUBMED: 1933198] - PubMed
Leff 2008
-
- Leff B, Finucane TE. Gizmo idolatry. JAMA 2008;299(15):1830‐2. [PUBMED: 18413879] - PubMed
Lijmer 1999
-
- Lijmer JG, Mol BW, Heisterkamp S, Bonsel GJ, Prins MH, Meulen JH, et al. Empirical evidence of design‐related bias in studies of diagnostic tests. JAMA 1999;282(11):1061‐6. [PUBMED: 10493205] - PubMed
Linos 2009
Lister 1997
-
- Lister RK, Black MM, Calonje E, Burnand KG. Squamous cell carcinoma arising in chronic lymphoedema. British Journal of Dermatology 1997;136(3):384‐7. [PUBMED: 9115922] - PubMed
Lo 1991
-
- Lo JS, Snow SN, Reizner GT, Mohs FE, Larson PO, Hruza GJ. Metastatic basal cell carcinoma: report of twelve cases with a review of the literature. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 1991;24(5 Pt 1):715‐9. [PUBMED: 1869642] - PubMed
Lomas 2012
-
- Lomas A, Leonardi‐Bee J, Bath‐Hextall F. A systematic review of worldwide incidence of nonmelanoma skin cancer. British Journal of Dermatology 2012;166(5):1069‐80. [PUBMED: 22251204] - PubMed
MacKie 1990
Madan 2010
-
- Madan V, Lear JT, Szeimies RM. Non‐melanoma skin cancer. Lancet 2010;375(9715):673‐85. [PUBMED: 20171403] - PubMed
Maglogiannis 2009
Maia 1995
-
- Maia M, Proenca NG, Moraes JC. Risk factors for basal cell carcinoma: a case‐control study. Revista de Saude Publica 1995;29(1):27‐37. [PUBMED: 8525311] - PubMed
Maloney 1996
-
- Maloney ME. Arsenic in dermatology. Dermatologic Surgery 1996;22(3):301‐4. [PUBMED: 8599743] - PubMed
Marchesini 1995
-
- Marchesini R, Tomatis S, Bartoli C, Bono A, Clemente C, Cupeta C, et al. In vivo spectrophotometric evaluation of neoplastic and non‐neoplastic skin pigmented lesions. III. CCD camera‐based reflectance imaging. Photochemistry and Photobiology 1995;62(1):151‐4. [PUBMED: 7638259] - PubMed
Marsden 2010
-
- Marsden JR, Newton‐Bishop JA, Burrows L, Cook M, Corrie PG, Cox NH, et al. BAD Guidelines: Revised UK guidelines for the management of cutaneous melanoma 2010. British Journal of Dermatology 2010;163(2):238‐56. [PUBMED: 20608932] - PubMed
McCormack 1997
-
- McCormack CJ, Kelly JW, Dorevitch AP. Differences in age and body site distribution of the histological subtypes of basal cell carcinoma. A possible indicator of differing causes. Archives of Dermatology 1997;133(5):593‐6. [PUBMED: 9158412] - PubMed
McCusker 2014
-
- McCusker M, Basset‐Seguin N, Dummer R, Lewis K, Schadendorf D, Sekulic A, et al. Metastatic basal cell carcinoma: Prognosis dependent on anatomic site and spread of disease. European Journal of Cancer 2014;50(4):774‐83. [PUBMED: 24412051] - PubMed
Mistry 2011
Moeckelmann 2018
-
- Moeckelmann N, Ebrahimi A, Dirven R, Liu J, Low TH, Gupta R, et al. Analysis and comparison of the 8th edition American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) nodal staging system in cutaneous and oral squamous cell cancer of the head and neck. Annals of Surgical Oncology 2018; Vol. 25, issue 6:1730‐6. [DOI: 10.1245/s10434-018-6340-x] - DOI - PubMed
Moons 1997
-
- Moons KG, Es GA, Deckers JW, Habbema JD, Grobbee DE. Limitations of sensitivity, specificity, likelihood ratio, and Bayes' theorem in assessing diagnostic probabilities: a clinical example. Epidemiology 1997;8(1):12‐7. [PUBMED: 9116087] - PubMed
Motley 2009
-
- Motley RJ, Preston PW, Lawrence CM. Multi‐professional guidelines for the management of the patient with primary cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. www.bsds.org.uk/uploads/pdfs/SCCguide2009.pdf (accessed 15 November 2017).
Murchie 2017
-
- Murchie P, Amalraj Raja E, Brewster DH, Iversen L, Lee AJ. Is initial excision of cutaneous melanoma by General Practitioners (GPs) dangerous? Comparing patient outcomes following excision of melanoma by GPs or in hospital using national datasets and meta‐analysis. European Journal of Cancer 2017;86:373‐84. [PUBMED: 29100192] - PubMed
Musah 2013
-
- Musah A, Gibson JE, Leonardi‐Bee J, Cave MR, Ander EL, Bath‐Hextall F. Regional variations of basal cell carcinoma incidence in the UK using The Health Improvement Network database (2004‐10). British Journal of Dermatology 2013;169(5):1093‐9. [PUBMED: 23701520] - PubMed
Nart 2015
-
- Nart IF, Armayones SG, Medina FV, Orti MB, Orpinell XB. Basal cell carcinoma treated with ingenol mebutate. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2015;5(Suppl 1):AB180.
Newcombe 1998
-
- Newcombe RG. Interval estimation for the difference between independent proportions: comparison of eleven methods. Statistics in Medicine 1998;17(8):873‐90. - PubMed
NICE 2010
-
- National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. NICE guidance on cancer services. Improving outcomes for people with skin tumours including melanoma (update): The management of low‐risk basal cell carcinomas in the community. www.nice.org.uk/guidance/csg8/resources/improving‐outcomes‐for‐people‐wi.... NICE, (accessed 27 November 2017).
NICE 2015
-
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Melanoma: assessment and management. www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng14. London: National Institute for Health and Care Excellence, (accessed prior to 2 May 2018).
NICE 2017
-
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Vismodegib for treating basal cell carcinoma. www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ta489. London: NICE, (accessed prior to 2 May 2018).
Norman 2009
O'Gorman 2014
-
- O'Gorman SM, Murphy GM. Photosensitizing medications and photocarcinogenesis. Photodermatology, Photoimmunology & Photomedicine 2014;30(1):8‐14. [PUBMED: 24393207] - PubMed
Pasquali 2018
Rallan 2004
-
- Rallan D, Harland CC. Skin imaging: is it clinically useful?. Clinical Dermatology 2004;29(5):453‐59. [PUBMED: 15347322] - PubMed
Randle 1996
-
- Randle HW. Basal cell carcinoma. Identification and treatment of the high‐risk patient. Dermatologic Surgery 1996;22(3):255‐61. [PUBMED: 8599737] - PubMed
Reitsma 2005
-
- Reitsma JB, Glas AS, Rutjes AW, Scholten RJ, Bossuyt PM, Zwinderman AH. Bivariate analysis of sensitivity and specificity produces informative summary measures in diagnostic reviews. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2005;58(10):982‐90. [PUBMED: 16168343] - PubMed
Roozeboom 2012
-
- Roozeboom MH, Arits AH, Nelemans PJ, Kelleners‐Smeets NW. Overall treatment success after treatment of primary superficial basal cell carcinoma: a systematic review and meta‐analysis of randomized and nonrandomized trials. British Journal of Dermatology 2012;167(4):733‐56. [PUBMED: 22612571] - PubMed
Roozeboom 2016
-
- Roozeboom MH, Arits AH, Mosterd K, Sommer A, Essers BA, Rooij MJ, et al. Three‐year follow‐up results of photodynamic therapy vs. imiquimod vs. fluorouracil for treatment of superficial basal cell carcinoma: a single‐blind, noninferiority, randomized controlled trial. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2016;136(8):1568‐74. [PUBMED: 27113429] - PubMed
Rozeman 2017
Rutjes 2005
-
- Rutjes AW, Reitsma JB, Vandenbroucke JP, Glas AS, Bossuyt PM. Case‐control and two‐gate designs in diagnostic accuracy studies. Clinical Chemistry 2005;51(8):1335‐41. [PUBMED: 15961549] - PubMed
Sekulic 2012
Siegel 2015
-
- Siegel R, Miller K, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2015. CA: a Cancer Journal for Clinicians 2015;65(1):5‐29. [PUBMED: 25559415] - PubMed
SIGN 2017
-
- Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network. Cutaneous Melanoma. www.sign.ac.uk/sign‐146‐melanoma.html. Scotland: SIGN, (accessed prior to 19 July 2017).
Sladden 2009
Slater 2014
-
- Slater D, Walsh M. Standards and datasets for reporting cancers: Dataset for the histological reporting of primary cutaneous malignant melanoma and regional lymph nodes, May 2014. www.rcpath.org/Resources/RCPath/Migrated%20Resources/Documents/G/G125_Da.... London: Royal College of Pathologists, (accessed 29 July 2015).
Smeets 2004
-
- Smeets NW, Krekels GA, Ostertag JU, Essers BA, Dirksen CD, Nieman FH, et al. Surgical excision vs Mohs' micrographic surgery for basal‐cell carcinoma of the face: randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2004;364(9447):1766‐72. [PUBMED: 15541449] - PubMed
Soyer 2000
-
- Soyer HP, Argenziano G, Chimenti S, Ruocco V. Dermoscopy of pigmented skin lesions. An atlas based on the Consensus Net Meeting on Dermoscopy 2000. Milan, Italy: EDRA Medical Publishing, 2001.
Stanganelli 2000
-
- Stanganelli I, Serafini M, Bucch L. A cancer‐registry‐assisted evaluation of the accuracy of digital epiluminescence microscopy associated with clinical examination of pigmented skin lesions. Dermatology 2000;200(1):11‐6. [PUBMED: 10681607] - PubMed
Stratigos 2015
-
- Stratigos A, Garbe C, Lebbe C, Malvehy J, Marmol V, Pehamberger H, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of invasive squamous cell carcinoma of the skin: European consensus‐based interdisciplinary guideline. European Journal of Cancer 2015;51(14):1989‐2007. [PUBMED: 26219687] - PubMed
Takwoingi 2013
-
- Takwoingi Y, Leeflang MM, Deeks JJ. Empirical evidence of the importance of comparative studies of diagnostic test accuracy. Annals of Internal Medicine 2013;158(7):544‐54. [PUBMED: 23546566] - PubMed
Takwoingi 2015
Tomatis 1998
-
- Tomatis S, Bartoli C, Bono A, Cascinelli N, Clemente C, Marchesini R. Spectrophotometric imaging of cutaneous pigmented lesions: discriminant analysis, optical properties and histological characteristics. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology. B, Biology 1998;42(1):32‐9. - PubMed
Usher‐Smith 2016
Van Loo 2014
-
- Loo E, Mosterd K, Krekels GA, Roozeboom MH, Ostertag JU, Dirksen CD, et al. Surgical excision versus Mohs' micrographic surgery for basal cell carcinoma of the face: A randomised clinical trial with 10 year follow‐up. European Journal of Cancer 2014;50(17):3011‐20. [PUBMED: 25262378] - PubMed
Verkouteren 2017
Walker 2006
-
- Walker P, Hill D. Surgical treatment of basal cell carcinomas using standard postoperative histological assessment. Australasian Journal of Dermatology 2006;47(1):1‐12. [PUBMED: 16405477] - PubMed
Whiting 2011
-
- Whiting PF, Rutjes AW, Westwood ME, Mallett S, Deeks JJ, Reitsma JB, et al. QUADAS‐2: a revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Annals of Internal Medicine 2011;155(8):529‐36. [PUBMED: 22007046] - PubMed
WHO 2003
-
- World Health Organiation. INTERSUN: The Global UV Project. A guide and compendium. www.who.int/uv/publications/en/Intersunguide.pdf 2003 (accessed 20 May 2015).
Williams 2017
-
- Williams HC, Bath‐Hextall F, Ozolins M, Armstrong SJ, Colver GB, Perkins W, et al. Surgery versus 5% imiquimod for nodular and superficial basal cell carcinoma: 5‐year results of the SINS randomized controlled trial. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2017;137(3):614‐9. [PUBMED: 27932240] - PubMed
Wong 2017
Youl 2007
-
- Youl PH, Raasch BA, Janda M, Aitken JF. The effect of an educational programme to improve the skills of general practitioners in diagnosing melanocytic/pigmented lesions. Clinical and Experimental Dermatology 2007;32(4):365‐70. [PUBMED: 17433042] - PubMed
Zak‐Prelich 2004
-
- Zak‐Prelich M, Narbutt J, Sysa‐Jedrzejowska A. Environmental risk factors predisposing to the development of basal cell carcinoma. Dermatologic Surgery 2004;30(2 Pt 2):248–52. [PUBMED: 14871217] - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Dinnes 2015a
-
- Dinnes J, Matin RN, Moreau JF, Patel L, Chan SA, Wong KY, et al. Tests to assist in the diagnosis of cutaneous melanoma in adults: a generic protocol. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2015, Issue 10. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD011902] - DOI
Dinnes 2015b
-
- Dinnes J, Wong KY, Gulati A, Chuchu N, Leonardi‐Bee J, Bayliss SE, et al. Tests to assist in the diagnosis of keratinocyte skin cancers in adults: a generic protocol. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2015, Issue 10. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD011901] - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

